Question: /** blur.c - Apply blur kernel to image */ #include #include util.h /** Calculate the blur kernel on a single pixel */ int calculate_blur(int width,
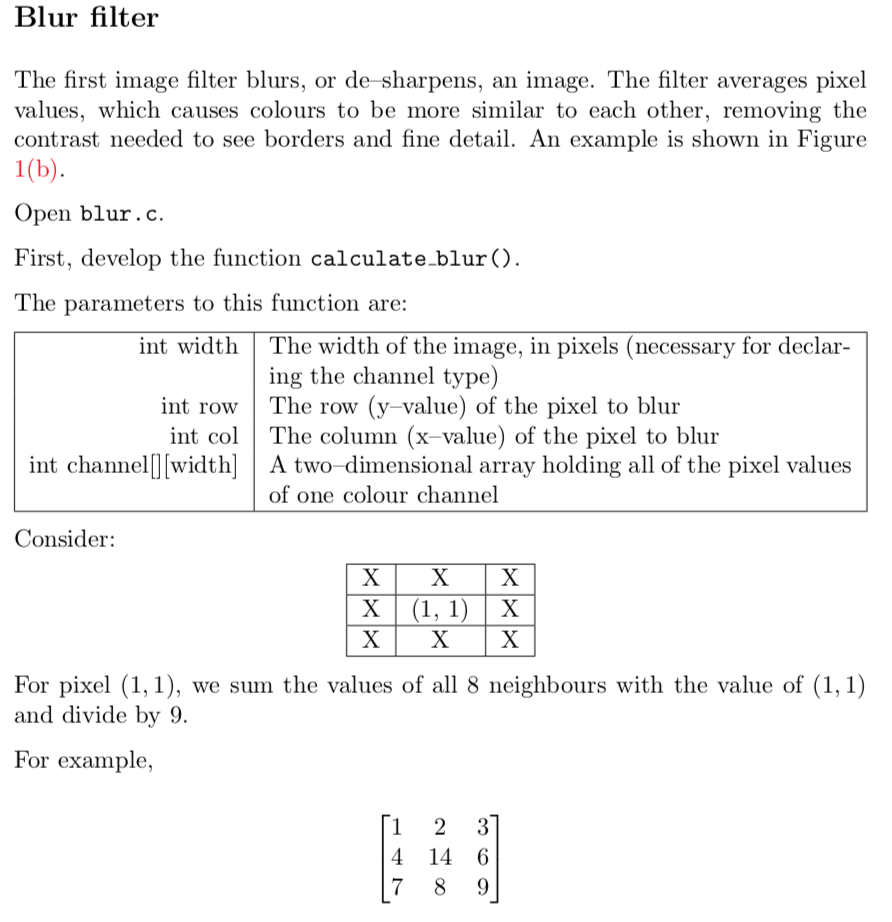

![calculate_blur(int width, int row, int col, int channel[][width]) { // // for](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3d47172c37_66466f3d470e3b05.jpg)

/** blur.c - Apply blur kernel to image */ #include
#include "util.h"
/** Calculate the blur kernel on a single pixel */ int calculate_blur(int width, int row, int col, int channel[][width]) { // // for a blur, sum all of the cells around (col, row), and divide by 9: // // +---+---+---+ // | a | b | c | // +---+---+---+ // | d | e | f | , where e = (col, row) // +---+---+---+ // | g | h | i | // +---+---+---+ // // blur'd value = ( a + b + c + d + e + f + g + h + i ) / 9 // return 2; // FIXME }
/** Given a colour channel, blur all of the pixels in it * * To do this, create a new array to store the blurred values, and then, * once all the calculations are done, call copy_channel() to write the * values back into the input channel */ void blur_channel(int w, int h, int channel[][w]) { int new_channel[h][w];
// // blur all the pixels (calling calculate_blur), and // saving the results in new_channel // // // call the copy_channel() function // }
/** Blur the image * * Call blur_channel() for all of the colour channels */ void apply_blur(int w, int h, int r[][w], int g[][w], int b[][w]) { printf("Applying blur.. ");
// FIXME }
/** outlining.c -- Apply outlining kernel to image */ #include
#include "util.h"
/** Calculate the outlining kernel on a single pixel
for the outlining, subtract all of the cells around (col, row), and add back 8 times the value of (col, row) +---+---+---+ | X | X | X | +---+---+---+ | X | e | X | , where e = (col, row) +---+---+---+ | X | X | X | +---+---+---+ outline'd value = 8 * e - (sum of all the X's)
*/ int calculate_outlining(int width, int row, int col, int channel[][width]) { return 2; // FIXME }
/** Given a colour channel, apply the outlining kernel to all of the pixels in it * * To do this, create a new array to store the blurred values, and then, * once all the calculations are done, call copy_channel() to write the * values back into the input channel */ void outline_channel(int w, int h, int channel[][w]) { int new_channel[h][w];
// FIXME }
/* Outline the image * * Call outline_channel() for all of the colour channels * */ void apply_outlining(int w, int h, int r[][w], int g[][w], int b[][w]) { printf("Applying outlining.. ");
// FIXME }
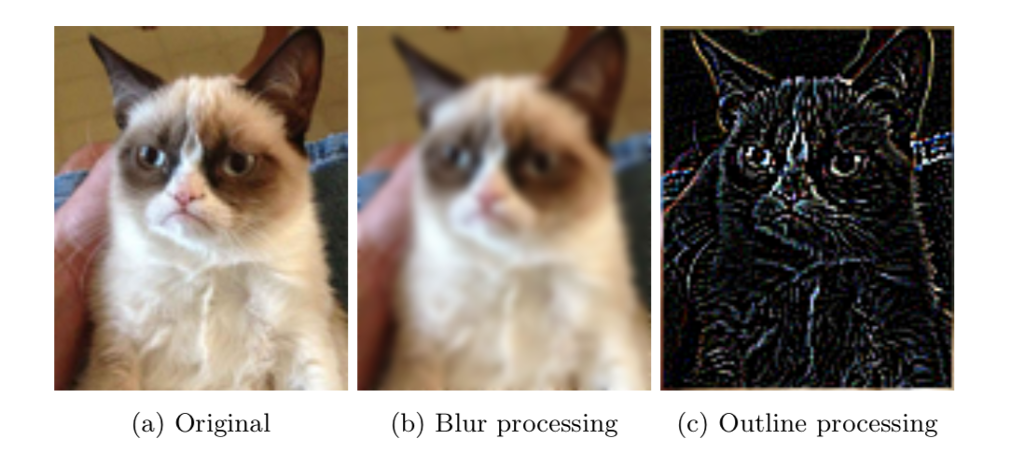
Blur filter The first image filter blurs, or de -sharpens, an image. The filter averages pixel values, which causes colours to be more similar to each other, removing the contrast needed to see borders and fine detail. An example is shown in Figure 1(b) Open blur.c. First, develop the function calculate blur() The parameters to this function are: int width The width of the image, in pixels (necessary for declar- ing the channel type) int row The row (y-value) of the pixel to blur int col The column (x-value) of the pixel to blur int channell|[width]A two-dimensional array holding all of the pixel values of one colour channel Consider For pixel (1,1), we sum the values of all 8 neighbours with the value of (1,1) and divide by 9 For example, 4 14 6 Blur filter The first image filter blurs, or de -sharpens, an image. The filter averages pixel values, which causes colours to be more similar to each other, removing the contrast needed to see borders and fine detail. An example is shown in Figure 1(b) Open blur.c. First, develop the function calculate blur() The parameters to this function are: int width The width of the image, in pixels (necessary for declar- ing the channel type) int row The row (y-value) of the pixel to blur int col The column (x-value) of the pixel to blur int channell|[width]A two-dimensional array holding all of the pixel values of one colour channel Consider For pixel (1,1), we sum the values of all 8 neighbours with the value of (1,1) and divide by 9 For example, 4 14 6
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


