Question: Chap 12-Handout 1 12.1 Conceptual Issues in Cash Flow Estimation The cash flows that occur if and only if the project is accepted. Asset purchases

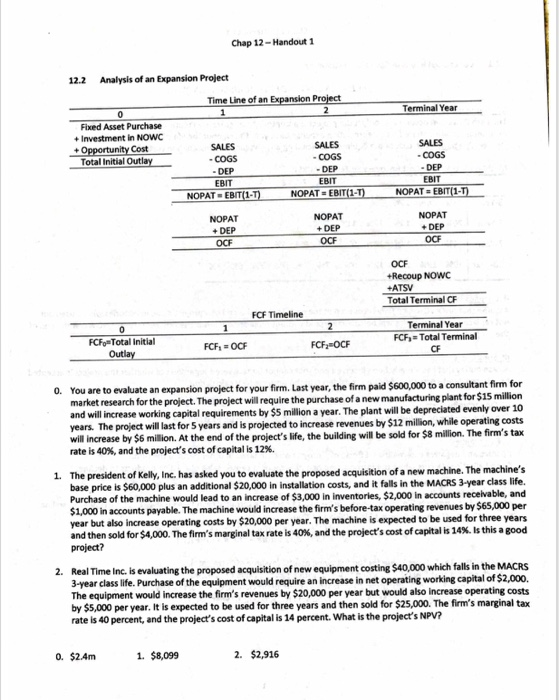
Chap 12-Handout 1 12.1 Conceptual Issues in Cash Flow Estimation The cash flows that occur if and only if the project is accepted. Asset purchases represent negative cash flows. Accounting treatment: Deduct a depreciation expense each year throughout the lfe of the asset Depreciable basis- Full cost of the equipment, including any shipping and installation costs. Modified Accelerated Cost 1 2 3 4 5 6 78910 11 3-Year 33% 5-Year 120% 7-Year | 14% 10-Year|10% 45% 32% 25% 18% 15% 19% 17% 14% 756 12% 13% 12% 6% 9% 7% 11% 9% 9% 9% 4% 3% 6% 7% 7% 7% Assume that ANOWC will be fully recovered at the end. Toward the end of a project'slife, inventories will be used but not replaced and receivables will be collected/paid without replacement. Thus the firm recaptures the projects life. 0wC at the end of A cash outlay that has already been incurred and that cannot be recovered regardless of whether the project is accepted or rejected. Sunk costs should not be considered in the projects NPV calculation. The return on the best alternative use of an asset. It's what you give up by using the asset. Positive and negative externalities. Effects of a project on cash flows in other parts of the firm. Cannibalization: Occurs when the introduction of a new product causes sales of existing products to decline. At the end of a projects life some assets can be sold to generate terminal cash flows (savage value). However, selling depreciated assets can generate a tax liability or refund. ATSV Salvage Value Tax Tax = (Salvage Value-Book Value)(T) Find the After-Tax Salvage Value for the following assets: (assume 40% tax rate): 1. Machine that cost $40,000, 50% depreciated, with a salvage value of $28,000. 2. Building that cost $700,000, using 20-year straight-line depreciation, to be sold in 12 years for $200k. 3. Equipment costing $100k, MACRS 7-year, to be sold for $30,000 10 years later Chap 12-Handout 1 Analysis of an Expansion Project 12.2 Time Line of an Terminal Year Fixed Asset Purchase + Investment in NOWC SALES SALES Cost Total Initial DEP EBIT DEP EBIT DEP EBIT NOPAT EBIT(1-T NOPAT = EBIT(1 NOPAT- EBIT NOPAT DEP OOF NOPAT +DEP NOPAT DEP OCF OCF +Recoup NOWC +ATSV Total Terminal CF FCF Timeline Terminal Year FCF-Total Terminal CF FCFo Total initial You are to evaluate an expansion project for your firm. Last year, the firm paid $600,000 to a consultant firm for market research for the project. The project will require the purchase of a new manufacturing plant for $15 million and will increase working capital requirements by $5 million a year. The plant will be depreciated evenly over 10 years. The project will last for 5 years and is projected to increase revenues by $12 million, while operating costs will increase by $6 million. At the end of the project's life, the building wil be sold for $8 million. The firm's tax rate is 40%, and the project's cost of capital is 12%. o. 1. The president of Kelly, Inc. has asked you to evaluate the proposed acquisition of a new machine. The machine's class life. base price is $60,000 plus an additional $20,000 in installation costs, and it falls in the MACRS 3-year Purchase of the machine would lead to an increase of $3,000 in inventories, $2,000 in accounts receivable, and 1,000 in accounts payable. The machine would increase the firm's before-tax operating revenues by $65,000 per year but also increase operating costs by $20,000 per year. The machine is expected to be used for three years project? and then sold for $4,000. The firm's marginal tax rate is 40%, and the project's cost of capital is 14%. Is this a good Real Time Inc. is evaluating the proposed acquisition of new equipment costing $40,000 which falls in the MACRS 3-year class life. Purchase of the equipment would require an increase in net operating working capital of $2,000. The equipment would increase the firm's revenues by $20,000 per year but would also increase operating costs by $5,000 per year. It is expected to be used for three years and then sold for $25,000. The firm's marginal tax rate is 40 percent, and the project's cost of capital is 14 percent. What is the project's NPV? 2. 2. $2,916 1. $8,099 0. $2.4m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


