Question: Chapter 10 Problem Set Mastery Problem: Activity-Based Costing (Basic) Indirect costs are allocated to the cost of a product in a manufacturing environment, or to
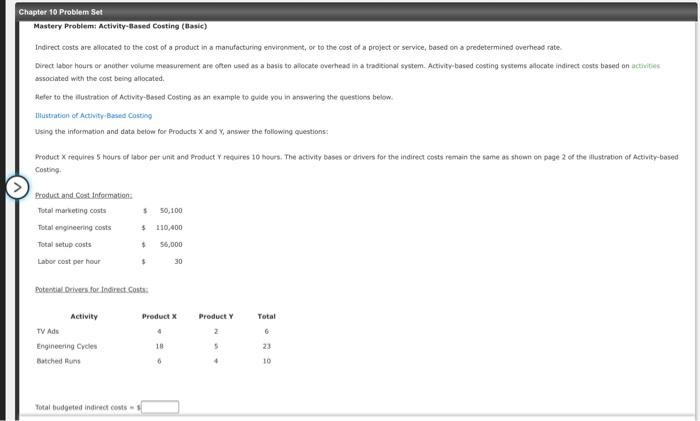
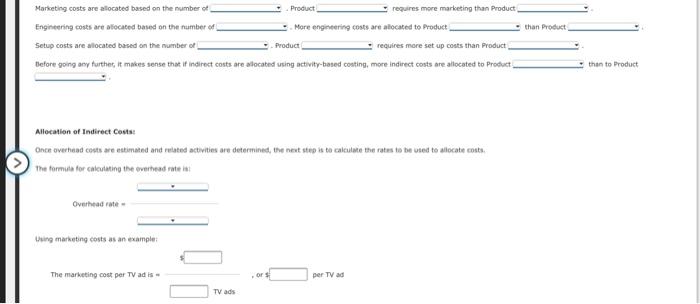
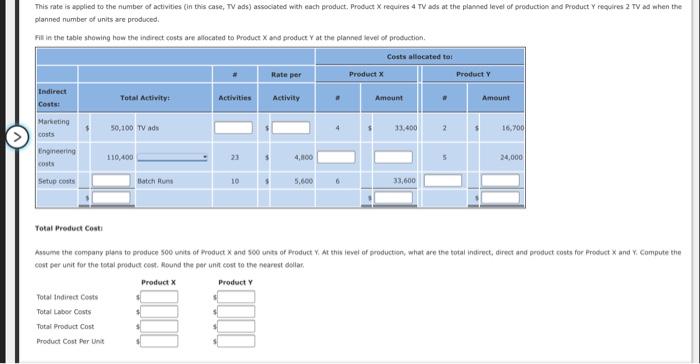
Chapter 10 Problem Set Mastery Problem: Activity-Based Costing (Basic) Indirect costs are allocated to the cost of a product in a manufacturing environment, or to the cost of a project or service, based on a predetermined overhead rate Direct labor hours or another volume measurement are often used as a basis to allocate overhead in a traditional system. Activity-based costing systems allocate indirect costs based on activities associated with the cost being allocated Hefer to the lustration of Activity-Based Costing as an example to guide you in answering the question below. Illustration of Activity Based Costing Using the information and data below for Products and answer the following questions: Product X requires 5 hours of tabor per unit and Product Y requires 10 hours. The activity bases or drivers for the indirect costs remain the same as shown on page 2 of the lustration of Activity-based Costing $ 50,100 Product and Cost Information Total marketing costs Total engineering costs Total setup costs Labor cost per hour $ 110,400 56,000 $ 30 Potential Drivers for direct costs Product Product Y Total Activity TV Ads Engineering Cycles Batched uns 23 18 0 10 Total budgeted indirect costs than Product Marketing costs are allocated based on the number of Product requires more marketing than Product Engineering costs are located based on the number of More engineering costs are allocated to Product Setup costs are located based on the number of Product requires more set up costs than Product Before going any further, it makes sense that if indirect costs are allocated using activity-based costing, more Indirect costs are allocated to Product than to Product Allocation of Indirect costs Once overhead costs are estimated and related activities are determined, the next step is to calculate the rates to be used to allocate costs The formula for conting the overhead rotest Overhead rate- Using marketing costs as an example The marketing cost per TV ad is per TV ad TV ads This rate is applied to the number of activities in this case, TV ads) associated with each product, Product X requires 4 TV ads at the planned level of production and Product requires 2 TV od when the planned number of units are produced Fill in the table showing how the indirect costs are allocated to Product X and product Yat the planned level of production Costs allocated to Rate per Product Product Indirect Total Activity: Activities Activity Amount Amount Costs Marketing costs 50,100 TV ads 33.400 2 16,700 Engineering costs 110,400 23 $ 4.800 5 24.000 Setup costs Batch Pune 10 5.600 33,600 Total Product Costi IY Assume the company plans to produce 500 units of Product X and scounts of Product Y. At this level of production, what are the total indirect, direct and product costs for Product and Y. Compute the cost per unit for the total product cost. Round the per un cost to the nearest dollar Product Product Total Indirect costs Total Labor Costs Total Product Cost Product Cost Per Unit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


