Question: c++ language Setting up your development environment: READ FIRST: Setting up C++ development environment and tools Purposes of this assignment: 1. Continue with the concept
c++ language

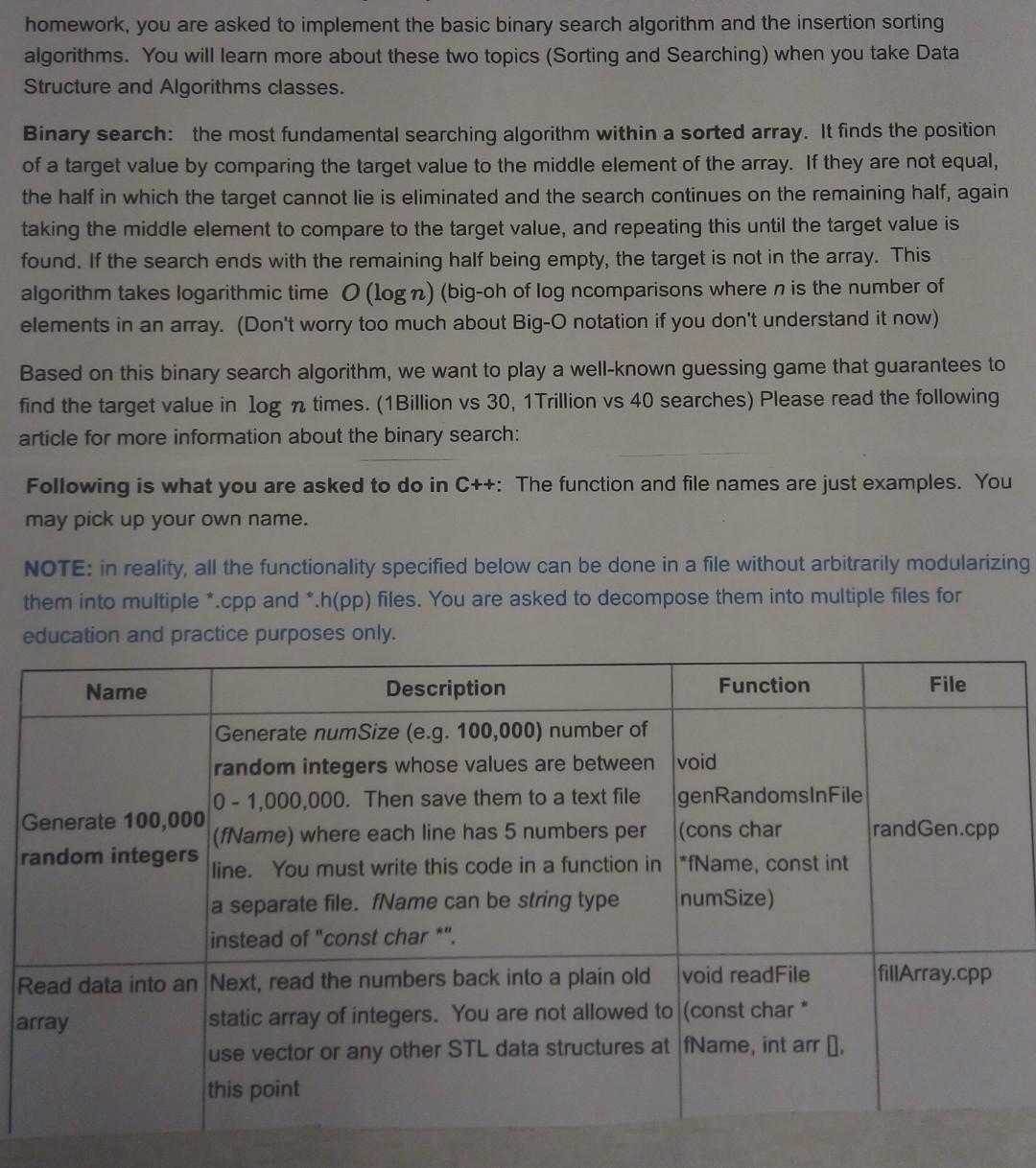
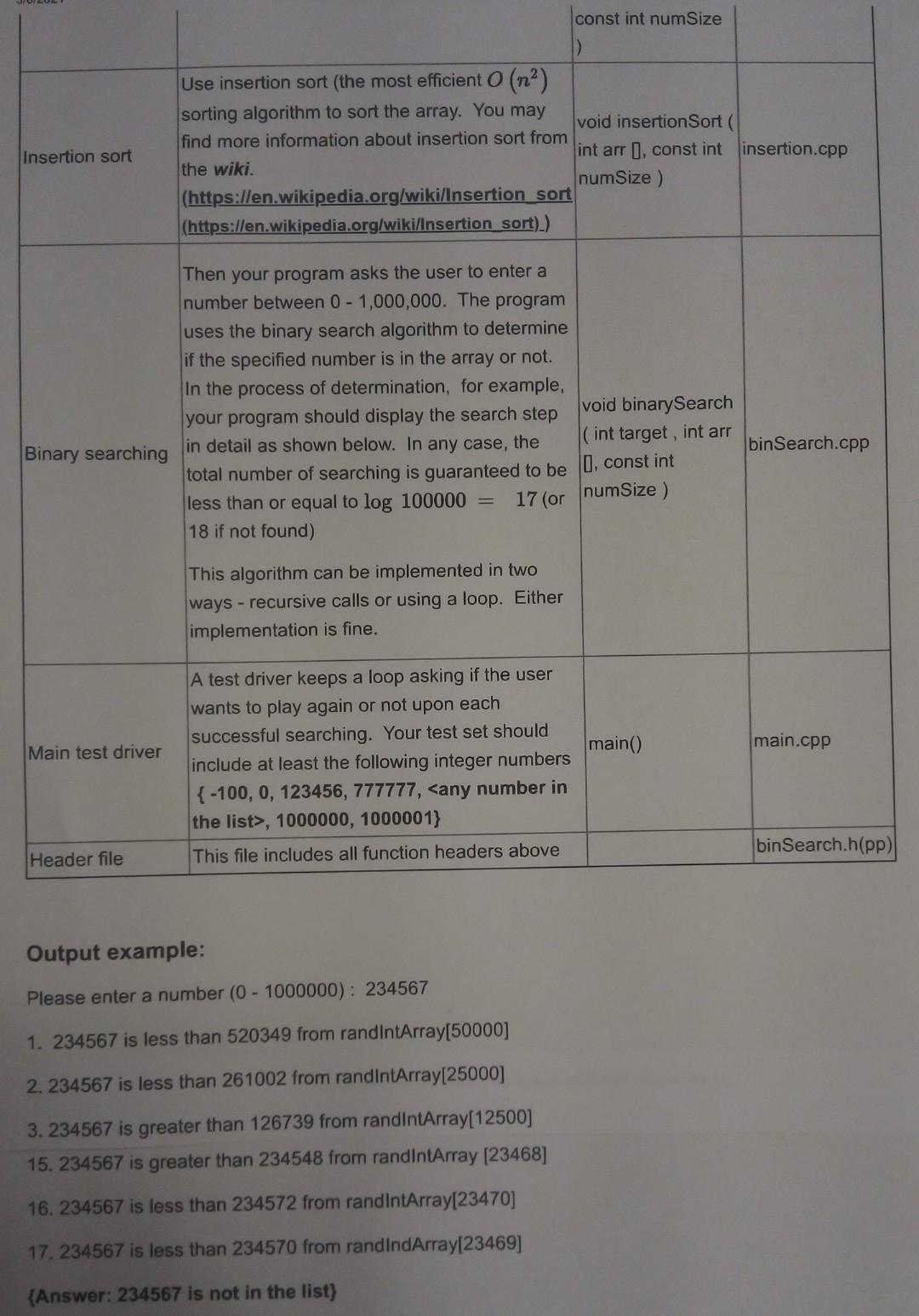
Setting up your development environment: READ FIRST: Setting up C++ development environment and tools Purposes of this assignment: 1. Continue with the concept and methods of procedural abstraction. 2. Modularizing the functionality and separating function headers from the implementations header (.h vs. .cpp) 3. Exercising enum type and switch statements 4. Building a project with multiple source code files 5. Learning a rudimentary sorting (insertion sort) and searching (binary search) algorithm This assignment consists of two parts. Each part earns 15 points, a total of 30 points which is 10 points more than the previous program assignments. PART 1: Insertion Sorting and Binary Searching (15 points) We live in the sea of information. It gets even more serious with the Internet. Think about all the information and data sorted globally waiting to be shared. We often need to find one particular item amongst so many of them. There are too many examples to name a few - trying to find someone's phone number on your phone, the most popular Ethiopian restaurant in Colorado, how to interpret a dream you had last night, 1998 Super bowl Winner, ... This is why fast searching algorithms are critical. If you linearly (sequentially) traverse each item in an available data set - for example of each phone number in your phone - individually, to see whether it is what you are looking for, in a very large set of data, it will take a few hours or days to finish it. Instead, the binary searching algorithm can be used to help find the item in a much shorter time. However, with un-preprocessed data (completely random data), there is no way you can do better than linear search (a.k.a. sequential search, Textbook page 211). But, if the data is pre-processed (sorted), then you can use the Binary Search (wiki) algorithm to lmprove the search time dramatically. In this homework, you are asked to implement the basic binary search algorithm and the insertion sorting algorithms. You will learn more about these two topics (Sorting and Searching) when you take Data Structure and Algorithms classes. Binary search: the most fundamental searching algorithm within a sorted array. It finds the position of a target value by comparing the target value to the middle element of the array. If they are not equal, the half in which the target cannot lie is eliminated and the search continues on the remaining half, again taking the middle element to compare to the target value, and repeating this until the target value is found. If the search ends with the remaining half being empty, the target is not in the array. This algorithm takes logarithmic time (log n) (big-oh of log ncomparisons where n is the number of elements in an array. (Don't worry too much about Big-O notation if you don't understand it now) Based on this binary search algorithm, we want to play a well-known guessing game that guarantees to find the target value in log n times. (1Billion vs 30, 1Trillion vs 40 searches) Please read the following article for more information about the binary search: Following is what you are asked to do in C++: The function and file names are just examples. You may pick up your own name. NOTE: in reality, all the functionality specified below can be done in a file without arbitrarily modularizing them into multiple *.cpp and h(pp) files. You are asked to decompose them into multiple files for education and practice purposes only. Name Description Function File Generate num Size (e.g. 100,000) number of random integers whose values are between void 10 - 1,000,000. Then save them to a text file genRandomsInFile Generate 100,000 (fName) where each line has 5 numbers per (cons char randGen.cpp random integers line. You must write this code in a function in "fName, const int a separate file. fName can be string type numSize) instead of "const char *". Read data into an Next, read the numbers back into a plain old void readFile fillArray.cpp array static array of integers. You are not allowed to (const char * use vector or any other STL data structures at fName, int arr I. this point const int num Size ) Use insertion sort (the most efficient 0 (na) sorting algorithm to sort the array. You may void insertion Sort find more information about insertion sort from int arr , const int insertion.cpp the wiki. numSize) (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insertion sort (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insertion sort).) Insertion sort Then your program asks the user to enter a number between 0 - 1,000,000. The program uses the binary search algorithm to determine if the specified number is in the array or not. In the process of determination, for example, void binary Search your program should display the search step (int target, int arr in detail as shown below. In any case, the Binary searching total number of searching is guaranteed to be 0. const int less than or equal to log 100000 18 if not found) bin Search.cpp 17 (or num Size ) This algorithm can be implemented in two ways - recursive calls or using a loop. Either implementation is fine. main.cpp Main test driver main() A test driver keeps a loop asking if the user wants to play again or not upon each successful searching. Your test set should include at least the following integer numbers {-100, 0, 123456, 777777,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


