Question: C A i = ( 1 . 0 3 ) ( 0 . 1 1 3 6 ) = 0 . 1 1 7 kmo
kmo
because of the small contact time, the depth of penetration of the solute in the jet will be small and the bulk liquid free from
The given rate of absorption of iekmo
Using Eqs. i and ii and the given rate of absorption note that
Diffusivity of in water at reported in the literature
EXAMPLE Gas absorption from bubbles A mixture of and is bubbling through water in a laboratory column at and atm. The depth of water in the column is A singlenozzle gas distributor is used. The gas flow rate is per minute and the bubbles are of diameter on the average. The bubble rise velocity is Calculate the rate of absorption of carbon dioxide. The diffusivity of in water is Henry's law can be used to calculate the solubility of in water at the given temperature, partial pressure of in atm; is its mole fraction in water at equilibrium
Hints: Contact time of a liquid element with a gas bubble, Mass transfer coefficient, Residence time of a single bubble in the liquid liquid depth
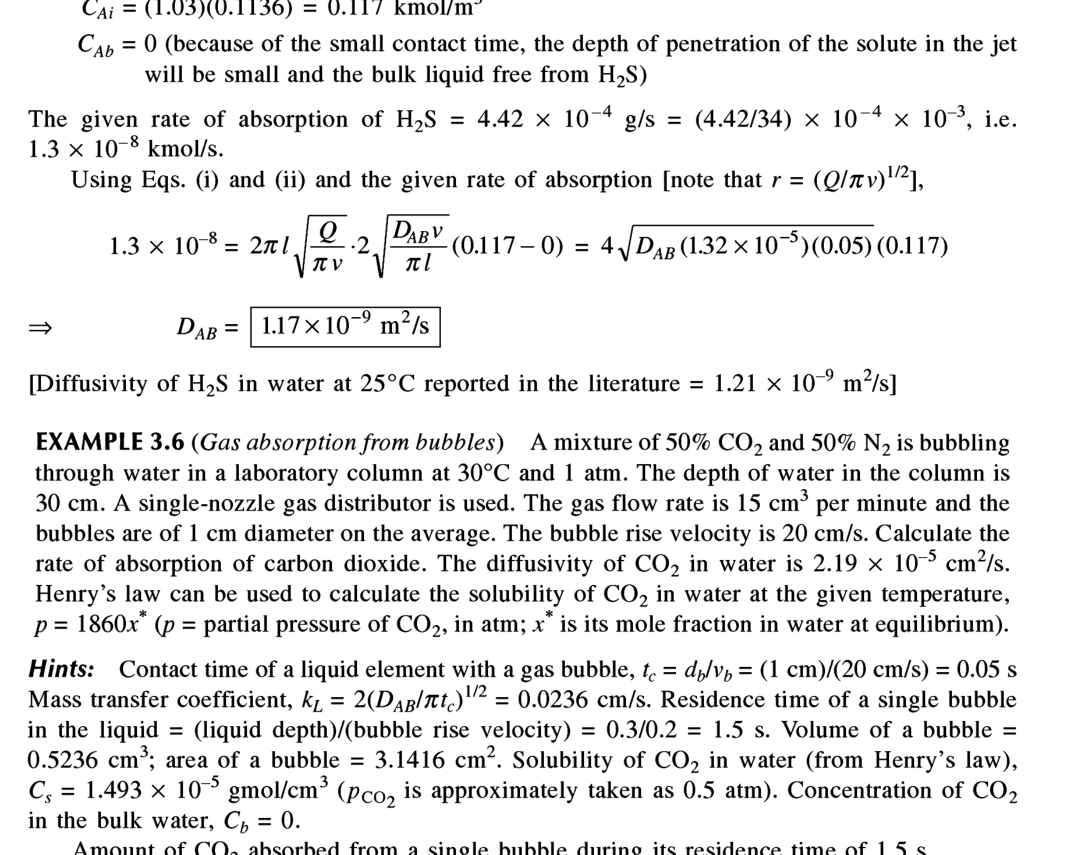
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


