Question: CHEN 2650 - Lab 3: Analytical Solutions to Simple System Dynamics Table of Contents 1 - Second-order reaction. 1.1 - Coding Examples. 1.2 - Lab
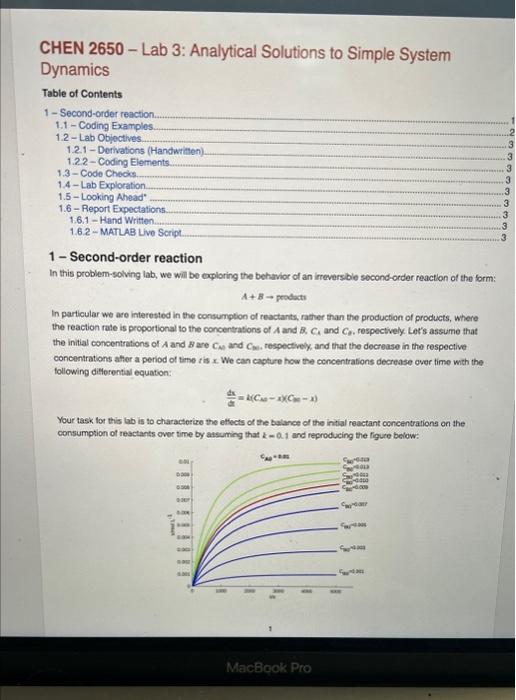
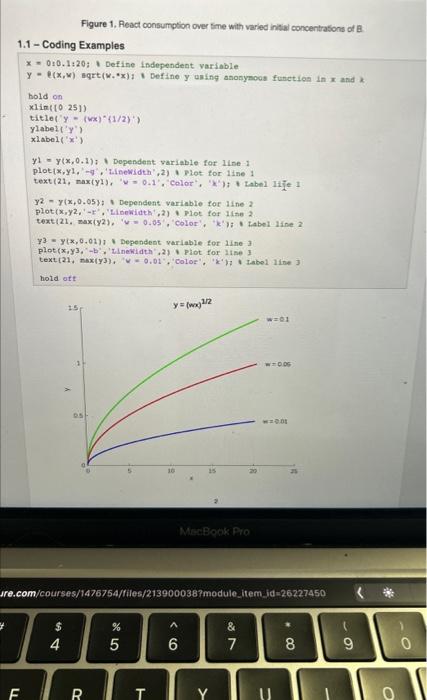
CHEN 2650 - Lab 3: Analytical Solutions to Simple System Dynamics Table of Contents 1 - Second-order reaction. 1.1 - Coding Examples. 1.2 - Lab Objectives. 1.2.1 - Dorvations (Handwititen). 1.2.2 - Coding Elements. 1.3 - Code Cheoks. 1.4 - Lab Exploration 1.5-Looking Ahead" 1.6 - Report Expectations. 1.6.1 - Hand Written. 1.6.2 - MATLAB Live Script. 1 - Second-order reaction In this problem-solving lab, we will be exploring the behavior of an irreversbie second-order reaction of the form: A+Bprodicts In particular we are interested in the consumption of reactants, rather than the production of products, where the reaction rate is proportional to the concentrations of A and B,C, and C3. respectively. Lot's assume that the initial concentrations of A and B are CA and CW, respectively, and that the decrease in the respective concentrations afier a period of time t is x. We can capture how the concentrations decrease over time with the following diflorential equation: didx=d(Csex)(Cnx) Your task for this lab is to charactorice the etfects of the balance of the intial reactant concentrations on the consumption of resctants ovor time by assuming that k=a.1 and reproducing the fguce below: Figure 1. Peact consumption over time with varied initial concentrasons of a. 1.1 - Coding Examples Figure 2. Plot of y vs x with varied values of w. 1.2 - Lab Objectives 1.2.1 - Derivations (Handwrittea) 1. Derive an expression for x over time for any inhial concentrabion of A and B, where CM+CM 2. Using your answer to (1), dertive an expressige for x over sme for when Ca=Cm. 1.2.2-Coding Elements 1. Write anonymous lunctions that detine your derivod expressions for x in the two scenarion. 2. Write code that uses the anomymous tunctions to reproduce Figure 1 abcve. 1.3 - Code Checks Use odets to check your dorivasions. Generate a single tigure with two plots comparing x over ime based on vour deevition and with ode45 tor the scenaries when Cu=Cm and Cs+Cm. Fepresent the ode 45 solution. as poins on a plot and your derived (handweinen) eolvtion as a selid line. Choose values ter Cin based on Finure 1. 1.4 - Lab Exploration Explore the encet of k on x (oonsumption of nonactants). Describe your ebstrvations. 1.5 - Looking Ahead Nit. 1.6 - Report Expectations This Lab cen be completed in trial grougs if or kes people), and ithe nemas of at inaviduals hat ooctr butod (and only your greup) 1.6.t - Hand Writien 1.6.2 - MarLAe Lhe feript Check wnt Lab Explormione petbons: CHEN 2650 - Lab 3: Analytical Solutions to Simple System Dynamics Table of Contents 1 - Second-order reaction. 1.1 - Coding Examples. 1.2 - Lab Objectives. 1.2.1 - Dorvations (Handwititen). 1.2.2 - Coding Elements. 1.3 - Code Cheoks. 1.4 - Lab Exploration 1.5-Looking Ahead" 1.6 - Report Expectations. 1.6.1 - Hand Written. 1.6.2 - MATLAB Live Script. 1 - Second-order reaction In this problem-solving lab, we will be exploring the behavior of an irreversbie second-order reaction of the form: A+Bprodicts In particular we are interested in the consumption of reactants, rather than the production of products, where the reaction rate is proportional to the concentrations of A and B,C, and C3. respectively. Lot's assume that the initial concentrations of A and B are CA and CW, respectively, and that the decrease in the respective concentrations afier a period of time t is x. We can capture how the concentrations decrease over time with the following diflorential equation: didx=d(Csex)(Cnx) Your task for this lab is to charactorice the etfects of the balance of the intial reactant concentrations on the consumption of resctants ovor time by assuming that k=a.1 and reproducing the fguce below: Figure 1. Peact consumption over time with varied initial concentrasons of a. 1.1 - Coding Examples Figure 2. Plot of y vs x with varied values of w. 1.2 - Lab Objectives 1.2.1 - Derivations (Handwrittea) 1. Derive an expression for x over time for any inhial concentrabion of A and B, where CM+CM 2. Using your answer to (1), dertive an expressige for x over sme for when Ca=Cm. 1.2.2-Coding Elements 1. Write anonymous lunctions that detine your derivod expressions for x in the two scenarion. 2. Write code that uses the anomymous tunctions to reproduce Figure 1 abcve. 1.3 - Code Checks Use odets to check your dorivasions. Generate a single tigure with two plots comparing x over ime based on vour deevition and with ode45 tor the scenaries when Cu=Cm and Cs+Cm. Fepresent the ode 45 solution. as poins on a plot and your derived (handweinen) eolvtion as a selid line. Choose values ter Cin based on Finure 1. 1.4 - Lab Exploration Explore the encet of k on x (oonsumption of nonactants). Describe your ebstrvations. 1.5 - Looking Ahead Nit. 1.6 - Report Expectations This Lab cen be completed in trial grougs if or kes people), and ithe nemas of at inaviduals hat ooctr butod (and only your greup) 1.6.t - Hand Writien 1.6.2 - MarLAe Lhe feript Check wnt Lab Explormione petbons
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


