Question: CHAPTER PROBLEMS: NON-PARAMIETRIC TESTING 10 questions, 30 points Chapter 10 Multiple Choice 1. A new drug for pain relief is being tested within a given
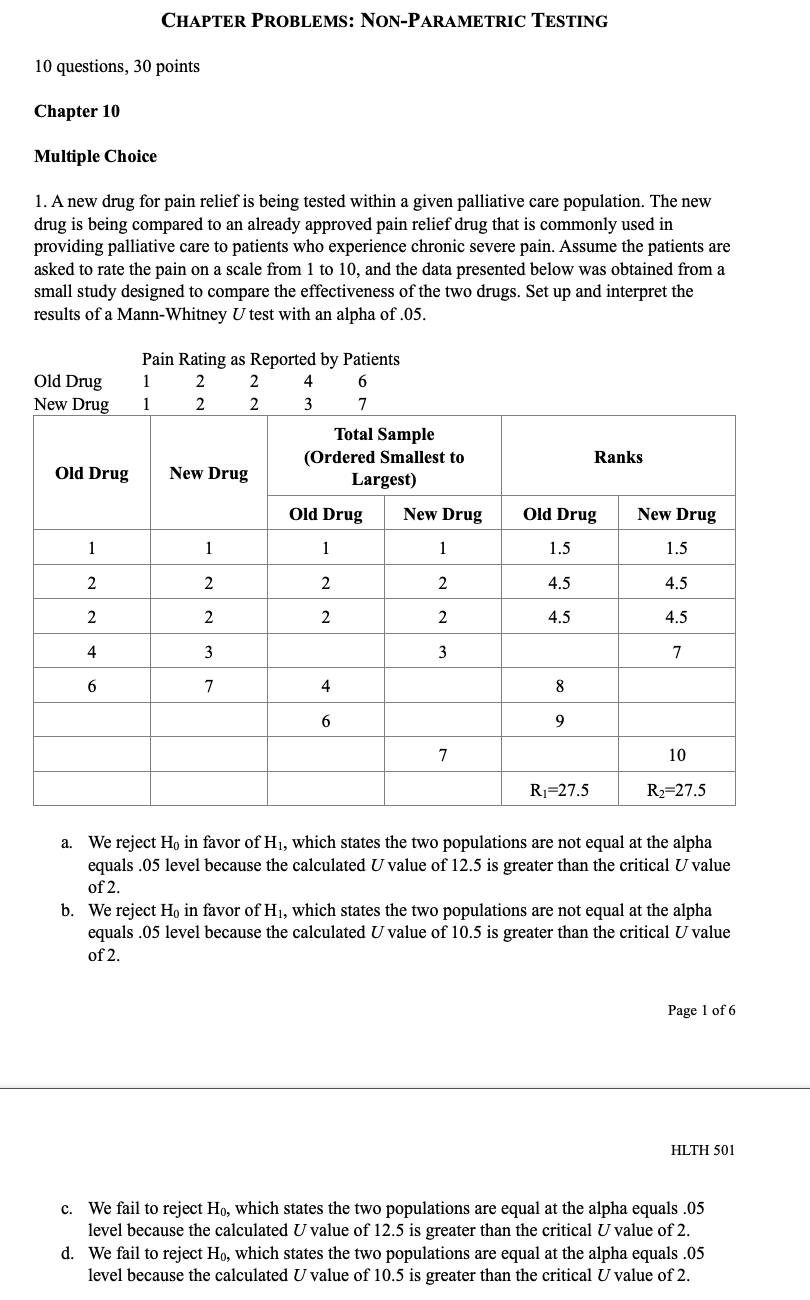
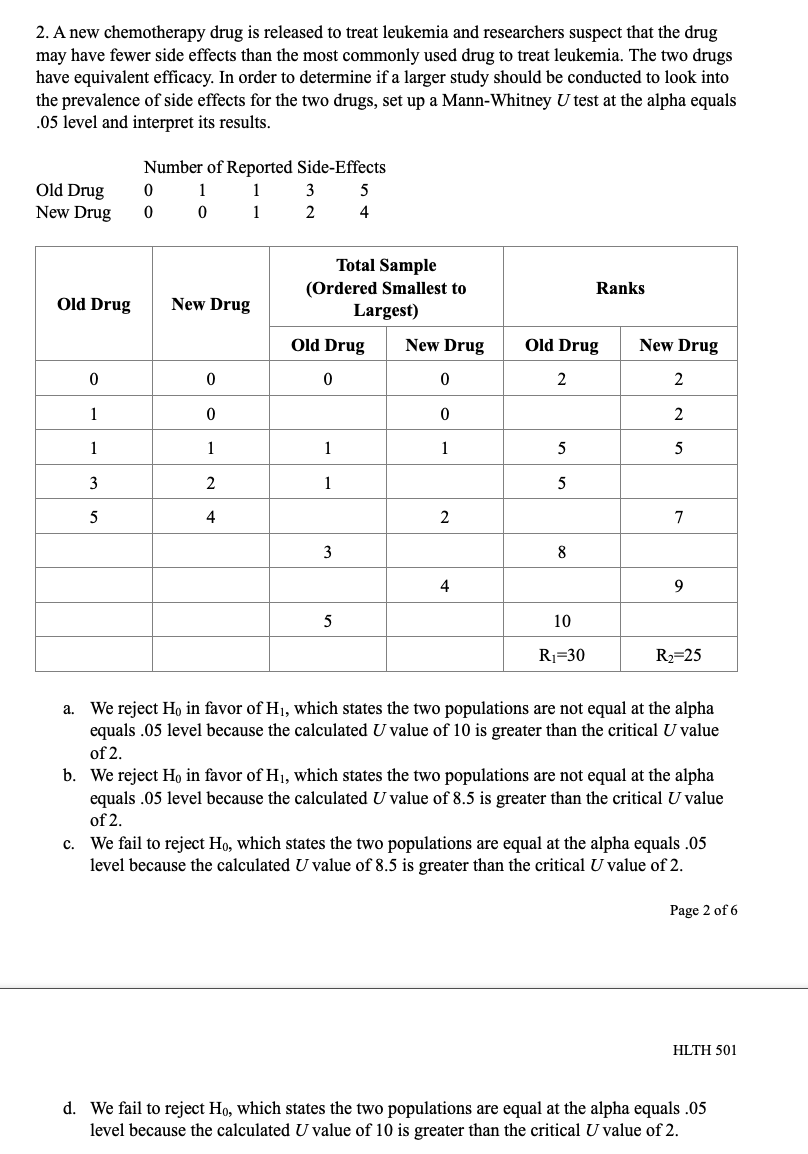
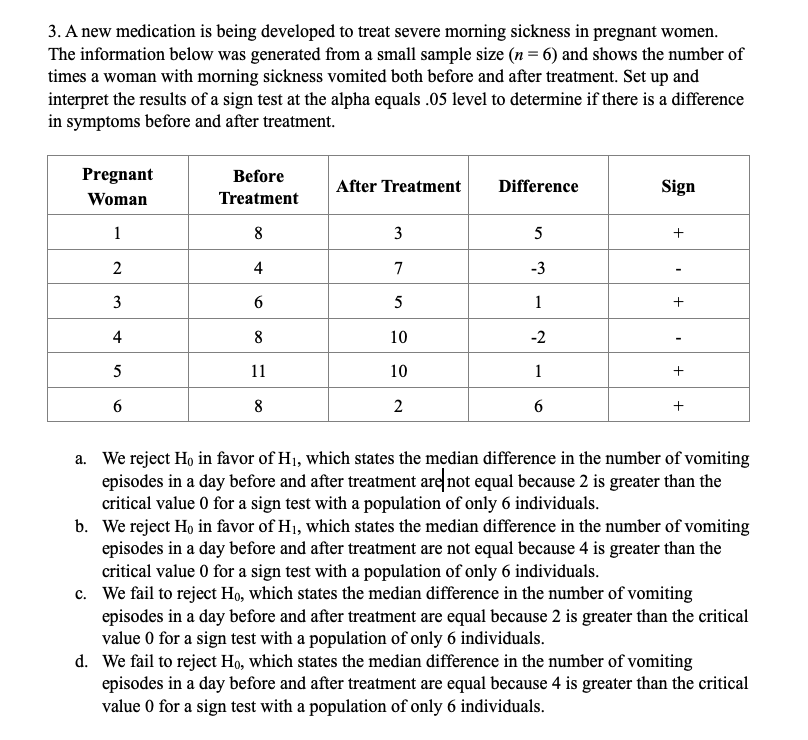
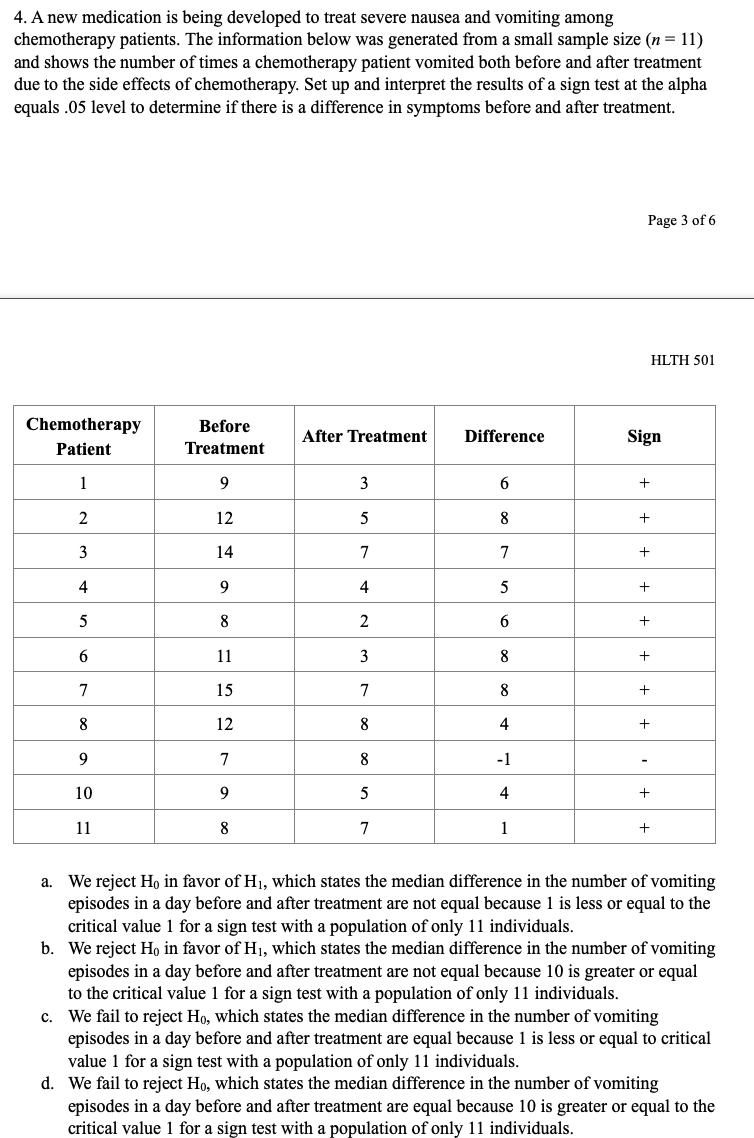
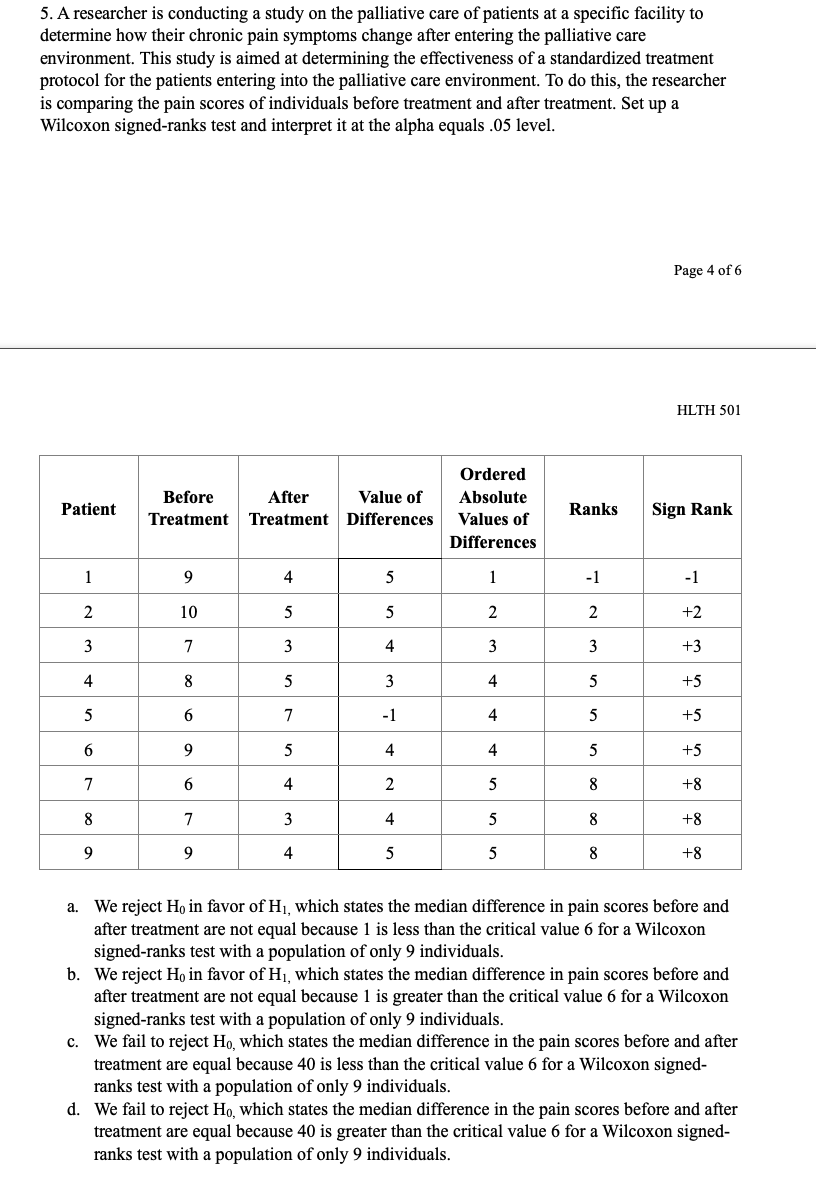

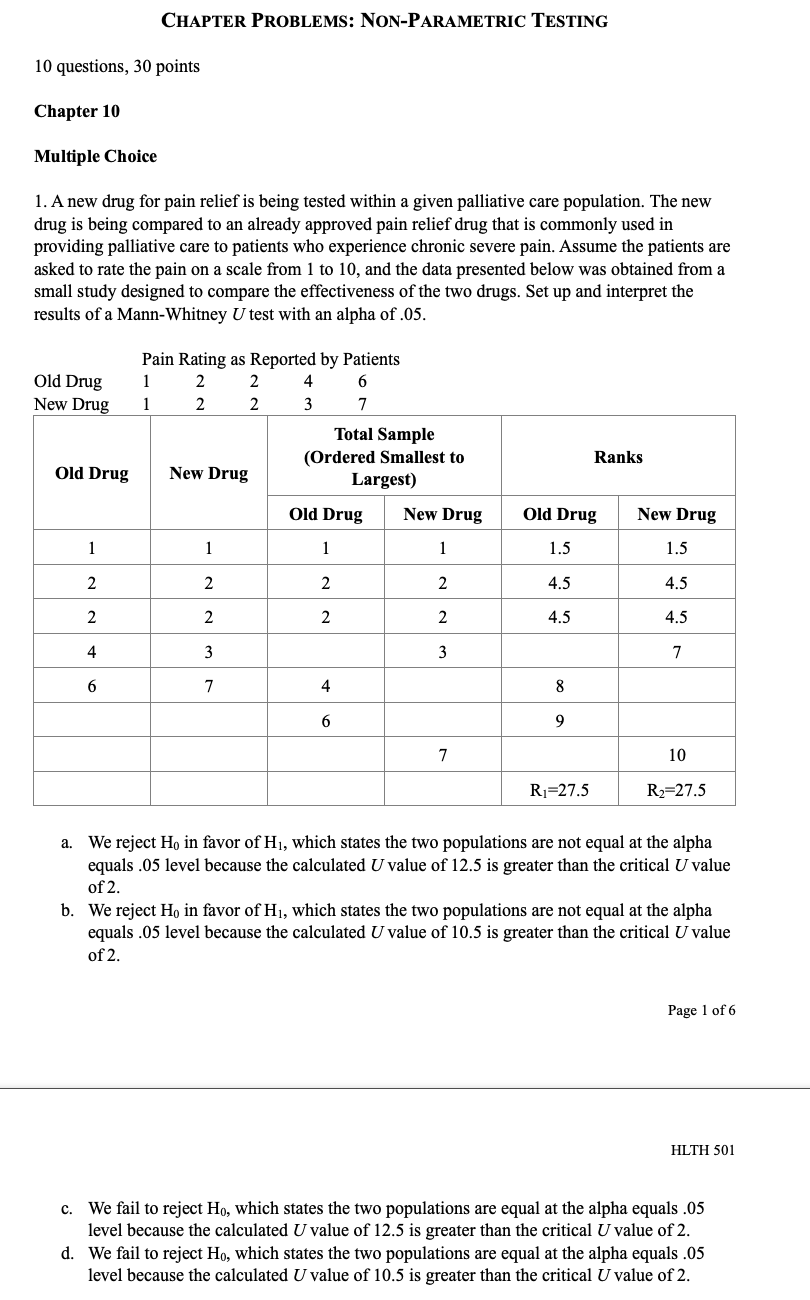
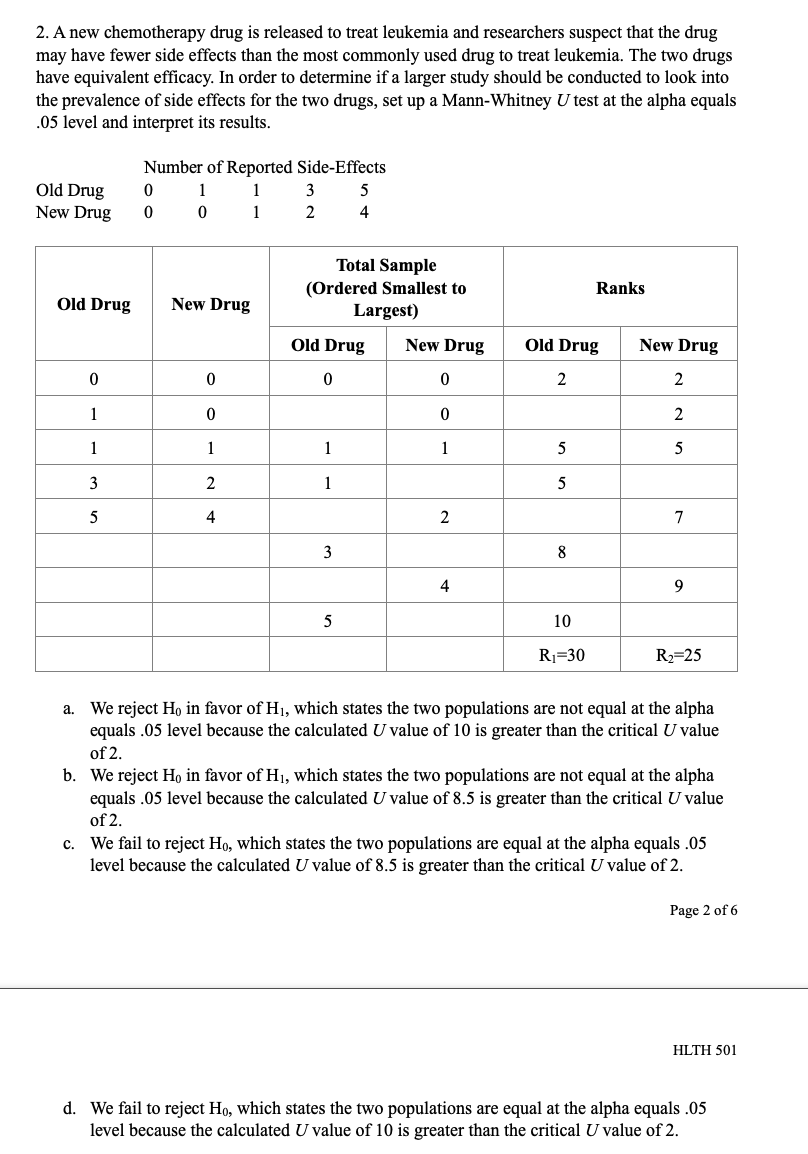
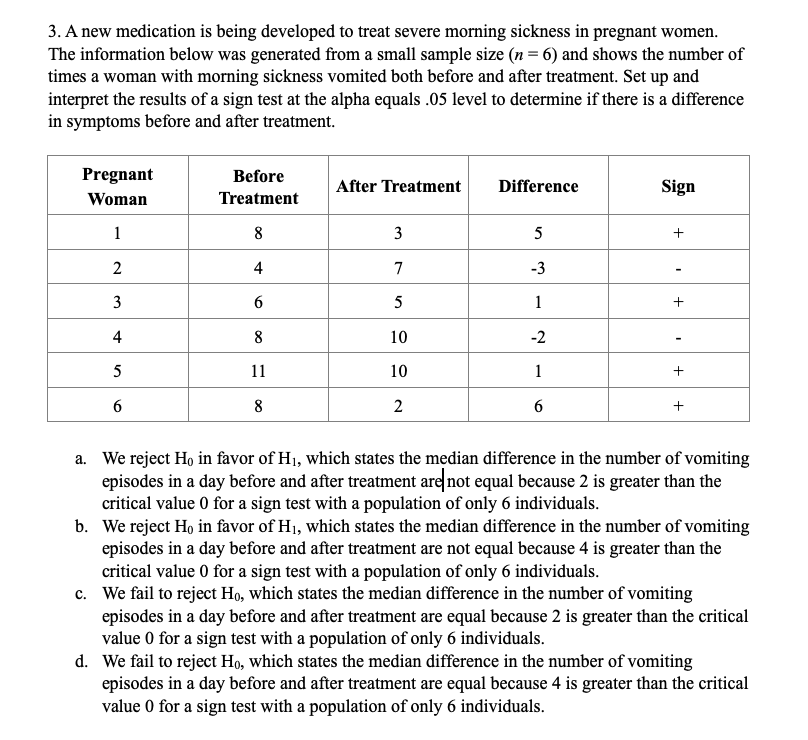
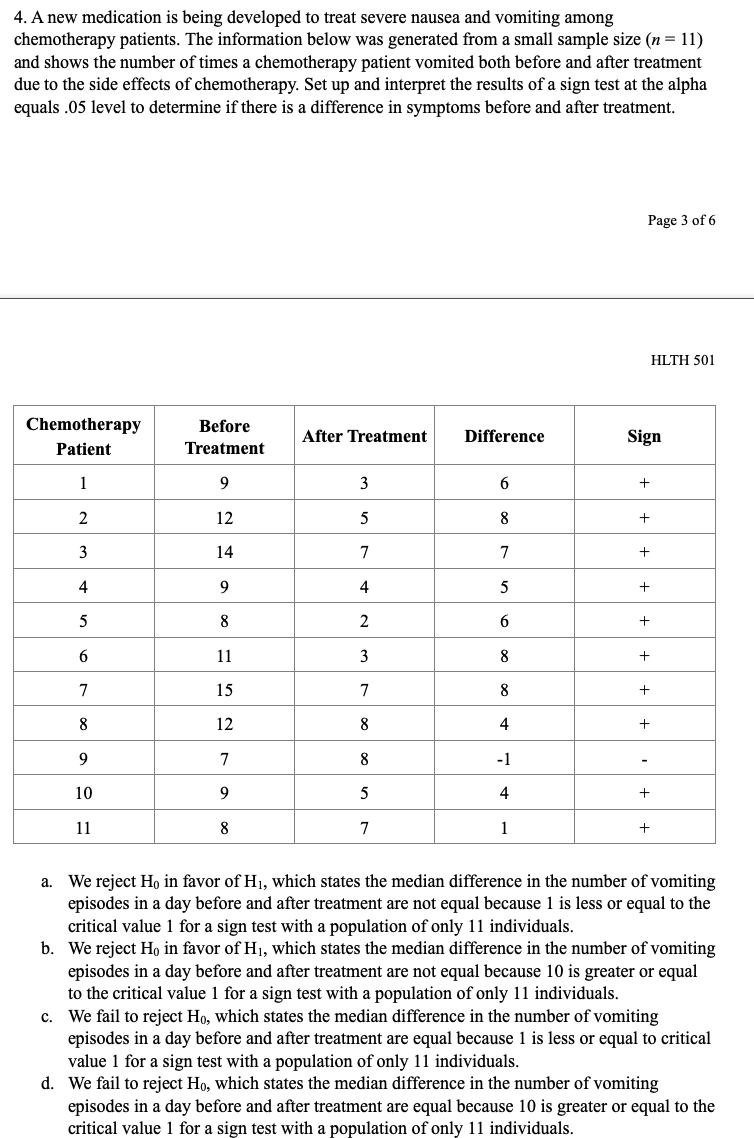
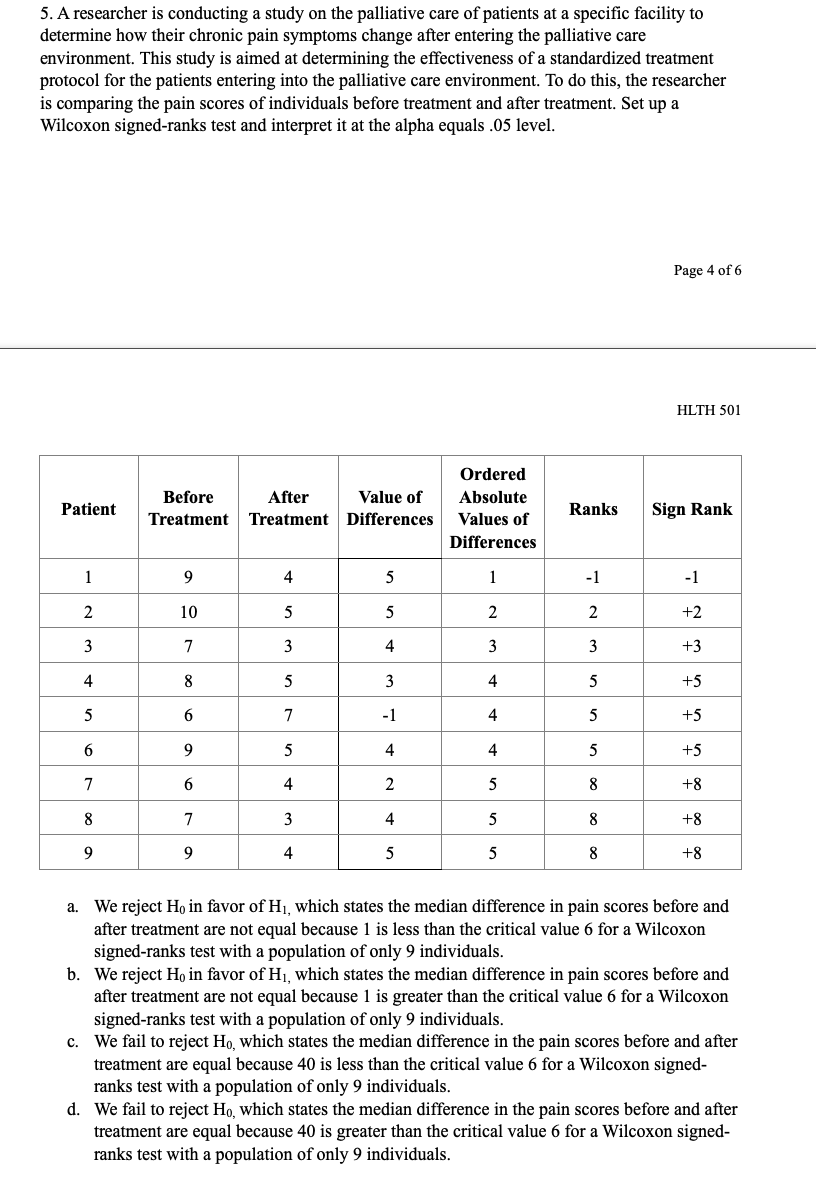

CHAPTER PROBLEMS: NON-PARAMIETRIC TESTING 10 questions, 30 points Chapter 10 Multiple Choice 1. A new drug for pain relief is being tested within a given palliative care population. The new drug is being compared to an already approved pain relief drug that is commonly used in providing palliative care to patients who experience chronic severe pain. Assume the patients are asked to rate the pain on a scale from 1 to 10, and the data presented below was obtained from a small study designed to compare the effectiveness of the two drugs. Set up and interpret the results of a Mann-Whitney U test with an alpha of .05. Pain Rating as Reported by Patients Old Drug l 2 2 4 6 New Drug l 2 2 3 '1' 'Ihtal Sample {Ordered Smallest to Ranks Largest) Old Drug New Drug Old Drug New Drug Old Drug New Drug QhNNnt \"-JMNNIl a. We reject Hg in favor of H1, which states the two populations are not equal at the alpha equals .05 level because the calculated Uvalue of 12.5 is greater than the critical Uvalue of 2. b. We reject H0 in favor of H1, which states the two populations are not equal at the alpha equals .05 level because the calculated Uvalue of 10.5 is greater than the critical Uvalue of 2. Page 1 of 6 HLTH 501 c. We fail to reject Ho, which states the two populations are equal at the alpha equals .05 level because the calculated U value of 12.5 is greater than the critical U value of 2. d. We fail to reject Ho, which states the two populations are equal at the alpha equals .05 level because the calculated U value of 10.5 is greater than the critical U value of 2. 2. A new chemotherapy drug is released to treat leukemia and researchers suspect that the drug may have fewer side effects than the most commonly used drug to treat leukemia. The two drugs have equivalent efficacy. In order to determine if a larger study should be conducted to look into the prevalence of side effects for the two drugs, set up a Mann-Whitney U test at the alpha equals 05 level and interpret its results. Number of Reported Side-Effects Old Drug 0 New Drug 0 4 Total Sample (Ordered Smallest to Ranks Old Drug New Drug Largest) Old Drug New Drug Old Drug New Drug O 0 0 2 2 O 0 2 U U U N 2 7 8 4 9 5 10 R1=30 R2=25 a. We reject Ho in favor of Hi, which states the two populations are not equal at the alpha equals .05 level because the calculated U value of 10 is greater than the critical U value of 2. b. We reject Ho in favor of Hi, which states the two populations are not equal at the alpha equals .05 level because the calculated U value of 8.5 is greater than the critical U value of 2. We fail to reject Ho, which states the two populations are equal at the alpha equals .05 level because the calculated U value of 8.5 is greater than the critical U value of 2. Page 2 of 6 HLTH 501 d. We fail to reject Ho, which states the two populations are equal at the alpha equals .05 level because the calculated U value of 10 is greater than the critical U value of 2.3. Anew medication is being developed to treat severe morning sickness in pregnant women. The information below was generated from a small sample size (n = 6) and shows the number of times a woman with morning sickness vomited both before and after treatment. Set up and interpret the results of a sign test at the alpha equals .05 level to determine if there is a di'erence in symptoms before and after treatment. mt \"2:31:11! After Treatment Difference Sign l 8 3 5 __ 2 4 7 -3 _ 3 6 5 1 __ 4 3 10 .2 _ 5 11 10 1 __ 6 g 2 6 + a. We reject H0 in favor of H1, which states the median difference in the number of vomiting episodes in a day before and after treatment are! not equal because 2 is greater than the critical value 0 for a sign test with a population of only 6 individuals. h. We reject Hg in favor of H1, which states the median difference in the number of vomiting episodes in a day before and after treatment are not equal because 4 is greater than the critical value 0 for a sign test with a population of only 6 individuals. c. We fail to reject Ho, which states the median difference in the number of vomiting episodes in a day before and after treatment are equal because 2 is greater than the critical value 0 for a sign test with a population of only 6 individuals. d. We fail to reject Ho, which states the median difference in the number of vomiting episodes in a day before and after treatment are equal because 4 is greater than the critical value I} for a sign test with a population of only 6 individuals. 4. A new medication is being developed to treat severe nausea and vomiting among chemotherapy patients. The information below was generated from a small sample size (n = 11) and shows the number of times a chemotherapy patient vomited both before and after treatment due to the side effects of chemotherapy. Set up and interpret the results of a sign test at the alpha equals .05 level to determine if there is a difference in symptoms before and after treatment. Page 3 of 6 HLTH 501 Chemotherapy Before After Treatment Difference Sign Patient Treatment 9 6 + N 12 5 + w 14 + 9 4 UI + UI 8 2 + 11 W + 15 + 12 + 7 L 10 9 UI + 11 8 7 + a. We reject Ho in favor of Hi, which states the median difference in the number of vomiting episodes in a day before and after treatment are not equal because 1 is less or equal to the critical value 1 for a sign test with a population of only 11 individuals. b. We reject Ho in favor of Hi, which states the median difference in the number of vomiting episodes in a day before and after treatment are not equal because 10 is greater or equal to the critical value 1 for a sign test with a population of only 11 individuals. c. We fail to reject Ho, which states the median difference in the number of vomiting episodes in a day before and after treatment are equal because 1 is less or equal to critical value 1 for a sign test with a population of only 11 individuals. d. We fail to reject Ho, which states the median difference in the number of vomiting episodes in a day before and after treatment are equal because 10 is greater or equal to the critical value 1 for a sign test with a population of only 11 individuals.5. A researcher is conducting a study on the palliative care of patients at a specific facility to determine how their chronic pain symptoms change after entering the palliative care environment. This study is aimed at determining the effectiveness of a standardized treatment protocol for the patients entering into the palliative care environment. To do this, the researcher is comparing the pain scores of individuals before treatment and after treatment. Set up a Wilcoxon signed-ranks test and interpret it at the alpha equals .05 level. Page 4 of 6 HLTH 501 Ordered Before After Value of Absolute Patient Ranks Sign Rank Treatment Treatment Differences Values of Differences 1 9 4 -1 -1 2 10 5 5 N 2 +2 3 7 4 +3 4 8 5 3 4 5 +5 5 -1 5 +5 5 4 5 +5 7 2 5 8 +8 8 3 8 +8 9 9 4 5 5 8 +8 a. We reject Ho in favor of Hi, which states the median difference in pain scores before and after treatment are not equal because 1 is less than the critical value 6 for a Wilcoxon signed-ranks test with a population of only 9 individuals. b. We reject Ho in favor of HI, which states the median difference in pain scores before and after treatment are not equal because 1 is greater than the critical value 6 for a Wilcoxon signed-ranks test with a population of only 9 individuals. C. We fail to reject Ho, which states the median difference in the pain scores before and after treatment are equal because 40 is less than the critical value 6 for a Wilcoxon signed- ranks test with a population of only 9 individuals. d. We fail to reject Ho, which states the median difference in the pain scores before and after treatment are equal because 40 is greater than the critical value 6 for a Wilcoxon signed- ranks test with a population of only 9 individuals.True/False 1. True or False? A Kruskal-Wallis test is used to compare a continuous outcome in more than two independent samples. 2. True or False? Ho for a Mann-Whitney U test is always that the two populations are not equal. 3. True or False? When performing a Mann-Whitney U test, one should always use the lower value of the calculated U values to compare to the critical U value while making the decision rule. Page 5 of 6 HLTH 501 4. True or False? Ho for the sign test always states that the mean difference between the matched or paired samples is zero. 5. True or False? The test statistic for a sign test is always the larger of the number of positive or negative signs
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


