Question: C. | | C b) Decision tree with 11 errors a) Decision tree with 8 errors Consider the decision trees shown above. Assume they are
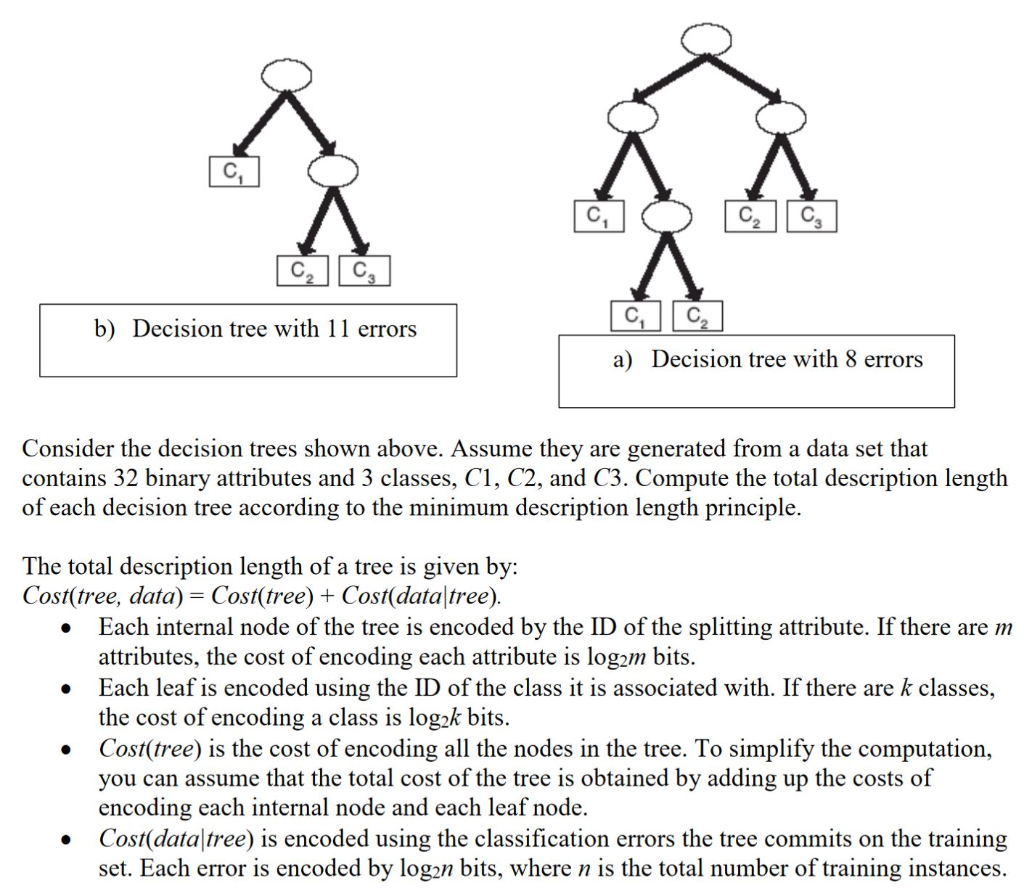
C. | | C b) Decision tree with 11 errors a) Decision tree with 8 errors Consider the decision trees shown above. Assume they are generated from a data set that contains 32 binary attributes and 3 classes, C1, C2, and C3. Compute the total description length of each decision tree according to the minimum description length principle. The total description length of a tree is given by: Cost(tree, data) - Cost(tree) + Cost(dataltree) . Each internal node of the tree is encoded by the ID of the splitting attribute. If there are m attributes, the cost of encoding each attribute is log2m bits. Each leaf is encoded using the ID of the class it is associated with. If there are k classes, the cost of encoding a class is log2k bits. Cost(tree) is the cost of encoding all the nodes in the tree. To simplify the computation you can assume that the total cost of the tree is obtained by adding up the costs of encoding each internal node and each leaf node. . . Cost(data tree) is encoded using the classification errors the tree commits on the training set. Each error is encoded by log2n bits, where n is the total number of training instances. C. | | C b) Decision tree with 11 errors a) Decision tree with 8 errors Consider the decision trees shown above. Assume they are generated from a data set that contains 32 binary attributes and 3 classes, C1, C2, and C3. Compute the total description length of each decision tree according to the minimum description length principle. The total description length of a tree is given by: Cost(tree, data) - Cost(tree) + Cost(dataltree) . Each internal node of the tree is encoded by the ID of the splitting attribute. If there are m attributes, the cost of encoding each attribute is log2m bits. Each leaf is encoded using the ID of the class it is associated with. If there are k classes, the cost of encoding a class is log2k bits. Cost(tree) is the cost of encoding all the nodes in the tree. To simplify the computation you can assume that the total cost of the tree is obtained by adding up the costs of encoding each internal node and each leaf node. . . Cost(data tree) is encoded using the classification errors the tree commits on the training set. Each error is encoded by log2n bits, where n is the total number of training instances
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


