Question: Can you complete this code and send me the original code, please. Thank you. send me the Breadth-First Search In this exercise, you will implement
Can you complete this code and send me the original code, please. Thank you. send me the Breadth-First Search
In this exercise, you will implement BFS for a adjacency list representation for a graph. The function, BFS(), takes three arguments: the graph to traverse, the start node, and the end node. It should return a shortest path from start to node, inclusive, as a list. For example, given the graph below, BFS(graph, 0, 6) should return [0, 1, 6] or [0, 5, 6]. If there is no path, return an empty list, [].
1. Create an empty set of closed nodes and an empty dictionary to store each node's parent
2. Initialize the open queue to contain the start node
3. While the open queue is not empty, dequeue the next node from the open queue and set it to the current node
1. If it is the goal node, reconstruct the path back to the start using the parent mapping
2. Otherwise, for each of its neighbors, add it to the open queue if it's not in there or in the closed set and store the current node as its parent. Add the current node to the set of closed nodes.
4. If you empty the open queue without reaching the goal node, there is no path.
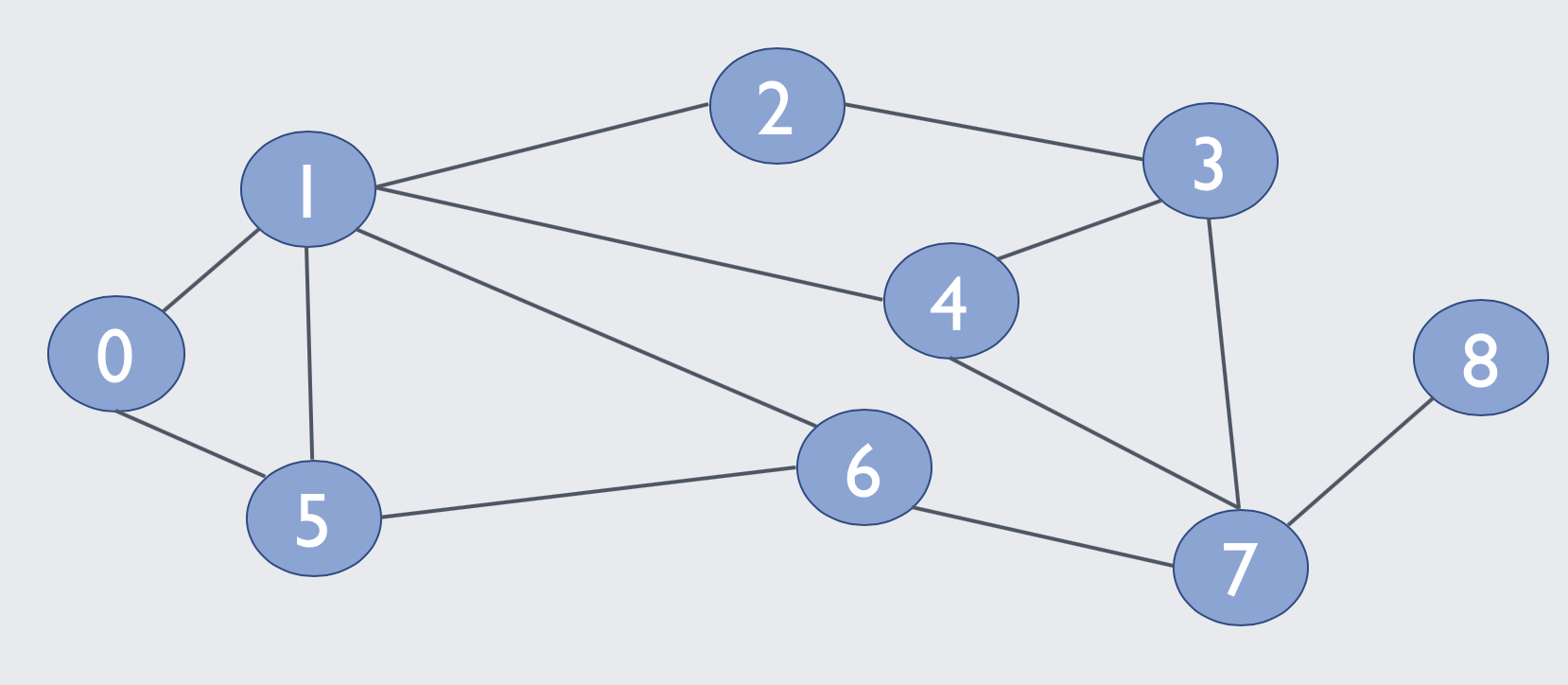
graph = [
[1,5],
[0,2,4,5,6],
[1,3],
[2,4,7],
[1,3,7],
[0,1,6],
[1,5,7],
[3,4,6,8],
[7],
]
len(BFS(graph, 0, 6)) == 3
len(BFS(graph, 1, 8)) == 4
len(BFS(graph, 2, 3)) == 2
from collections import deque
def BFS(graph, start, goal): # Step 1: initialize variables parent = {} # holds mapping between every node and it's parent in the path current_node = start closed_set = {} # Step 2: initialize open queue open_queue = deque() open_queue.append(start) # Step 3: while loop setting current node while len(open_queue) > 0: current_node = open_queue.popleft() # Step 3.1 return path if we're at the goal if current_node == goal: # Step 3.2a: iterate over neighbors of current node # and add to open queue if not already there or in closed # Remember to store the parent information for neighbor in graph[current_node]: if neighbor not in open_queue and neighbor not in closed_set: open_queue.append(neighbor) parent[neighbor] = current_node closed_set.add(current_node) # Step 4: return failure condition if there is no path return None
3 0 6 3 0 6
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


