Question: cobb douglas function : log(Y)=beta1+beta2(log(L))+beta3(log(k))+e N=332 Dependent Variable LOG(Y) Method: Least Squares Date: 12/15/20 Time: 14:16 Sample (adjusted): 1 332 Included observations: 332 after adjustments
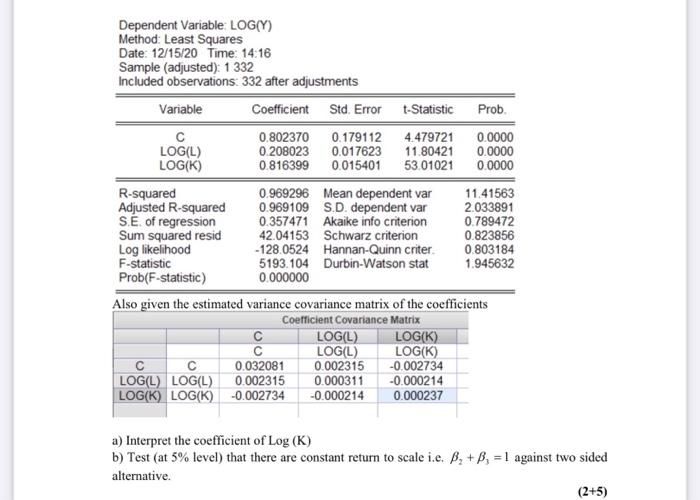
Dependent Variable LOG(Y) Method: Least Squares Date: 12/15/20 Time: 14:16 Sample (adjusted): 1 332 Included observations: 332 after adjustments Variable Coefficient Std. Error - Statistic Prob. 0.802370 0.179112 4.479721 0.0000 LOG(L) 0 208023 0.017623 11.80421 0.0000 LOG(K) 0.816399 0.015401 53.01021 0.0000 R-squared 0.969296 Mean dependent var 11.41563 Adjusted R-squared 0.969109 S.D. dependent var 2.033891 S.E. of regression 0.357471 Akaike info criterion 0.789472 Sum squared resid 42.04153 Schwarz criterion 0.823856 Log likelihood -128.0524 Hannan-Quinn criter 0.803184 F-statistic 5193.104 Durbin-Watson stat 1.945632 Prob(F-statistic) 0.000000 Also given the estimated variance covariance matrix of the coefficients Coefficient Covariance Matrix C LOG(L) LOG(K) LOG(L) LOG(K) 0.032081 0.002315 -0.002734 LOG(L) LOG(L) 0.002315 0.000311 -0.000214 LOG(K) LOG(K) -0.002734 -0.000214 0.000237 a) Interpret the coefficient of Log (K) b) Test (at 5% level) that there are constant return to scale i.e. Be + B, = 1 against two sided alternative. (2+5)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


