Question: Budget Performance Report Sarah has learned a lot from you over the past two months, and has compiled the following data for Sole Purpose Shoe
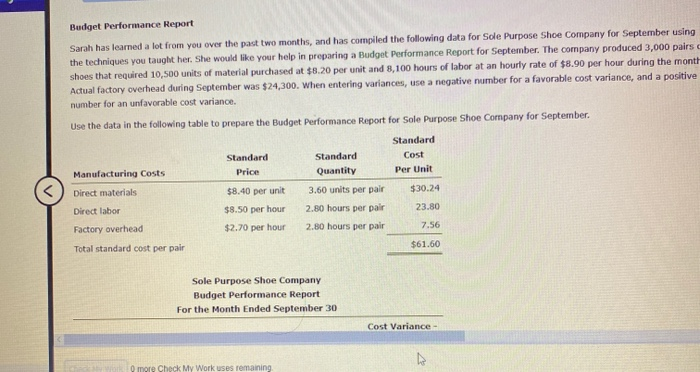
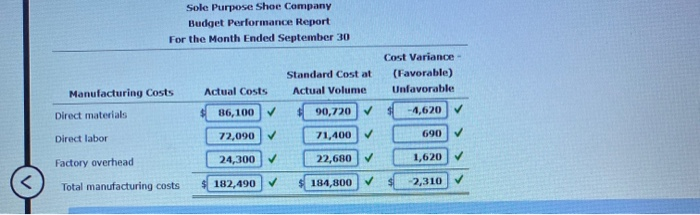


Budget Performance Report Sarah has learned a lot from you over the past two months, and has compiled the following data for Sole Purpose Shoe Company for September using the techniques you taught her. She would like your help in preparing a Budget Performance Report for September. The company produced 3,000 pairs shoes that required 10,500 units of material purchased at $8.20 per unit and 8,100 hours of labor at an hourly rate of $8.90 per hour during the month Actual factory overhead during September was $24,300. When entering variances, use a negative number for a favorable cost variance, and a positive number for an unfavorable cost variance. Use the data in the following table to prepare the Budget Performance Report for Sole Purpose Shoe Company for September. Standard Standard Standard Cost Manufacturing Costs Price Quantity Per Unit Direct materials $8.40 per unit 3.60 units per pair $30.24 Direct labor $8.50 per hour 2.80 hours per pair 23.80 Factory overhead $2.70 per hour 2.80 hours per pair 7.56 Total standard cost per pair $61.60 Sole Purpose Shoe Company Budget Performance Report For the Month Ended September 30 Cost Variance- more Check My Work uses remaining Sole Purpose Shoe Company Budget Performance Report For the Month Ended September 30 Standard Cost at Actual Volume Cost Variance - (Favorable) Unfavorable Manufacturing Costs Actual Costs Direct materials 36,100 90,720 -4,620 72,090 690 Direct labor 71,400 Factory overhead 24,300 22,680 1,620 Total manufacturing costs 182,490 -2,310 184,800 Final Questions Before Sarah makes any changes based on the Budget Performance Report for September, she wants to be sure she understands the results, and has the following questions for you. Answer the following questions (1) and (2). All questions pertain to the September data. 1. What caused the total cost variance for direct materials? a. The actual quantity of direct materials per unit was less than the standard quantity. b. The actual price for direct materials per unit was less than the standard price. c. The favorable price variance dominated the unfavorable quantity variance, causing the total cost variance for direct materials to be favorable. d. The unfavorable quantity variance dominated the favorable price variance, causing the total cost variance for direct materials to be unfavorable. e. A factor other than those listed caused the total cost variance for direct materials.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


