Question: c++ file is accounts.dat Each record in the accounts database is assigned a record number based on that records relative position within the database file.
c++ file is "accounts.dat"
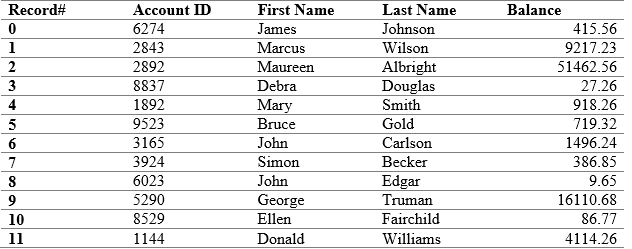
Each record in the accounts database is assigned a record number based on that records relative position within the database file. You could use a record number to retrieve a record directly, much as you can use an array index to reference an array data item directly. Record numbers are assigned by the database file mechanism and are not part od the account information. As a result. They are not meaningful to database users. These users require a different record retrieval mechanism, one that is based on an account ID (the key for the database) rather than a record number.
Retrievals based on account ID require an index that associates each account ID with the corresponding record number. You cam implement this index using a binary search tree in which each data item contains the two fields: an account ID (the key) and a record number.
struct IndexEntry {int acctID; // (key) Account identifier long recNum; // Record number };
You build the index by reading through the database account-by-account, inserting successive (account ID, record number) pairs into the tree as you progress through the file.
Given an account ID, retrieval of the corresponding account record is a two-step process. First. You retrieve the data item from the index tree that has the specified account ID. Then using the record number stored in the index data item, you read the corresponding account record from the database file. The result is an efficient retrieval process that is based on account ID
SAMPLE:
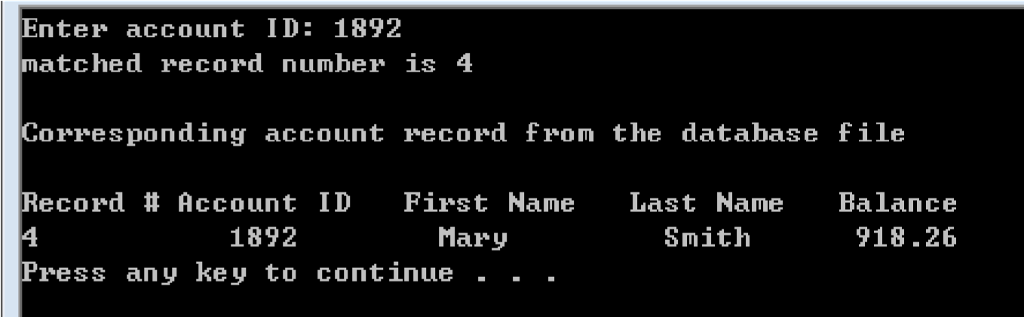
HERE IS WHAT I HAVE SO FAR
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct accountInfo
{
int RecNum;
int accountID;
string firstName;
string lastName;
double balance;
};
struct IndexEntry
{
int acctID; // (key) Account identifier
long recNum; // Record number
int getKey() const
{
return acctID;
}
};
struct node
{
IndexEntry value;
node *left;
node *right;
};
class BST {
node * root;
public:
BST();
void search(node*, node*);
void insert(node*, node*);
void inorderTraverse(node *);
};
BST::BST()
{
root = NULL;
}
int main()
{
ifstream inFile("accounts.dat");
accountInfo record;
long recNumInput;
cout
cin >> recNumInput;
if (!inFile)
{
cout
}
while (!inFile.eof())
{
inFile >> record.accountID >> record.RecNum >> record.firstName
>> record.lastName >> record.balance;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//search account number and return record number
void BST::search(node *root, node *target)
{
}
//Insert value into search tree
void BST::insert(node *root, node *temp)
{
}
void BST::inorderTraverse(node *binTree)
{
if (binTree != NULL)
{
inorderTraverse(binTree->left);
cout value;
inorderTraverse(binTree->right);
}
}
636662455876 525223286672 572789669064 9743 1-8-1 1 5 DSGCBETF 0432723543 749392622 288885190251 A622-819336581 01 RO-2345678-911 636662455876 525223286672 572789669064 9743 1-8-1 1 5 DSGCBETF 0432723543 749392622 288885190251 A622-819336581 01 RO-2345678-911
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


