Question: Can someone help me on this problem, files must be main.cpp, dictionary.h , dictionary.cpp, DictEntry.h and DictEntry.cpp ? For this assignment, you will implement dictionary.h
Can someone help me on this problem, files must be main.cpp, dictionary.h , dictionary.cpp, DictEntry.h and DictEntry.cpp ?
For this assignment, you will implement dictionary.h
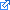 to create a dictionary that reads in a list of unsorted words into a
to create a dictionary that reads in a list of unsorted words into a STL (which is an implementation of a doubly linked list.) from a file called dictionary.txt

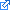 . Next, you must sort the list. The list STL has a member function .sort which works as long as you have overloaded the findwords.txt
. Next, you must sort the list. The list STL has a member function .sort which works as long as you have overloaded the findwords.txt
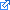 For each word in findwords.txt, you will search that list from the beginning of the list and if found, print (to the screen) how many searches/comparisons you had to make to find the word. Then you will search from the back of the list and print how many searches you had to make.
For each word in findwords.txt, you will search that list from the beginning of the list and if found, print (to the screen) how many searches/comparisons you had to make to find the word. Then you will search from the back of the list and print how many searches you had to make.
This will help you visualize that a Doubly Linked List might on average cut your search time in half by sorting the data, then choosing which end to start the search.
When complete print out each word with spaces in between in a file called revsorted.txt. Start at the back of the list so you end up with a reverse sorted list (words starting with z's first).
The reason you have a separate DictEntry.h
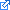 is to separate the dictionary methods from the type of data. If you were implementing your own doubly linked list, you would create a separate Node class. Remember, Nodes have data (which would be a dictionary entry), and forward and back pointers. Currently we are only using the word in DictEntry, but could easilly use the definition, pronunciation, word history etc.
is to separate the dictionary methods from the type of data. If you were implementing your own doubly linked list, you would create a separate Node class. Remember, Nodes have data (which would be a dictionary entry), and forward and back pointers. Currently we are only using the word in DictEntry, but could easilly use the definition, pronunciation, word history etc.
Some Important tips (please read): http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/ (Links to an external site.)
- Remember like a vector, you have a list of a particular type (dictionary in this case)
- A list
- There are member functions for a list .begin() which is pointing to the first item on the list and .end() which is the last pointer NULL. So, you generally want to loop from .begin() to != .end()
To start at the back (tail pointer) and work you way to the front you want to reverse the process. so instead of an iterator (which points to the head of the list), you want to use reverse_iterator. And instead of .begin() to != .end(), you want to go from .rbegin() to != .rend()
In order to use the .sort() function for lists, you must overload the operator
Remember if you are looking at the VALUE of what the pointer points to, you must dereference the pointer. An iterator or reverse_iterator is a pointer. If you are pointing to a class with a public member function called findValue, you would write that as xPtr->getWords(), NOT xPtr.findValue.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


