Question: EXISTING CODE class BinaryTree: def __init__(self, data, left=None, right=None): self.data = data self.left = left self.right = right def insert_left(self, new_data): if self.left == None:
EXISTING CODE
class BinaryTree: def __init__(self, data, left=None, right=None): self.data = data self.left = left self.right = right
def insert_left(self, new_data): if self.left == None: self.left = BinaryTree(new_data) else: t = BinaryTree(new_data, left=self.left) self.left = t
def insert_right(self, new_data): if self.right == None: self.right = BinaryTree(new_data) else: t = BinaryTree(new_data, right=self.right) self.right = t
def get_left(self): return self.left
def get_right(self): return self.right
def set_data(self, data): self.data = data
def get_data(self): return self.data
def set_left(self, left): self.left = left
def set_right(self, right): self.right = right
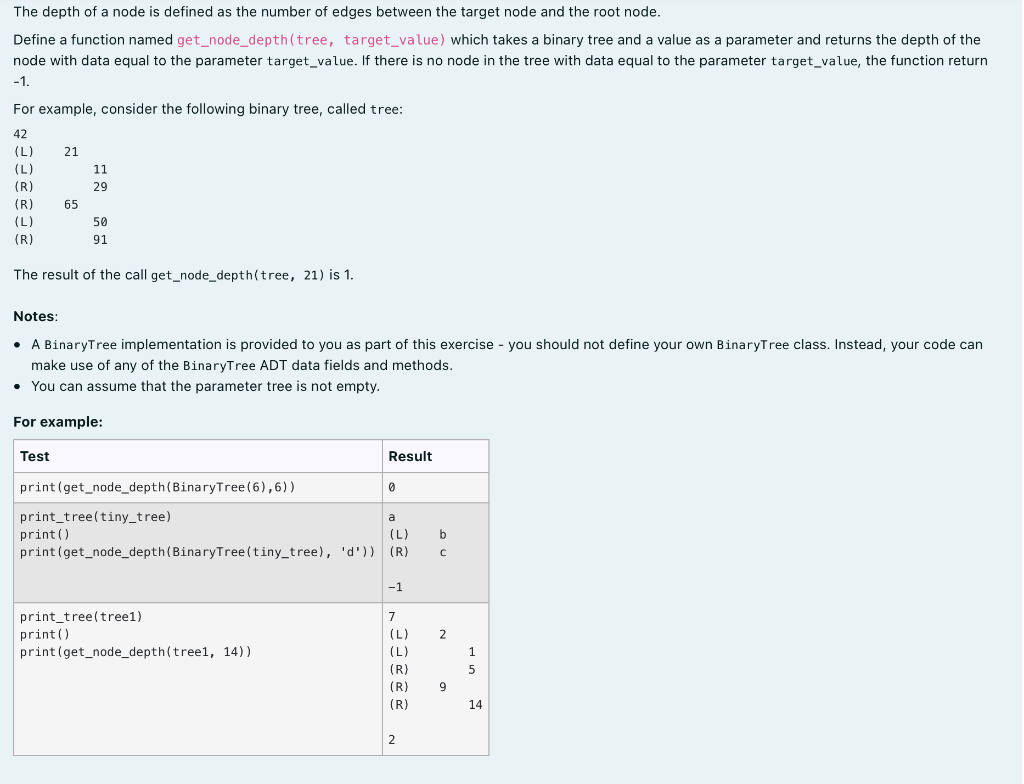
The depth of a node is defined as the number of edges between the target node and the root node. Define a function named get_node_depth(tree, target_value) which takes a binary tree and a value as a parameter and returns the depth of the node with data equal to the parameter target_value. If there is no node in the tree with data equal to the parameter target_value, the function return 1. For example, consider the following binary tree, called tree: 42 (L) 21 (L) 11 (R) 29 (R) 65 (L) 50 (R) 91 The result of the call get_node_depth(tree, 21) is 1. Notes: - A BinaryTree implementation is provided to you as part of this exercise - you should not define your own BinaryTree class. Instead, your code can make use of any of the BinaryTree ADT data fields and methods. - You can assume that the parameter tree is not empty. For example
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


