Question: Can you provide the solution for each question? ECON 333 - Games and Strategies Problem Set 3 1. (35 points) A robber decides whether to
Can you provide the solution for each question?
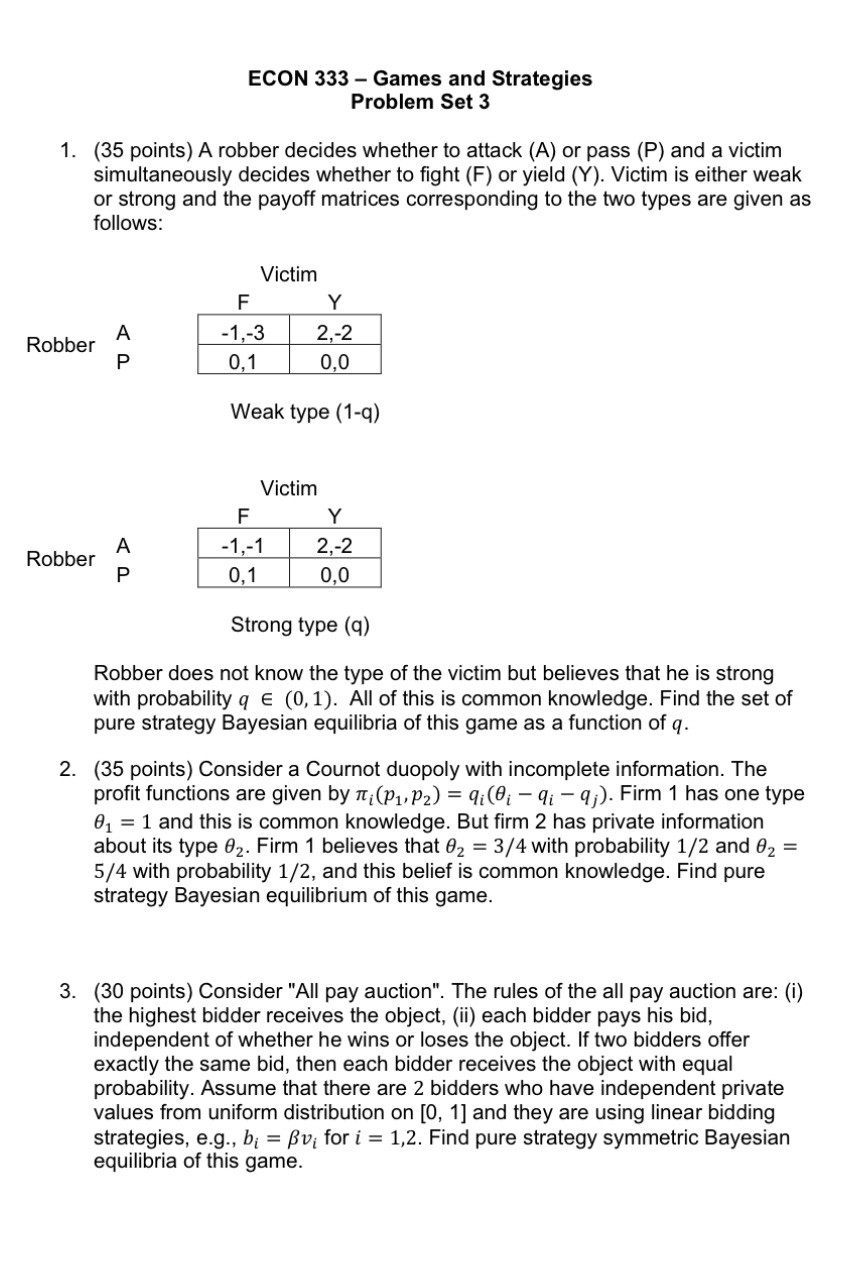
ECON 333 - Games and Strategies Problem Set 3 1. (35 points) A robber decides whether to attack (A) or pass (P) and a victim simultaneously decides whether to fight (F) or yield (Y). Victim is either weak or strong and the payoff matrices corresponding to the two types are given as follows: Victim F X Robber A 1,3 2,2 P 0.1 0,0 Weak type (1-q) Victim Robber 1.1 2;-2 0,1 Strong type (q) Robber does not know the type of the victim but believes that he is strong with probability g (0,1). All of this is common knowledge. Find the set of pure strategy Bayesian equilibria of this game as a function of q. 2. (35 points) Consider a Cournot duopoly with incomplete information. The profit functions are given by m;(p,,p,) = q;(6; q; q;)- Firm 1 has one type #, = 1 and this is common knowledge. But firm 2 has private information about its type 8,. Firm 1 believes that 8, = 3/4 with probability 1/2 and 8, = 5/4 with probability 1/2, and this belief is common knowledge. Find pure strategy Bayesian equilibrium of this game. 3. (30 points) Consider "All pay auction\". The rules of the all pay auction are: (i) the highest bidder receives the object, (ii) each bidder pays his bid, independent of whether he wins or loses the object. If two bidders offer exactly the same bid, then each bidder receives the object with equal probability. Assume that there are 2 bidders who have independent private values from uniform distribution on [0, 1] and they are using linear bidding strategies, e.g., b; = pv; fori = 1,2. Find pure strategy symmetric Bayesian equilibria of this game
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


