Question: BinarySearchTree #include #include #include #include CSVparser.hpp namespace csv { Parser::Parser(const std::string& data, const DataType& type, char sep) : _type(type), _sep(sep) { std::string line; if (type
BinarySearchTree
#include
namespace csv {
Parser::Parser(const std::string& data, const DataType& type, char sep) : _type(type), _sep(sep) { std::string line; if (type == eFILE) { _file = data; std::ifstream ifile(_file.c_str()); if (ifile.is_open()) { while (ifile.good()) { getline(ifile, line); if (line != "") _originalFile.push_back(line); } ifile.close();
if (_originalFile.size() == 0) throw Error(std::string("No Data in ").append(_file));
parseHeader(); parseContent(); } else throw Error(std::string("Failed to open ").append(_file)); } else { std::istringstream stream(data); while (std::getline(stream, line)) if (line != "") _originalFile.push_back(line); if (_originalFile.size() == 0) throw Error(std::string("No Data in pure content"));
parseHeader(); parseContent(); } }
Parser::~Parser(void) { std::vector
for (it = _content.begin(); it != _content.end(); it++) delete* it; }
void Parser::parseHeader(void) { std::stringstream ss(_originalFile[0]); std::string item;
while (std::getline(ss, item, _sep)) _header.push_back(item); }
void Parser::parseContent(void) { std::vector<:string>::iterator it;
it = _originalFile.begin(); it++; // skip header
for (; it != _originalFile.end(); it++) { bool quoted = false; int tokenStart = 0; unsigned int i = 0;
Row* row = new Row(_header);
for (; i != it->length(); i++) { if (it->at(i) == '"') quoted = ((quoted) ? (false) : (true)); else if (it->at(i) == ',' && !quoted) { row->push(it->substr(tokenStart, i - tokenStart)); tokenStart = i + 1; } }
//end row->push(it->substr(tokenStart, it->length() - tokenStart));
// if value(s) missing if (row->size() != _header.size()) throw Error("corrupted data !"); _content.push_back(row); } }
Row& Parser::getRow(unsigned int rowPosition) const { if (rowPosition
Row& Parser::operator[](unsigned int rowPosition) const { return Parser::getRow(rowPosition); }
unsigned int Parser::rowCount(void) const { return _content.size(); }
unsigned int Parser::columnCount(void) const { return _header.size(); }
std::vector<:string> Parser::getHeader(void) const { return _header; }
const std::string Parser::getHeaderElement(unsigned int pos) const { if (pos >= _header.size()) throw Error("can't return this header (doesn't exist)"); return _header[pos]; }
bool Parser::deleteRow(unsigned int pos) { if (pos
bool Parser::addRow(unsigned int pos, const std::vector<:string>& r) { Row* row = new Row(_header);
for (auto it = r.begin(); it != r.end(); it++) row->push(*it);
if (pos
void Parser::sync(void) const { if (_type == DataType::eFILE) { std::ofstream f; f.open(_file, std::ios::out | std::ios::trunc);
// header unsigned int i = 0; for (auto it = _header.begin(); it != _header.end(); it++) { f
for (auto it = _content.begin(); it != _content.end(); it++) f
const std::string& Parser::getFileName(void) const { return _file; }
/* ** ROW */
Row::Row(const std::vector<:string>& header) : _header(header) {}
Row::~Row(void) {}
unsigned int Row::size(void) const { return _values.size(); }
void Row::push(const std::string& value) { _values.push_back(value); }
bool Row::set(const std::string& key, const std::string& value) { std::vector<:string>::const_iterator it; int pos = 0;
for (it = _header.begin(); it != _header.end(); it++) { if (key == *it) { _values[pos] = value; return true; } pos++; } return false; }
const std::string Row::operator[](unsigned int valuePosition) const { if (valuePosition
const std::string Row::operator[](const std::string& key) const { std::vector<:string>::const_iterator it; int pos = 0;
for (it = _header.begin(); it != _header.end(); it++) { if (key == *it) return _values[pos]; pos++; }
throw Error("can't return this value (doesn't exist)"); }
std::ostream& operator
return os; }
std::ofstream& operator
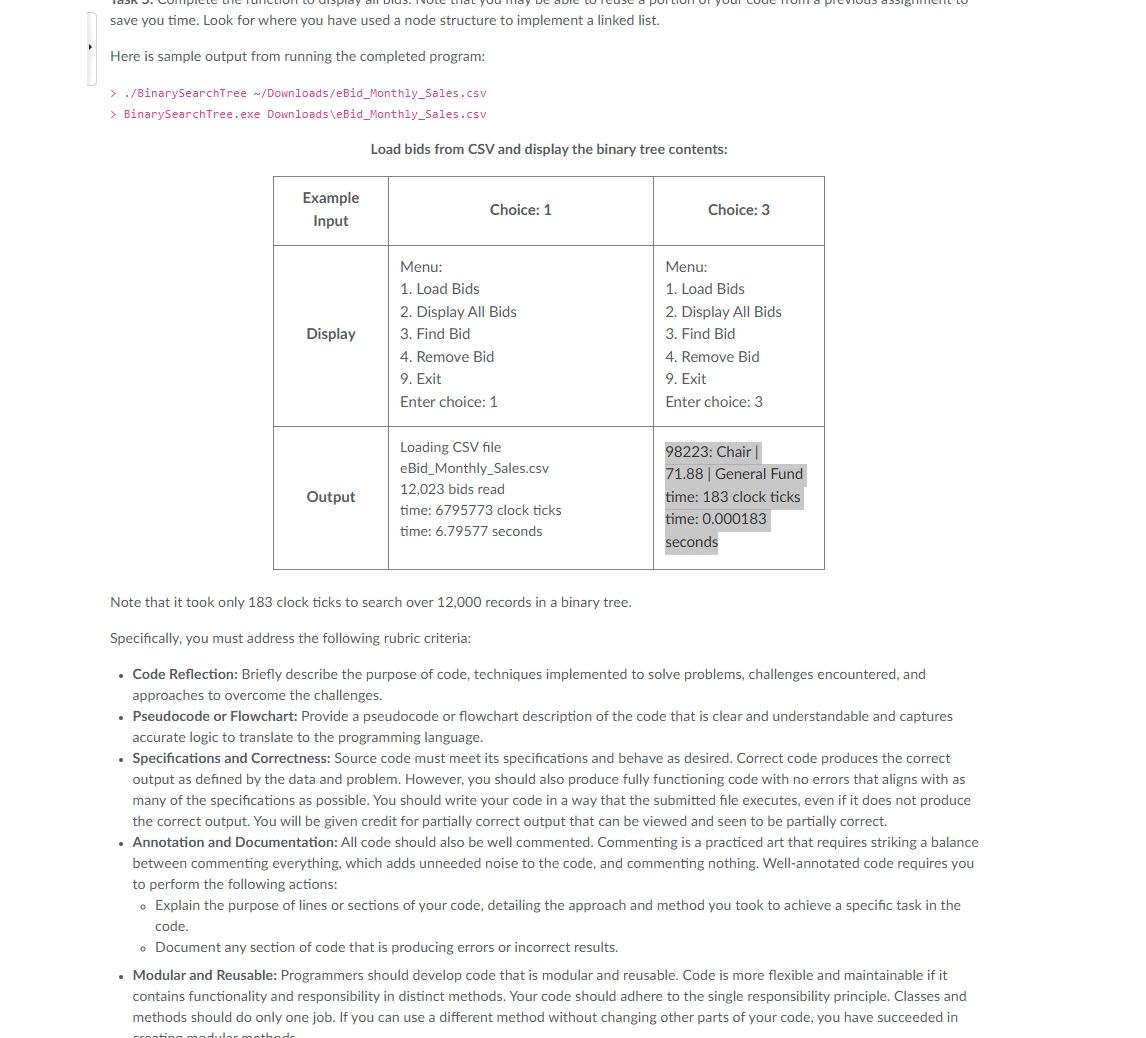
I need it to display 98223: Chair | 71.88 | General Fund time: 183 clock ticks time: 0.000183 seconds
when clicking choice 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


