Question: This is only one question, I explained the question in the detailed formated with instructions and example, you only have to edit the given code
This is only one question, I explained the question in the detailed formated with instructions and example, you only have to edit the given code to get the similar output in the example. Please help answer it in step by step format. Thank you!!
Finding the shortest path through a maze with cycles using breadth-first search.
In this third part of the assignment, you will write a program to find a shortest path in a graph from a source node to a destination node using breadth-first search. The graph representing the maze may contain cycles, so it is important avoid revisiting nodes that have already been visited.
Many important problems in artificial intelligence, robotics motion planning, and self-driving cars boil down to solving mazes on graphs. In classes such as AI and robotics, you will learn about advanced algorithms for solving mazes using heuristics (or informed guesses) that minimize search time.
Input format
Your program should take TWO command line arguments. The first argument specifies the path to an input file describing a graph like previous portions of this assignment. The second argument specifies the path to an input file describing a query. The first line of the query file specifies the source node where you begin your search. The second line of the query file specifies the target node you want to reach.
Output format
You should print a list of edges that, taken together, connect the source node to the target node in the graph. Again, the ordering of the nodes in each edge does not matter. The ordering of the edges does not matter. The autograder will check to see if you give a minimal set of edges that connect the source and target nodes.
Example input:
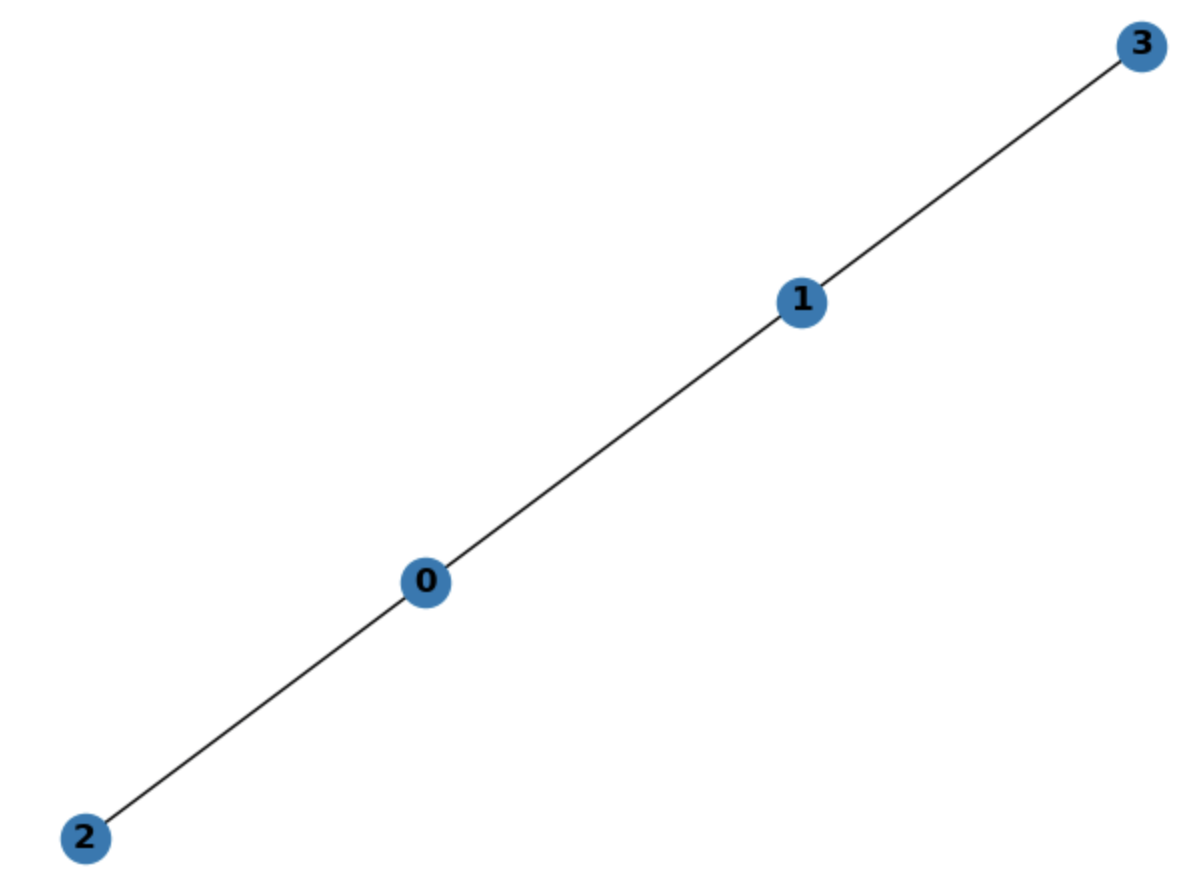
4
0 1 1 0
1 0 0 1
1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0
Output:
0 2
0 1
1 3
Edit the given code below:
#include "../graphutils.h" // header for functions to load and free adjacencyList
#include "../queue/queue.h" // header for queue
// A program to solve a maze that may contain cycles using BFS
int main ( int argc, char* argv[] ) {
// First, read the query file to get the source and target nodes in the maze
/* ... */
// READ INPUT FILE TO CREATE GRAPH ADJACENCY LIST
AdjacencyListNode* adjacencyList = NULL;
/* ... */
// USE A QUEUE TO PERFORM BFS
Queue queue = { .front=NULL, .back=NULL };
// An array that keeps track of who is the parent node of each graph node we visit
graphNode_t* parents = calloc( graphNodeCount, sizeof(graphNode_t) );
for (size_t i=0; i parents[i] = -1; // -1 indicates that a nodes is not yet visited } /* ... */ while ( current != target ) { // so long as we haven't found the target node yet, iterate through the adjacency list // add each neighbor that has not been visited yet (has no parents) to the queue of nodes to visit /* ... */ // Visit the next node at the front of the queue of nodes to visit /* ... */ } // Now that we've found the target graph node, use the parent array to print maze solution // Print the sequence of edges that takes us from the source to the target node /* ... */ // free any queued graph nodes that we never visited because we already solved the maze while ( queue.front ) { /* ... */ } free (parents); freeAdjList ( graphNodeCount, adjacencyList ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


