Question: please finish eveything, thanks. #include #include #include #include CSVparser.hpp namespace csv { Parser::Parser(const std::string &data, const DataType &type, char sep) : _type(type), _sep(sep) { std::string
please finish eveything, thanks.
#include
namespace csv {
Parser::Parser(const std::string &data, const DataType &type, char sep) : _type(type), _sep(sep) { std::string line; if (type == eFILE) { _file = data; std::ifstream ifile(_file.c_str()); if (ifile.is_open()) { while (ifile.good()) { getline(ifile, line); if (line != "") _originalFile.push_back(line); } ifile.close();
if (_originalFile.size() == 0) throw Error(std::string("No Data in ").append(_file)); parseHeader(); parseContent(); } else throw Error(std::string("Failed to open ").append(_file)); } else { std::istringstream stream(data); while (std::getline(stream, line)) if (line != "") _originalFile.push_back(line); if (_originalFile.size() == 0) throw Error(std::string("No Data in pure content"));
parseHeader(); parseContent(); } }
Parser::~Parser(void) { std::vector
for (it = _content.begin(); it != _content.end(); it++) delete *it; }
void Parser::parseHeader(void) { std::stringstream ss(_originalFile[0]); std::string item;
while (std::getline(ss, item, _sep)) _header.push_back(item); }
void Parser::parseContent(void) { std::vector<:string>::iterator it; it = _originalFile.begin(); it++; // skip header
for (; it != _originalFile.end(); it++) { bool quoted = false; int tokenStart = 0; unsigned int i = 0;
Row *row = new Row(_header);
for (; i != it->length(); i++) { if (it->at(i) == '"') quoted = ((quoted) ? (false) : (true)); else if (it->at(i) == ',' && !quoted) { row->push(it->substr(tokenStart, i - tokenStart)); tokenStart = i + 1; } }
//end row->push(it->substr(tokenStart, it->length() - tokenStart));
// if value(s) missing if (row->size() != _header.size()) throw Error("corrupted data !"); _content.push_back(row); } }
Row &Parser::getRow(unsigned int rowPosition) const { if (rowPosition
Row &Parser::operator[](unsigned int rowPosition) const { return Parser::getRow(rowPosition); }
unsigned int Parser::rowCount(void) const { return _content.size(); }
unsigned int Parser::columnCount(void) const { return _header.size(); }
std::vector<:string> Parser::getHeader(void) const { return _header; }
const std::string Parser::getHeaderElement(unsigned int pos) const { if (pos >= _header.size()) throw Error("can't return this header (doesn't exist)"); return _header[pos]; }
bool Parser::deleteRow(unsigned int pos) { if (pos
bool Parser::addRow(unsigned int pos, const std::vector<:string> &r) { Row *row = new Row(_header);
for (auto it = r.begin(); it != r.end(); it++) row->push(*it); if (pos
void Parser::sync(void) const { if (_type == DataType::eFILE) { std::ofstream f; f.open(_file, std::ios::out | std::ios::trunc);
// header unsigned int i = 0; for (auto it = _header.begin(); it != _header.end(); it++) { f
const std::string &Parser::getFileName(void) const { return _file; } /* ** ROW */
Row::Row(const std::vector<:string> &header) : _header(header) {}
Row::~Row(void) {}
unsigned int Row::size(void) const { return _values.size(); }
void Row::push(const std::string &value) { _values.push_back(value); }
bool Row::set(const std::string &key, const std::string &value) { std::vector<:string>::const_iterator it; int pos = 0;
for (it = _header.begin(); it != _header.end(); it++) { if (key == *it) { _values[pos] = value; return true; } pos++; } return false; }
const std::string Row::operator[](unsigned int valuePosition) const { if (valuePosition
const std::string Row::operator[](const std::string &key) const { std::vector<:string>::const_iterator it; int pos = 0;
for (it = _header.begin(); it != _header.end(); it++) { if (key == *it) return _values[pos]; pos++; } throw Error("can't return this value (doesn't exist)"); }
std::ostream &operator
return os; }
std::ofstream &operator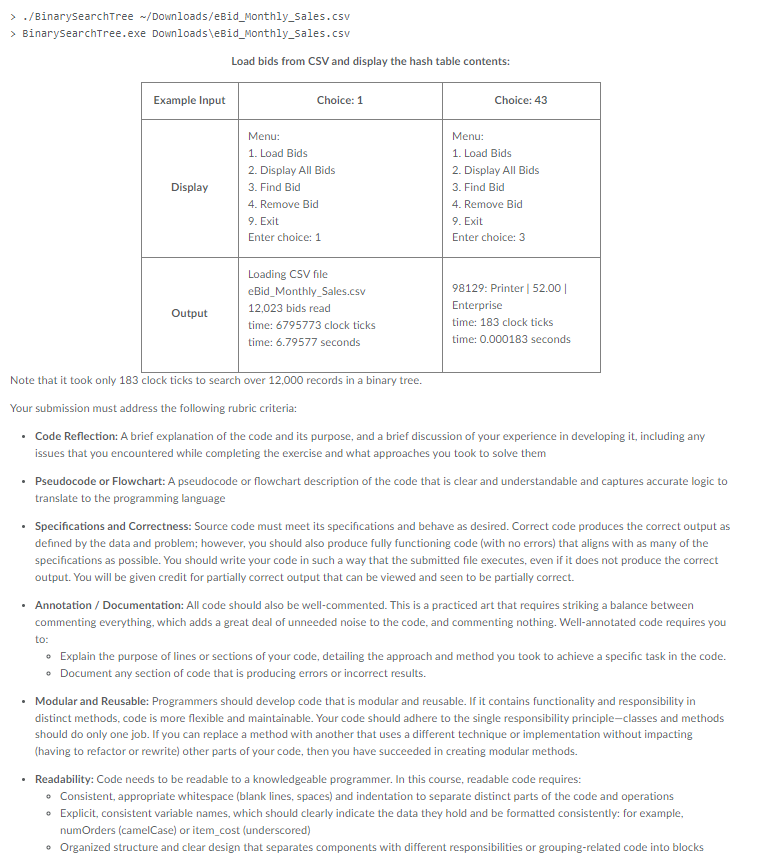

Overview GitHub 1. eBid_Monthly_Sales.csv (larger set of 12,023 bids) 2. eBid_Monthly_Sales_Dec_2016.csv (smaller set of 76 bids) This assignment is designed to explore linked lists, so you will implement a singly linked list to hold a collection of bids loaded from a CSV file. We provide a starter console program that uses a menu to enable testing of the hash table logic you will complete. It also allows you to pass in the path to the bids CSV file to be loaded, enabling you to try both files. In this version, the following menu is presented when the program is run: Menu: 1. Load Bids 2. Display All Bids 3. Find Bid 4. Remove Bid 9. Exit Enter choice: The BinarySearchTree.cpp program is partially completed. It contains empty methods representing the programming interface used to interact with a binary search tree. You will need to add logic to the methods to implement the necessary behavior. Here is the public API for BinarySearchTree.cpp that you have to complete: public: BinarySearchTree(); virtual BinarysearchTree(); void Insert(Bid bid); void Remove(string bidid); Bid Search(string bidId); Prompt You will need to perform the following steps to complete this activity: Setup: Begin by creating a new C++ project with a project type of "Hello World C++ Project". a. Name the project "BinarySearchTree". Remember to pick the correct compiler in Toolchains and click Finish. This will create a simple BinarySearchTree.cpp source file under the /src directory. b. Download the starter program files and copy them to the project's /src directory, replacing the existing auto-generated ones. Remember to right-click on the project in the Project Explorer pane on the left and Refresh the project so it adds all the new files to the src folder underneath. c. Because this activity uses C++11 features, you may need to add the std= c++11 compiler switch to the miscellaneous settings. Task 1: Define structures for tree node and housekeeping variables. Task 2: Implement inserting a bid into the tree. Task 3: Implement removing a bid from the tree. Task 4: Implement searching the tree for a bid. Task 5: Complete the function to display all bids. Note that you may be able to reuse a portion of your code from a previous assignment to save you time. Look for where you have used a Node structure to implement a linked list. Here is sample output from running the completed program: Load bids from CSV and display the hash table contents: Note that it took only 183 clock ticks to search over 12,000 records in a binary tree. Your submission must address the following rubric criteria: - Code Reflection: A brief explanation of the code and its purpose, and a brief discussion of your experience in developing it, including any issues that you encountered while completing the exercise and what approaches you took to solve them - Pseudocode or Flowchart: A pseudocode or flowchart description of the code that is clear and understandable and captures accurate logic to translate to the programming language - Specifications and Correctness: Source code must meet its specifications and behave as desired. Correct code produces the correct output as defined by the data and problem; however, you should also produce fully functioning code (with no errors) that aligns with as many of the specifications as possible. You should write your code in such a way that the submitted file executes, even if it does not produce the correct output. You will be given credit for partially correct output that can be viewed and seen to be partially correct. - Annotation / Documentation: All code should also be well-commented. This is a practiced art that requires striking a balance between commenting everything, which adds a great deal of unneeded noise to the code, and commenting nothing. Well-annotated code requires you to: - Explain the purpose of lines or sections of your code, detailing the approach and method you took to achieve a specific task in the code. - Document any section of code that is producing errors or incorrect results. - Modular and Reusable: Programmers should develop code that is modular and reusable. If it contains functionality and responsibility in distinct methods, code is more flexible and maintainable. Your code should adhere to the single responsibility principle-classes and methods should do only one job. If you can replace a method with another that uses a different technique or implementation without impacting (having to refactor or rewrite) other parts of your code, then you have succeeded in creating modular methods. - Readability: Code needs to be readable to a knowledgeable programmer. In this course, readable code requires: - Consistent, appropriate whitespace (blank lines, spaces) and indentation to separate distinct parts of the code and operations - Explicit, consistent variable names, which should clearly indicate the data they hold and be formatted consistently: for example, numOrders (camelCase) or item_cost (underscored) - Organized structure and clear design that separates components with different responsibilities or grouping-related code into blocks Guidelines for Submission To complete this assignment, submit the CPP code files and a code reflection and associated pseudocode or flowchart. Your written portion should be 1-2 paragraphs in length. Submit the written portion by typing in the Text Submission box, and submit the code as a separate file attachment. Overview GitHub 1. eBid_Monthly_Sales.csv (larger set of 12,023 bids) 2. eBid_Monthly_Sales_Dec_2016.csv (smaller set of 76 bids) This assignment is designed to explore linked lists, so you will implement a singly linked list to hold a collection of bids loaded from a CSV file. We provide a starter console program that uses a menu to enable testing of the hash table logic you will complete. It also allows you to pass in the path to the bids CSV file to be loaded, enabling you to try both files. In this version, the following menu is presented when the program is run: Menu: 1. Load Bids 2. Display All Bids 3. Find Bid 4. Remove Bid 9. Exit Enter choice: The BinarySearchTree.cpp program is partially completed. It contains empty methods representing the programming interface used to interact with a binary search tree. You will need to add logic to the methods to implement the necessary behavior. Here is the public API for BinarySearchTree.cpp that you have to complete: public: BinarySearchTree(); virtual BinarysearchTree(); void Insert(Bid bid); void Remove(string bidid); Bid Search(string bidId); Prompt You will need to perform the following steps to complete this activity: Setup: Begin by creating a new C++ project with a project type of "Hello World C++ Project". a. Name the project "BinarySearchTree". Remember to pick the correct compiler in Toolchains and click Finish. This will create a simple BinarySearchTree.cpp source file under the /src directory. b. Download the starter program files and copy them to the project's /src directory, replacing the existing auto-generated ones. Remember to right-click on the project in the Project Explorer pane on the left and Refresh the project so it adds all the new files to the src folder underneath. c. Because this activity uses C++11 features, you may need to add the std= c++11 compiler switch to the miscellaneous settings. Task 1: Define structures for tree node and housekeeping variables. Task 2: Implement inserting a bid into the tree. Task 3: Implement removing a bid from the tree. Task 4: Implement searching the tree for a bid. Task 5: Complete the function to display all bids. Note that you may be able to reuse a portion of your code from a previous assignment to save you time. Look for where you have used a Node structure to implement a linked list. Here is sample output from running the completed program: Load bids from CSV and display the hash table contents: Note that it took only 183 clock ticks to search over 12,000 records in a binary tree. Your submission must address the following rubric criteria: - Code Reflection: A brief explanation of the code and its purpose, and a brief discussion of your experience in developing it, including any issues that you encountered while completing the exercise and what approaches you took to solve them - Pseudocode or Flowchart: A pseudocode or flowchart description of the code that is clear and understandable and captures accurate logic to translate to the programming language - Specifications and Correctness: Source code must meet its specifications and behave as desired. Correct code produces the correct output as defined by the data and problem; however, you should also produce fully functioning code (with no errors) that aligns with as many of the specifications as possible. You should write your code in such a way that the submitted file executes, even if it does not produce the correct output. You will be given credit for partially correct output that can be viewed and seen to be partially correct. - Annotation / Documentation: All code should also be well-commented. This is a practiced art that requires striking a balance between commenting everything, which adds a great deal of unneeded noise to the code, and commenting nothing. Well-annotated code requires you to: - Explain the purpose of lines or sections of your code, detailing the approach and method you took to achieve a specific task in the code. - Document any section of code that is producing errors or incorrect results. - Modular and Reusable: Programmers should develop code that is modular and reusable. If it contains functionality and responsibility in distinct methods, code is more flexible and maintainable. Your code should adhere to the single responsibility principle-classes and methods should do only one job. If you can replace a method with another that uses a different technique or implementation without impacting (having to refactor or rewrite) other parts of your code, then you have succeeded in creating modular methods. - Readability: Code needs to be readable to a knowledgeable programmer. In this course, readable code requires: - Consistent, appropriate whitespace (blank lines, spaces) and indentation to separate distinct parts of the code and operations - Explicit, consistent variable names, which should clearly indicate the data they hold and be formatted consistently: for example, numOrders (camelCase) or item_cost (underscored) - Organized structure and clear design that separates components with different responsibilities or grouping-related code into blocks Guidelines for Submission To complete this assignment, submit the CPP code files and a code reflection and associated pseudocode or flowchart. Your written portion should be 1-2 paragraphs in length. Submit the written portion by typing in the Text Submission box, and submit the code as a separate file attachment
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


