Question: can anyone solve these?(top to bottom-1-13) no number 8 though. and do not worry about the drop down boxes! Werify that Rolle's Theorem can be
can anyone solve these?(top to bottom-1-13) no number 8 though. and do not worry about the drop down boxes!

![on the interval [2,4]. Then find all values of in the interval](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/10/6709306658cd4_4626709306642e5a.jpg)

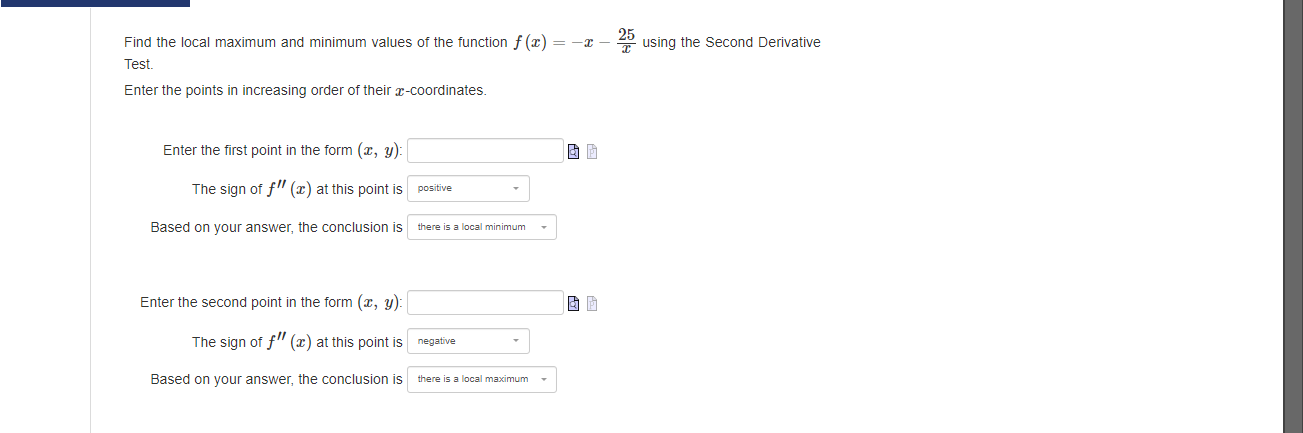
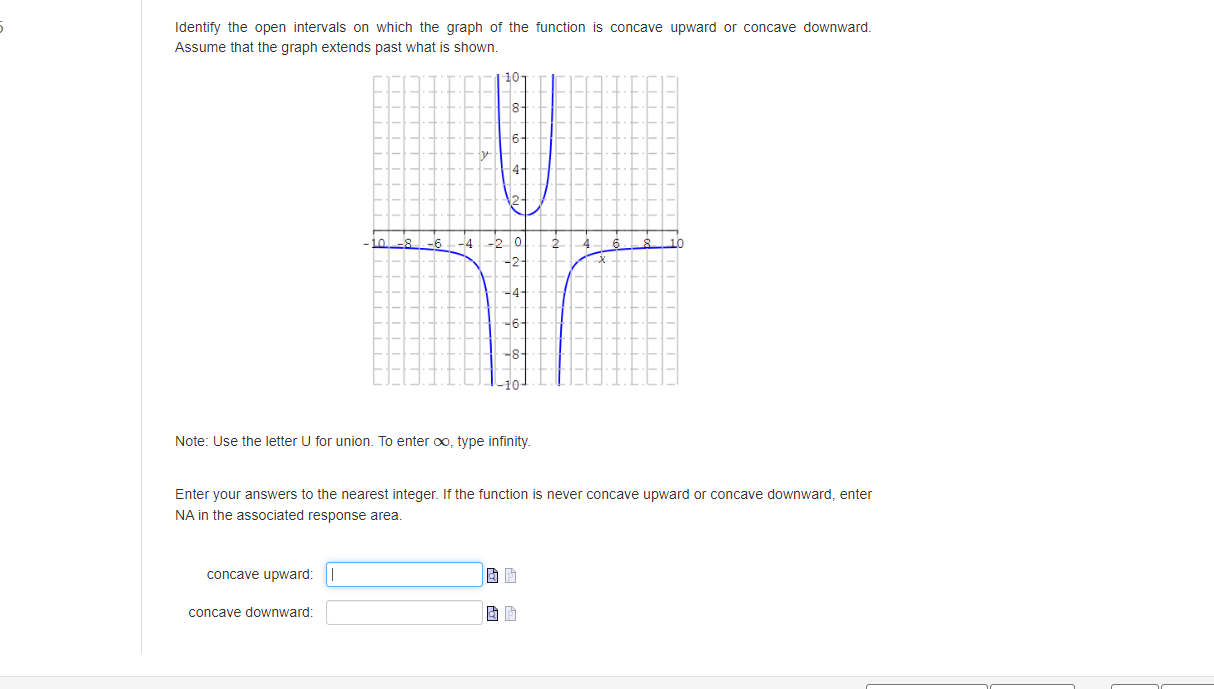
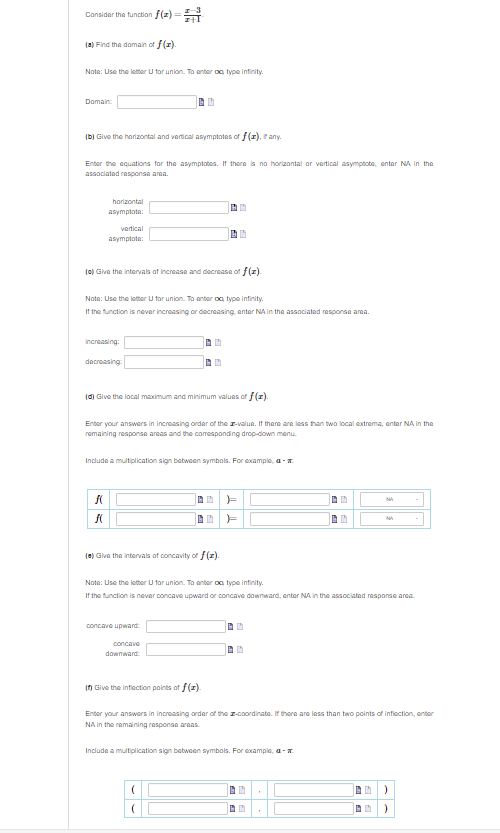
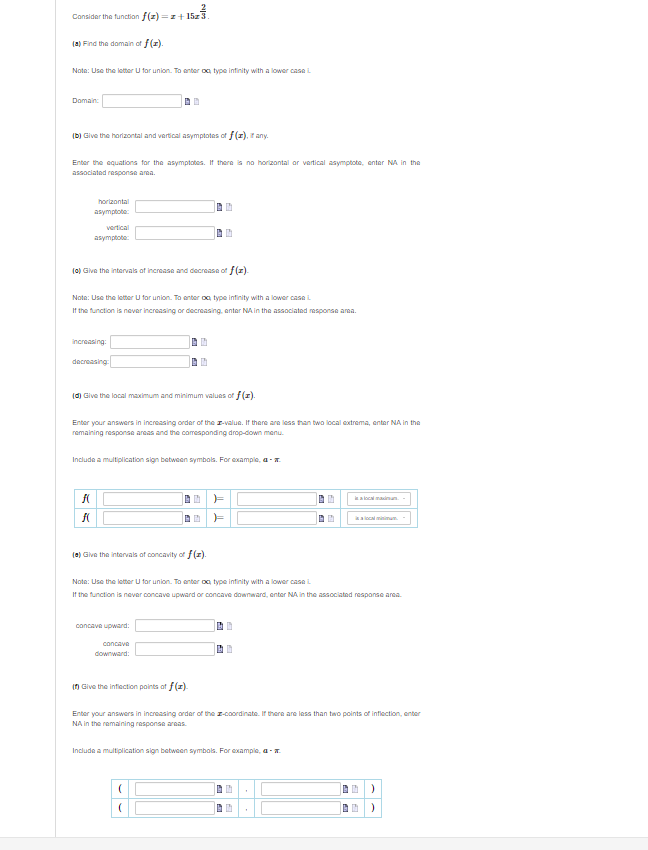
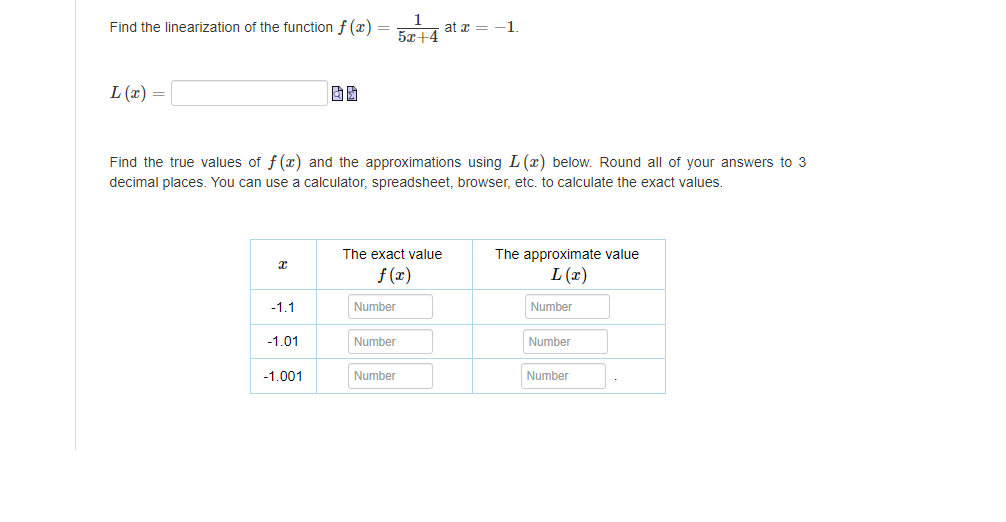
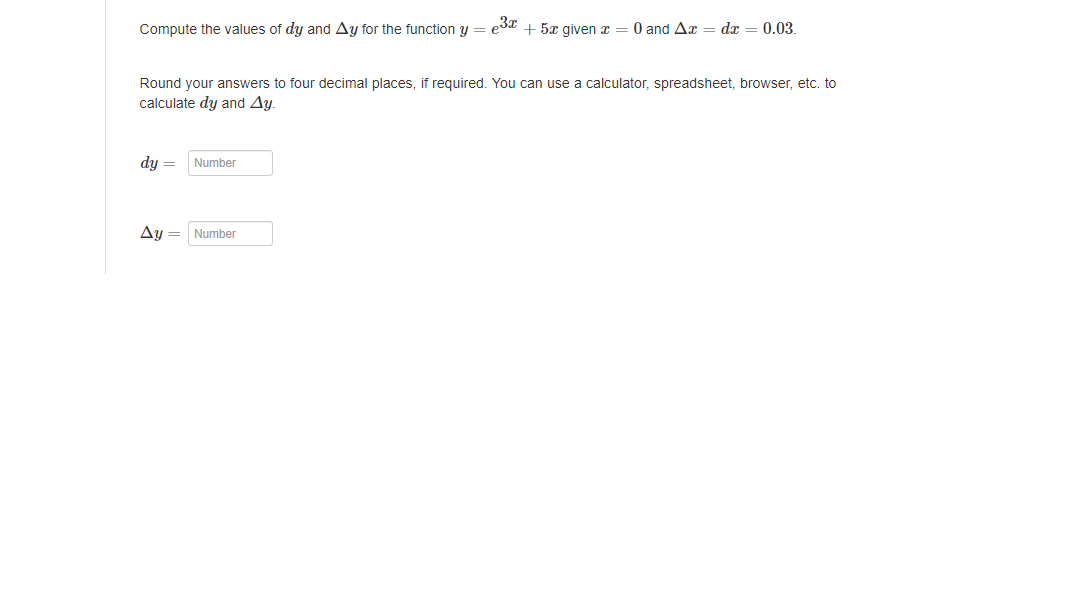
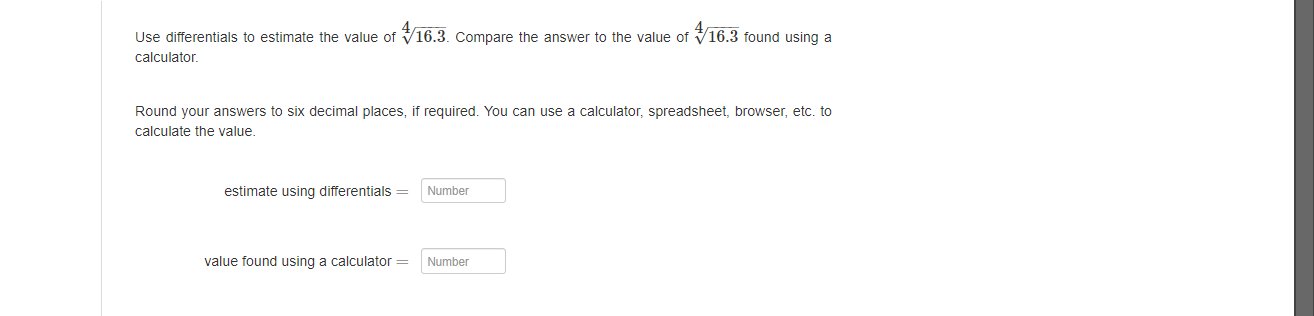
Werify that Rolle's Theorem can be applied 1o the function f(z) = 23 02 + 26z 24 on the interval [2,4]. Then find all values of in the interval such that / () = 0. Enter the exact answers in increasing order. To enter v/a, type sqrt(a). Compute the values of dy and Ay for the function y = es2 + 5x given x = 0 and Ax = da = 0.03. Round your answers to four decimal places, if required. You can use a calculator, spreadsheet, browser, etc. to calculate dy and Ay. dy = Number Ay = NumberUse differentials to estimate the value of V 16.3. Compare the answer to the value of V16.3 found using a calculator. Round your answers to six decimal places, if required. You can use a calculator, spreadsheet, browser, etc. to calculate the value. estimate using differentials = Number value found using a calculator = NumberThe radius of a circle is increasing at a rate of 10 centimeters per minute. Find the rate of change of the area when the radius is 2 centimeters. Round your answer 1o one decimal place The rate of change of the area is Number Units Assume that c and y are both differentiable functions of t and are related by the equation y = cos (4x). Find dy dt - when a = , given 41 = -4 when r = Enter the exact answer. dy dt NumberFind the local maximum and minimum values of the function f (x) = -x - 25 using the Second Derivative Test. Enter the points in increasing order of their -coordinates. Enter the first point in the form (I, y): The sign of f (x) at this point is positive Based on your answer, the conclusion is there is a local minimum Enter the second point in the form (I, y): The sign of f (x) at this point is negative Based on your answer, the conclusion is there is a local maximumIdentify the open intervals on which the graph of the function is concave upward or concave downward. Assume that the graph extends past what is shown. g b E Mote: Use the letter U for union. To enter oo, type infinity. Enter your answers to the nearest integer. I the function is never concave upward or concave downward, enter MA in the associated response area. concave upward: || &= concave downward: B B Consider the function / (=) = 2 3 [a) Find the domain of f (x). Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter ou type infinity. Domain: [bj Give the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of f (x), IF any. Enter the equations for the asymptotes. If there is no horizontal or vertical asymptote, enter NA in the associated response ama. horizontal asymptote: vertical asymptote: [o) Give the intervals of increase and decrease of f (x). Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter on type infinity. If the function is never increasing or decreasing, antar NAin the associated maponsa ama. increasing: dacronsing [dj Give the local maximum and minimum values of f (x). Enter your answers in increasing order of the I-value. If there are less than two local extrema, enter NA in the remaining response areas and the comesponding drop-down menu. Include a multiplication sign between symbols. For example, a - . NA INA [e) Give the intervals of concavity of f (x). Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter on type infinity. If the function is never concave upward or concave downward, enter NA in the associated response area. concave upwards ConCAVE downward: [f) Give the inflection points at f (xx). Enter your answers in increasing order of the I-coordinate. If there are less than two points of inflection, enter NA in the remaining response areas. Include a multiplication sign between symbols. For example, a - 5.Consider the function / (x) = x + 1523. [a) Find the domain of f (I). Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter on type infinity with a lower case i Domain: [bj Give the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of f (x), If any. Enter the equations for the asymptotes. If there is no horizontal or vertical asymptote, enter NA in the associated response ami. horizontal asymptote: vertical asymptote: To) Given the intervals of increase and decrease of f (x)- Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter on type infinity with a lower case i. If the function is never increasing or decreasing, antar NA in the associated msponse ama. increasing: dacronsing: [dj Give the local maximum and minimum values of f (x). Enter your answers in increasing order of the I-value. If there are less than two local extrema, antar NA in the remaining response areas and the comesponding drop-down manu. Include a multiplication sign between symbols. For example, a - a. In a local maximum. - [e) Give the intervals of concavity of f (x). Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter on type infinity with a lower case it If the function is never concave upward or concave downward, enter NA in the associated response anda. concave upward: concave downward: [f) Give the inflection points at f (x). Enter your answers in increasing order of the I-coordinate. If there are less than two points of inflection, enter NA in the remaining response areas. Include a multiplication sign between symbols. For example, a - a. GO .Find the linearization of the function f (x) = 51+4 at c = -1. L(I) = Find the true values of f (@) and the approximations using L (@) below. Round all of your answers to 3 decimal places. You can use a calculator, spreadsheet, browser, etc. to calculate the exact values. The exact value The approximate value f (I) L(x) -1.1 Number Number -1.01 Number Number -1.001 Number Number
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


