Question: Chemical Engineering how does young modulus depend on Ro in alkali halide compounds. Show mathematically and derive an expression for the same. VALUES OF MELTING
Chemical Engineering
how does young modulus depend on Ro in alkali halide compounds. Show mathematically and derive an expression for the same.
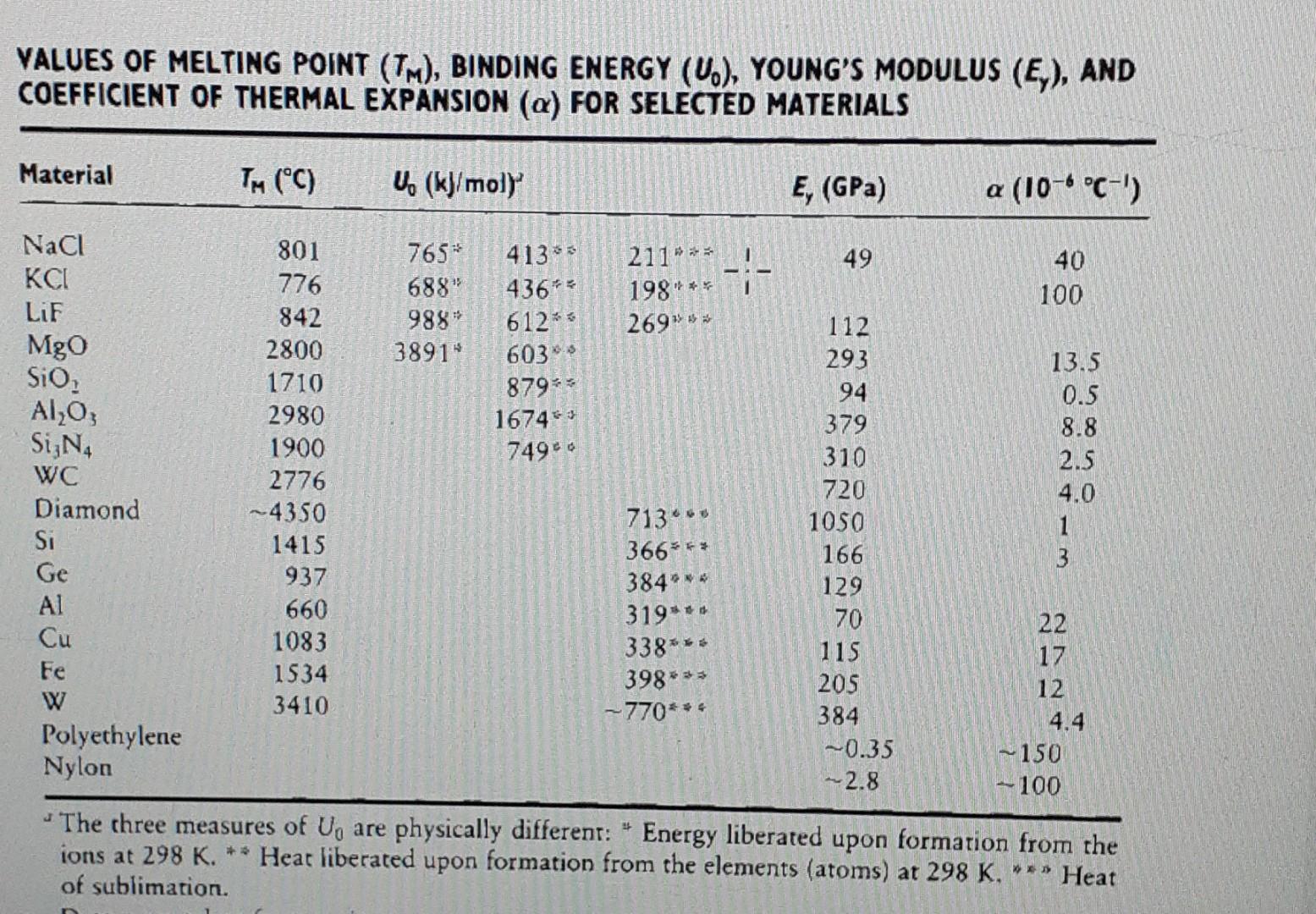
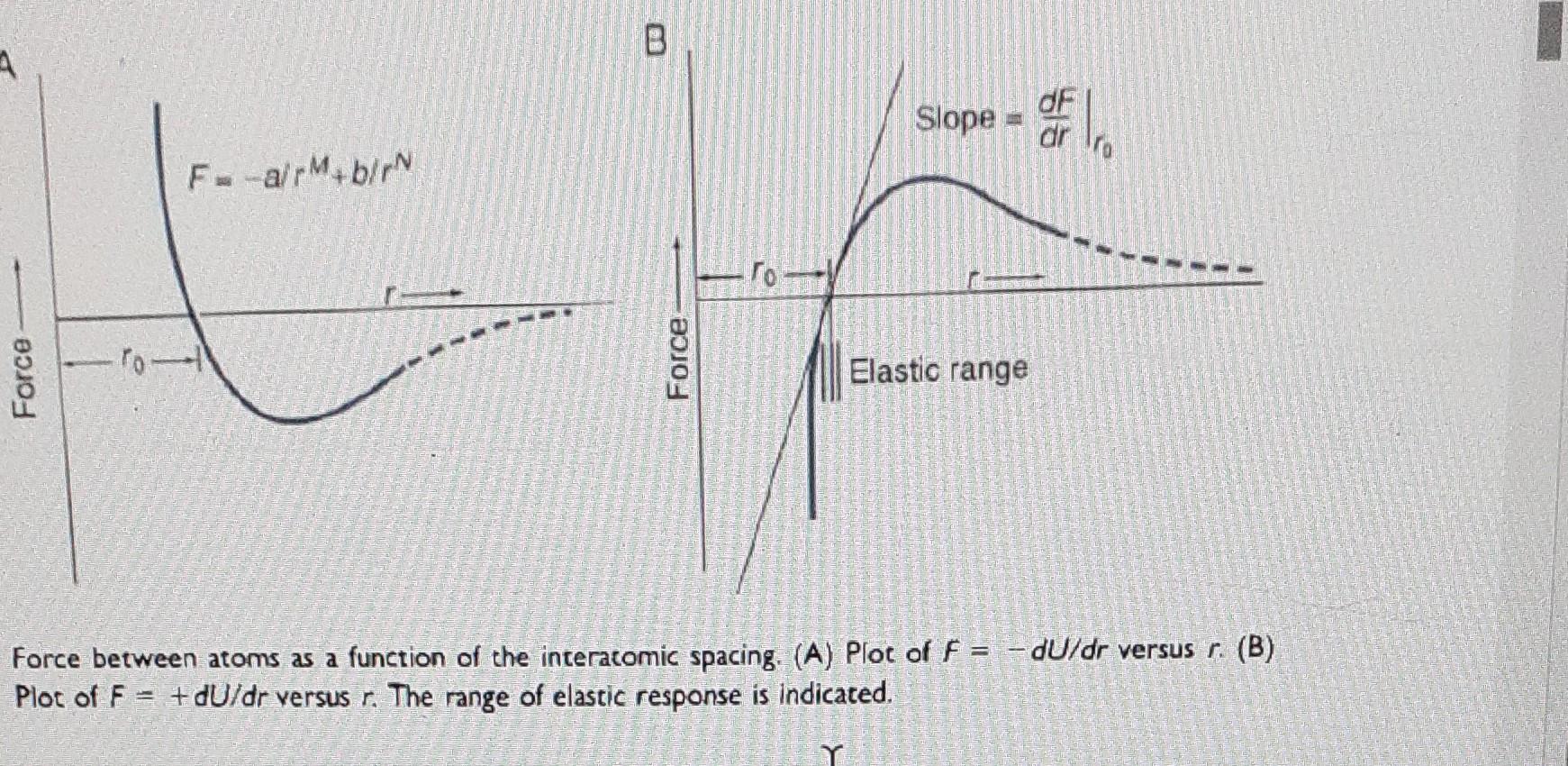
VALUES OF MELTING POINT (TM), BINDING ENERGY (U.), YOUNG'S MODULUS (E), AND COEFFICIENT OF THERMAL EXPANSION (a) FOR SELECTED MATERIALS Material TM (C) U (kJ/moly E, (GPa) a (106 C-') 4133 49 NaCl KCI LiF Mgo 765* 688" 988 3891" --- 211" ** 198" 269* 40 100 4362 Sio 612* - 603 879% 1674% 74940 Al2O3 Sign WC Diamond Si 801 776 842 2800 1710 2980 1900 2776 ~4350 1415 937 660 1083 1534 3410 13.5 0.5 8.8 2.5 4.0 1 3 2 112 293 94 379 310 720 1050 166 129 70 115 205 384 ~0.35 -- 2.8 713" 366% 384*** 319**. Ge 338 Al Cu Fe W Polyethylene Nylon 398*** --770*** 22 17 12 4.4 ~ 150 -100 The three measures of U, are physically different: * Energy liberated upon formation from the ions at 298 K. ** Heat liberated upon formation from the elements (atoms) at 298 K. ** Heat of sublimation. B dF Slope dr FarMub/rN Force Force Elastic range Force between atoms as a function of the interacomic spacing. (A) Plot of F = -dU/dr versus r. (B) Plot of F + dU/dr versus r. The range of elastic response is indicated
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


