Question: Chemical solid engineering how does young modulus depend on Ro in alkali halide compounds. derive an expression for the same. Con or E VALUES OF
Chemical solid engineering
how does young modulus depend on Ro in alkali halide compounds. derive an expression for the same.
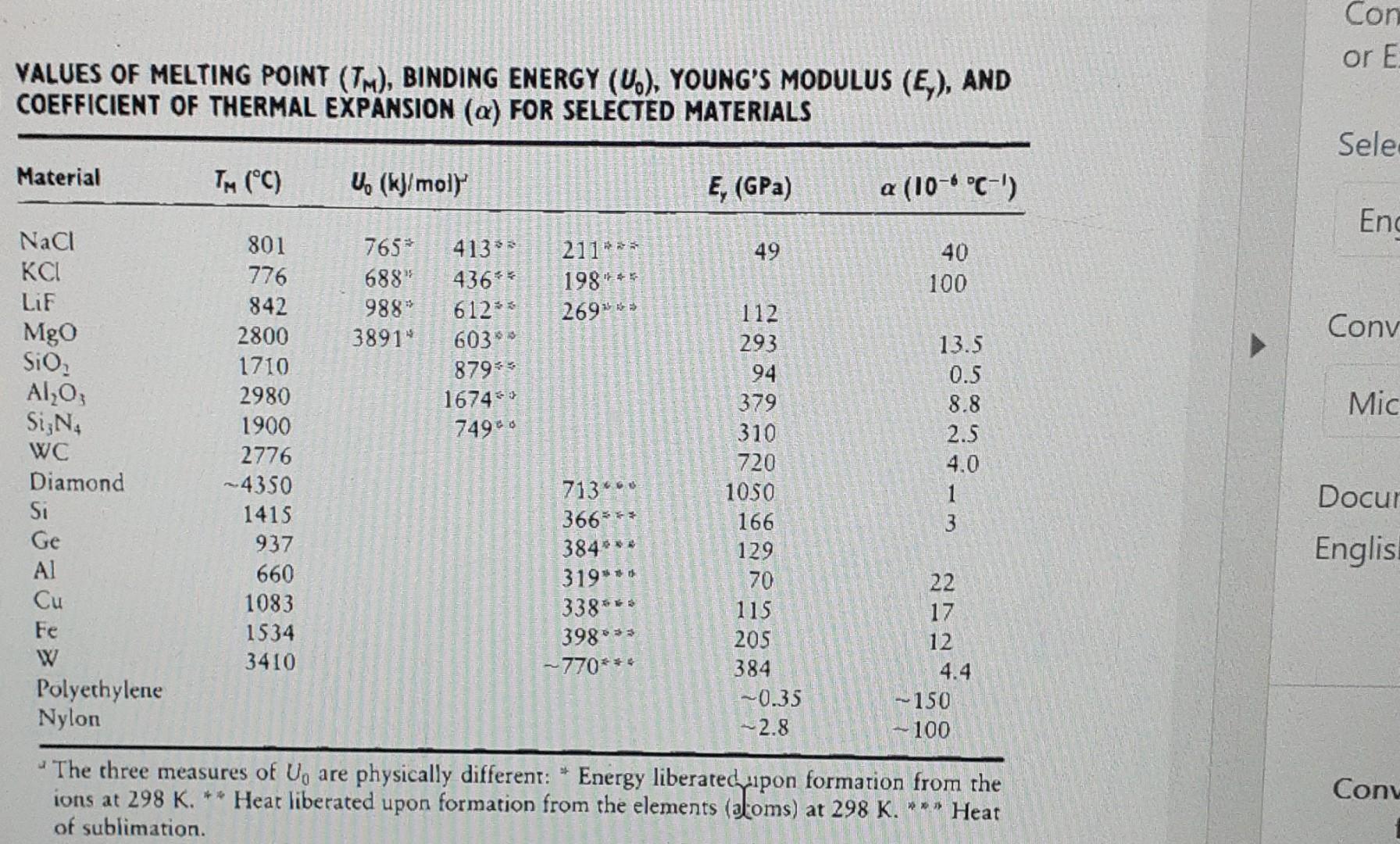
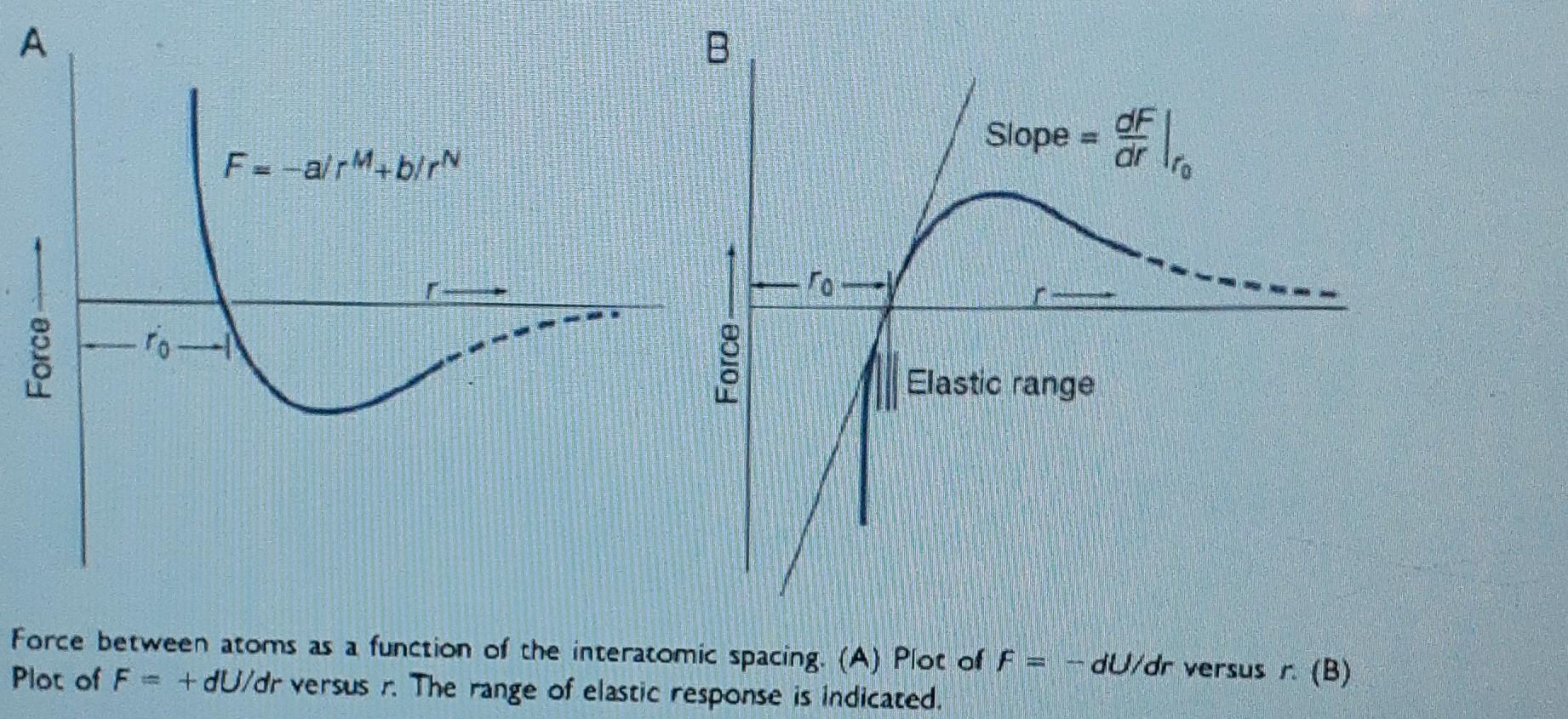
Con or E VALUES OF MELTING POINT (TM), BINDING ENERGY (U.), YOUNG'S MODULUS (EX), AND COEFFICIENT OF THERMAL EXPANSION (a) FOR SELECTED MATERIALS Sele Material TM (C) U (kJ/moly E, (GPa) a (10-* C-') End 211*** 49 765* 688" 988" 3891" 40 100 1985 2692 112 413** 436%* 612% 603** 8795 1674 7490 Conv 293 Mic NaCl Lif Mgo Sio AlO; SiN WC Diamond Si Ge Al Cu Fe W Polyethylene Nylon 801 776 842 2800 1710 2980 1900 2776 -4350 1415 937 660 1083 1534 3410 13.5 0.5 8.8 2.5 4.0 1 3 ITM Docur 94 379 310 720 1050 166 129 70 115 205 384 -0.35 --2.8 713. 366*** 384*** 319*** 338*** 398*** -770** Englis 22 17 12 4.4 -- 150 - 100 The three measures of U, are physically different: * Energy liberatecipon formation from the ions at 298 K. ** Heat liberated upon formation from the elements (atoms) at 298 K. *** Heat of sublimation. Cony A Slope of all F=-a/pM+b/rN dr Force ro-N Force Elastic range Force between atoms as a function of the interatomic spacing. (A) Plot of F = Plot of F = + dU/dr versus r. The range of elastic response is indicated. dU/dr versus r. (B)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


