Question: Below is thread2.c Use linux Copy thread2.c to threadsem.c, and modify threadsem.c to use an UNNAMED semaphore to synchronize the update of myglobal. You must

Below is thread2.c
Use linux
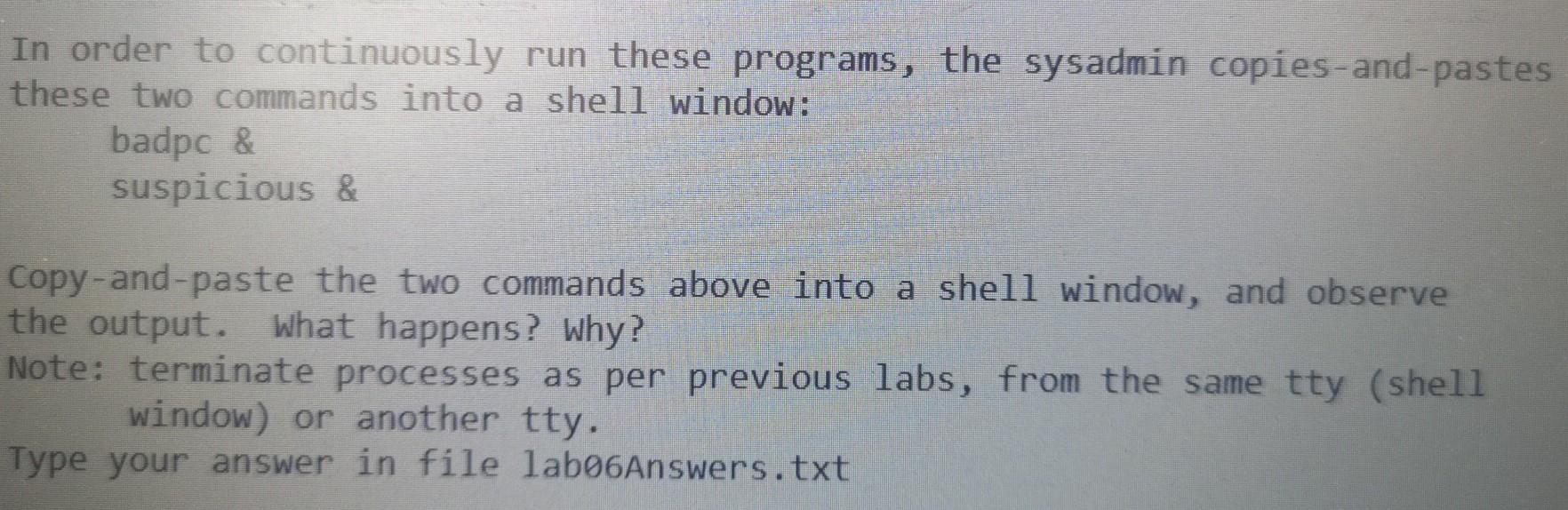
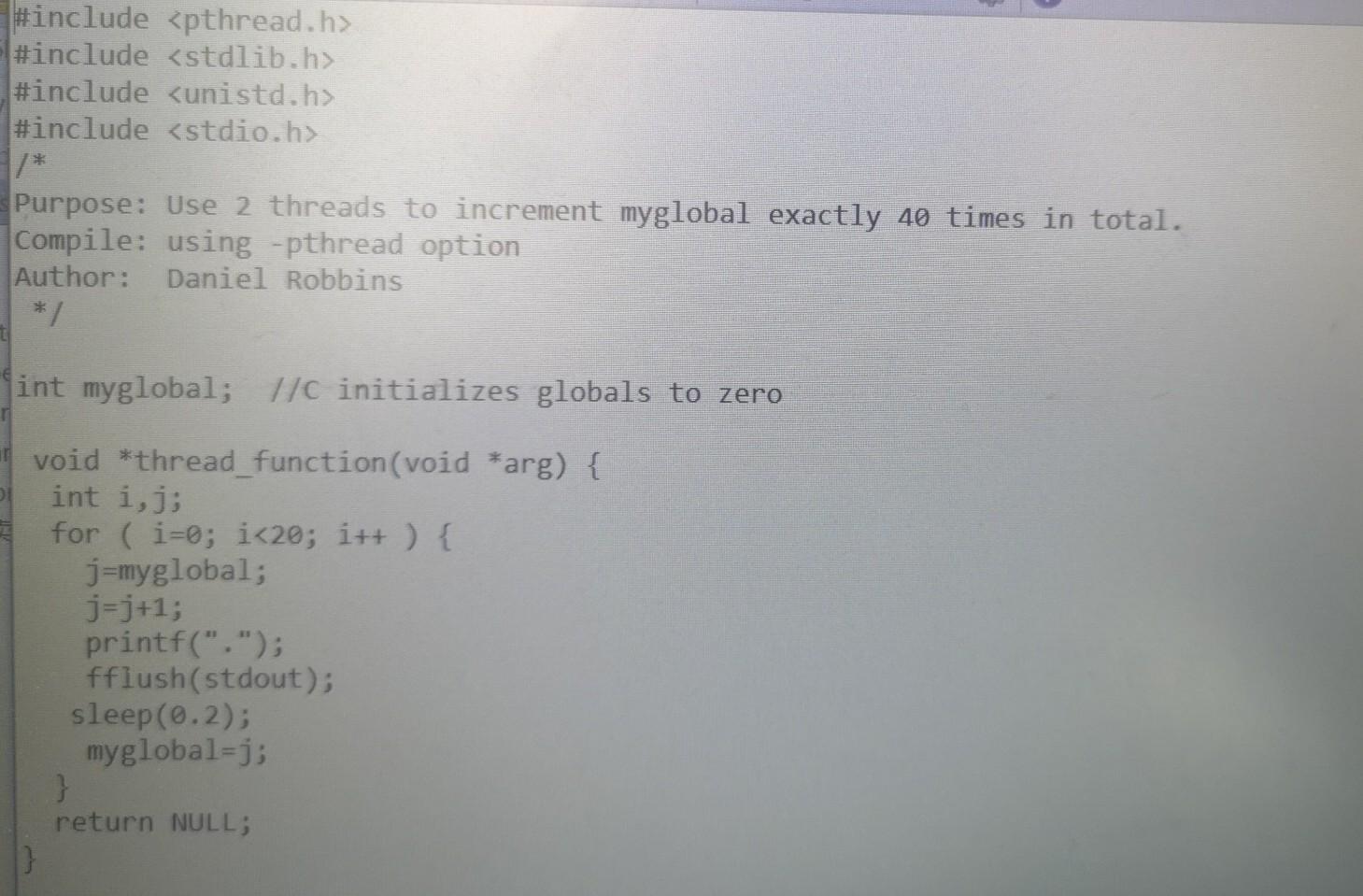
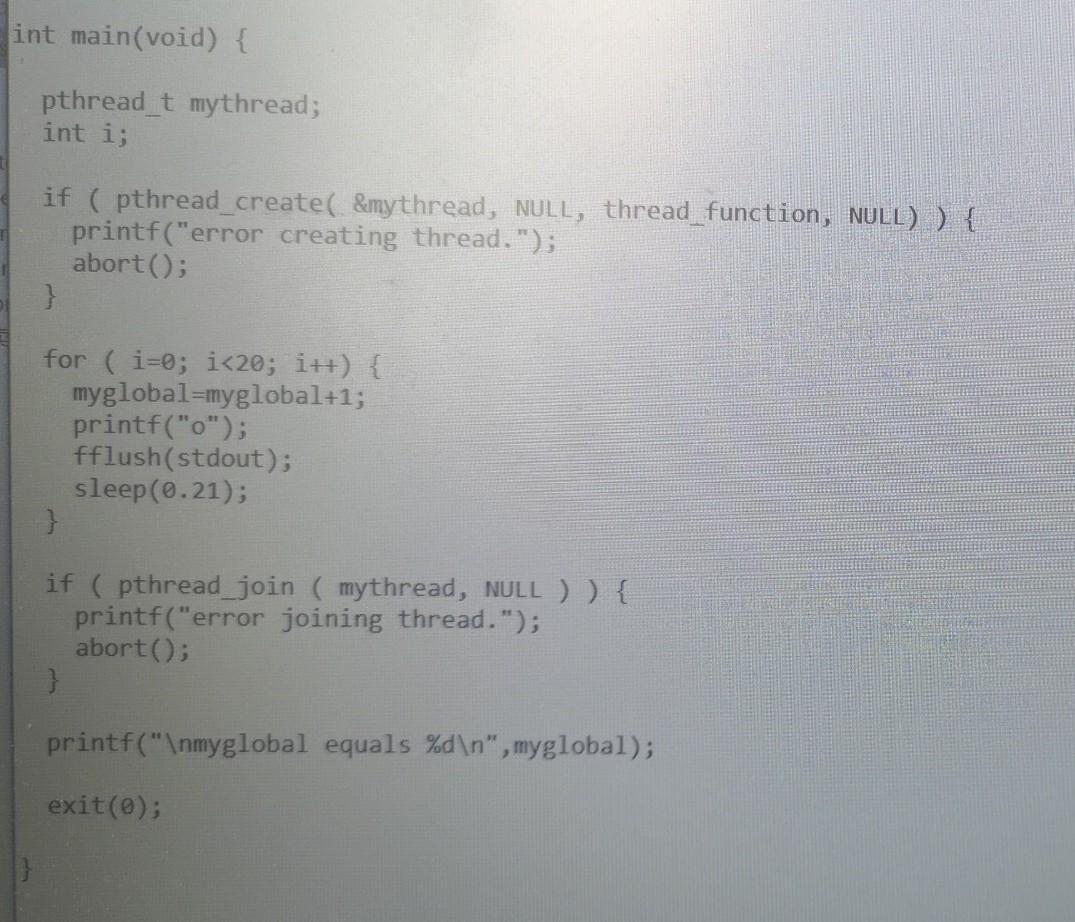
Copy thread2.c to threadsem.c, and modify threadsem.c to use an UNNAMED semaphore to synchronize the update of myglobal. You must use the semaphore efficiently, i.e., keep the critical sections as small as possible. You must use functions: sem wait sem_post sem init sem_destroy Run threadsem numerous times to verify myglobal is always 40. Given your various runs, what can you say about the interleaving of parent and child threads during run-time? Type your answer in file laboAnswers.txt In order to continuously run these programs, the sysadmin copies-and-pastes these two commands into a shell window: badpc & suspicious & Copy-and-paste the two commands above into a shell window, and observe the output. What happens? Why? Note: terminate processes as per previous labs, from the same tty (shell window) or another tty. Type your answer in file labo6Answers.txt #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


