Question: c C lang Consider a machine with a 12KB physical memory space running an OS that uses a 4KB virtual memory space for its processes.
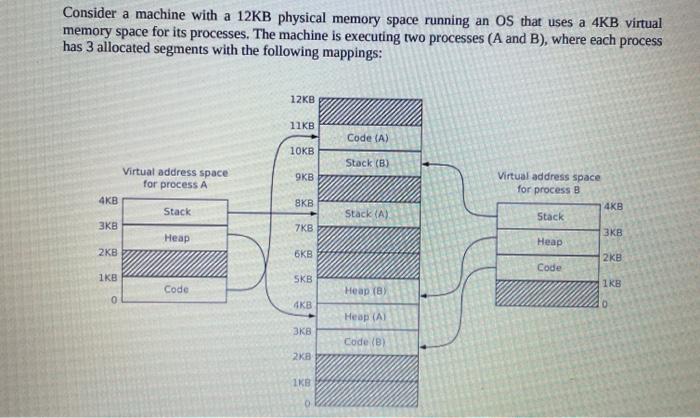


Consider a machine with a 12KB physical memory space running an OS that uses a 4KB virtual memory space for its processes. The machine is executing two processes (A and B), where each process has 3 allocated segments with the following mappings: 12KB 11KB Code (A) 10KB Stack (B) 9KB Virtual address space for process B SKB 4KB Virtual address space for process A 4KB Stack 3KB Heap 2KB Stack (A) Stack 7KB 3KB Heap 6KB 2KB Code 1KB SKB 1KB Code Heap (0) 0 4KB 0 Heap (A) 3KB Code (B) 2KB IKE 0 a) (1 pt.) Show the state of a basic segment table containing the information represented in the diagram above. The table should include the following columns: . Segment. The segment index, starting at 0. Sort segments by process (first A, then B), and by base virtual address (lower virtual address first). Process Process identifier. Virtual address. Base address in virtual address space. Size. The segment size. Physical address. Base address in physical address space. . . b) (3 pt.) Perform a set of address translations based on the segment table above. Use a table with the following columns to represent the state of each memory translation: . Process. Process accessing memory, as given below. Virtual address. Virtual address access by the process, as given below. Segment. Index of the segment affected by this access, or "_" for segmentation fault. Offset. Offset within the segment, or "-" for segmentation fault. Physical address. Final physical address, or "Segfault for segmentation fault. . Use the following memory accesses: . Process A, address 2148 Process A, address 1324 Process A, address 4095 Process B, address 512 . Process B, address 2048 Process B, address 3272 Consider a machine with a 12KB physical memory space running an OS that uses a 4KB virtual memory space for its processes. The machine is executing two processes (A and B), where each process has 3 allocated segments with the following mappings: 12KB 11KB Code (A) 10KB Stack (B) 9KB Virtual address space for process B SKB 4KB Virtual address space for process A 4KB Stack 3KB Heap 2KB Stack (A) Stack 7KB 3KB Heap 6KB 2KB Code 1KB SKB 1KB Code Heap (0) 0 4KB 0 Heap (A) 3KB Code (B) 2KB IKE 0 a) (1 pt.) Show the state of a basic segment table containing the information represented in the diagram above. The table should include the following columns: . Segment. The segment index, starting at 0. Sort segments by process (first A, then B), and by base virtual address (lower virtual address first). Process Process identifier. Virtual address. Base address in virtual address space. Size. The segment size. Physical address. Base address in physical address space. . . b) (3 pt.) Perform a set of address translations based on the segment table above. Use a table with the following columns to represent the state of each memory translation: . Process. Process accessing memory, as given below. Virtual address. Virtual address access by the process, as given below. Segment. Index of the segment affected by this access, or "_" for segmentation fault. Offset. Offset within the segment, or "-" for segmentation fault. Physical address. Final physical address, or "Segfault for segmentation fault. . Use the following memory accesses: . Process A, address 2148 Process A, address 1324 Process A, address 4095 Process B, address 512 . Process B, address 2048 Process B, address 3272
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


