Question: class BinaryTree: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None def insert_left(self, new_data): if self.left == None: self.left = BinaryTree(new_data) else:
class BinaryTree: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None
def insert_left(self, new_data): if self.left == None: self.left = BinaryTree(new_data) else: t = BinaryTree(new_data) t.left = self.left self.left = t
def insert_right(self, new_data): if self.right == None: self.right = BinaryTree(new_data) else: t = BinaryTree(new_data) t.right = self.right self.right = t
def get_left(self): return self.left
def get_right(self): return self.right
def set_data(self, data): self.data = data
def get_data(self): return self.data 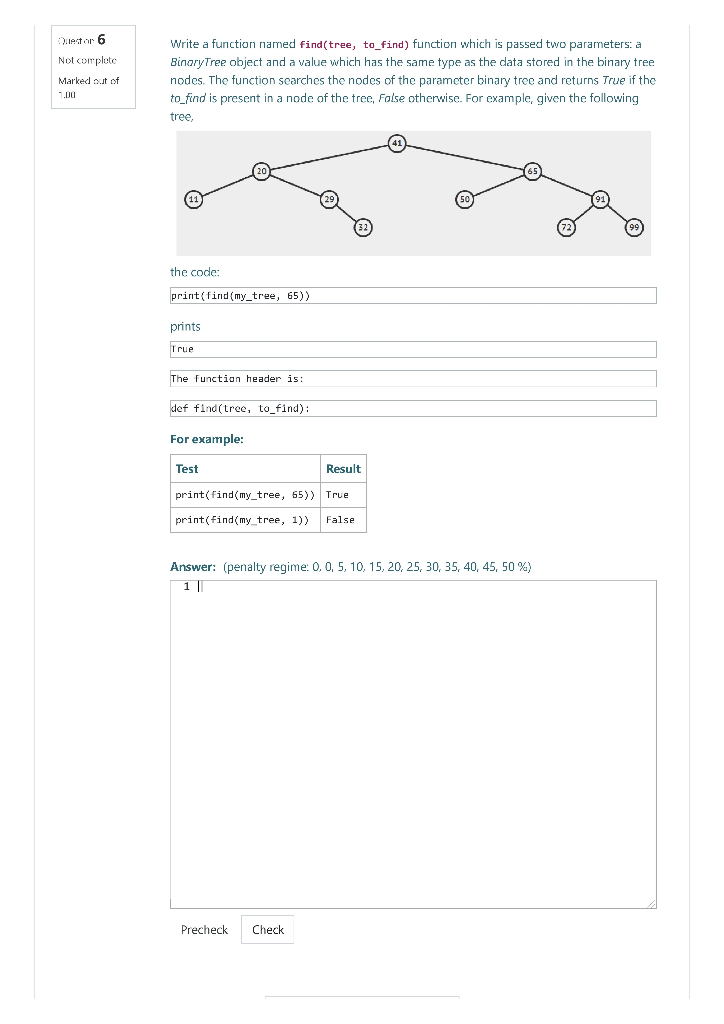
lector 6 Not completo Marked out of 1.00 Write a function named find(tree, to_find) function which is passed two parameters: a Binary Tree object and a value which has the same type as the data stored in the binary tree nodes. The function searches the nodes of the parameter binary tree and returns True if the to find is present in a node of the tree, Folse otherwise. For example, given the following tree, the code: print(find(my_tree, 65)) prints True The function header is: def find(tree, to_find): For example: Test Result print(find(my_tree, 55)) True print(find(my_tree, 1)) False Answer: (penalty regime: 0.0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 %) Precheck Check
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


