Question: Code in C/C++ Code in C/C++ Code in C/C++ Code in C/C++ Code in C/C++ 1. Linked lists may be used to implement many real
Code in C/C++
Code in C/C++
Code in C/C++
Code in C/C++
Code in C/C++
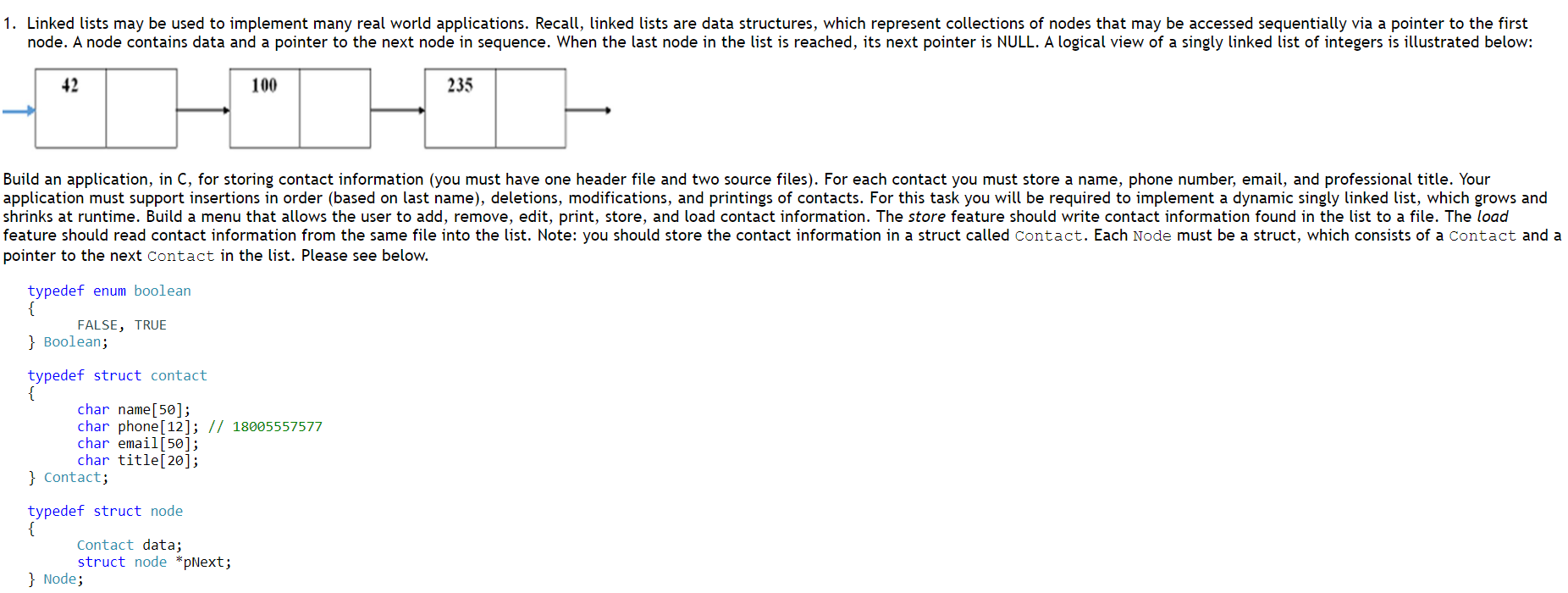
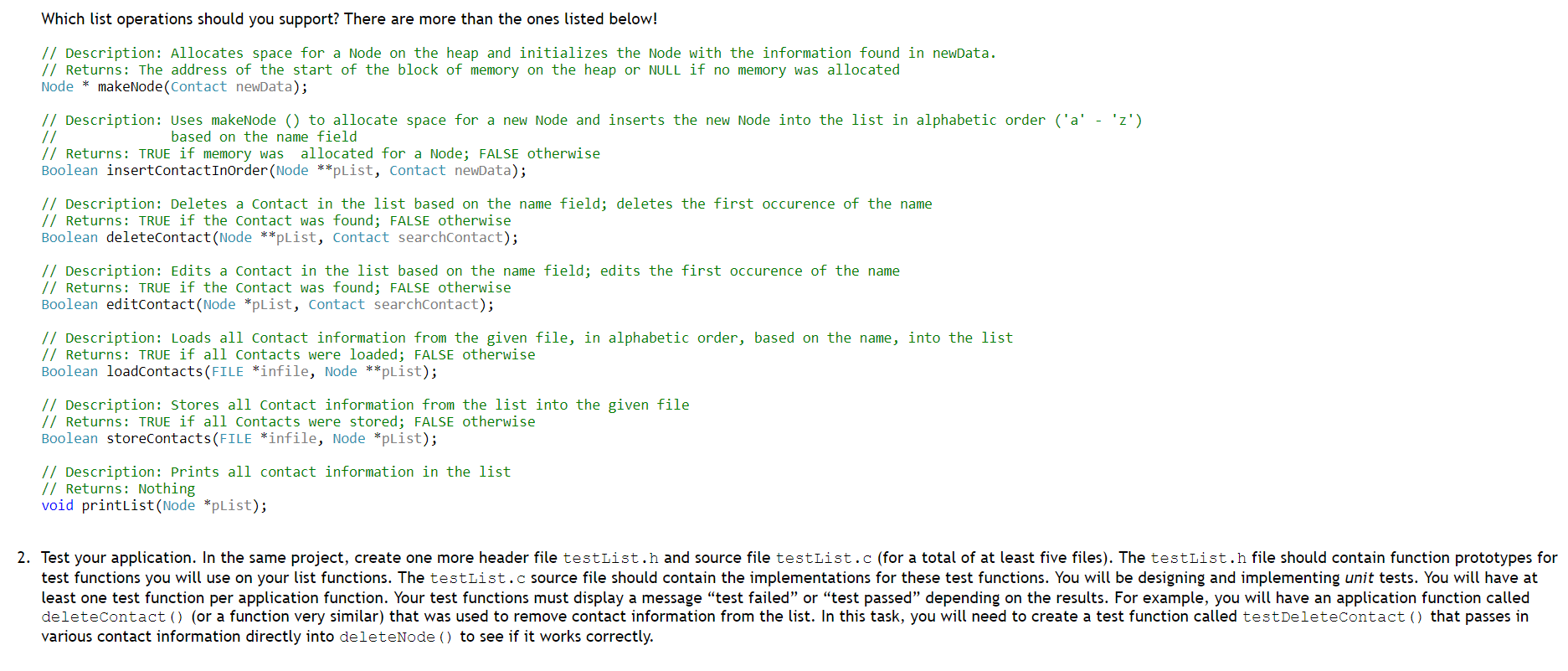
1. Linked lists may be used to implement many real world applications. Recall, linked lists are data structures, which represent collections of nodes that may be accessed sequentially via a pointer to the first node. A node contains data and a pointer to the next node in sequence. When the last node in the list is reached, its next pointer is NULL. A logical view of a singly linked list of integers is illustrated below: 42 100 235 Build an application, in C, for storing contact information (you must have one header file and two source files). For each contact you must store a name, phone number, email, and professional title. Your application must support insertions in order (based on last name), deletions, modifications, and printings of contacts. For this task you will be required to implement a dynamic singly linked list, which grows and shrinks at runtime. Build a menu that allows the user to add, remove, edit, print, store, and load contact information. The store feature should write contact information found in the list to a file. The load feature should read contact information from the same file into the list. Note: you should store the contact information in a struct called contact. Each Node must be a struct, which consists of a contact and a pointer to the next contact in the list. Please see below. typedef enum boolean { FALSE, TRUE } Boolean; typedef struct contact { char name[50]; char phone[12]; // 18005557577 char email[50]; char title[20]; } Contact; typedef struct node { Contact data; struct node *pNext; } Node; Which list operations should you support? There are more than the ones listed below! // Description: Allocates space for a Node on the heap and initializes the Node with the information found in newData. // Returns: The address of the start of the block of memory on the heap or NULL if no memory was allocated Node * makeNode(Contact newData); // Description: Uses makeNode () to allocate space for a new Node and inserts the new Node into the list in alphabetic order ('a' . 'z') // based on the name field // Returns: TRUE if memory was allocated for a Node; FALSE otherwise Boolean insertContactInOrder (Node **pList, Contact newData); // Description: Deletes a Contact in the list based on the name field; deletes the first occurence of the name // Returns: TRUE if the Contact was found; FALSE otherwise Boolean deleteContact(Node **pList, Contact searchcontact); // Description: Edits a Contact in the list based on the name field; edits the first occurence of the name // Returns: TRUE if the contact was found; FALSE otherwise Boolean editContact(Node *pList, Contact searchcontact); // Description: Loads all Contact information from the given file, in alphabetic order, based on the name, into the list // Returns: TRUE if all contacts were loaded; FALSE otherwise Boolean loadcontacts (FILE *infile, Node **plist); // Description: Stores all Contact information from the list into the given file // Returns: TRUE if all Contacts were stored; FALSE otherwise Boolean storeContacts (FILE *infile, Node *plist); // Description: Prints all contact information in the list // Returns: Nothing void printList(Node *plist); 2. Test your application. In the same project, create one more header file testList.h and source file testList.c (for a total of at least five files). The testList.h file should contain function prototypes for test functions you will use on your list functions. The testList.c source file should contain the implementations for these test functions. You will be designing and implementing unit tests. You will have at least one test function per application function. Your test functions must display a message "test failed" or "test passed" depending on the results. For example, you will have an application function called deleteContact() (or a function very similar) that was used to remove contact information from the list. In this task, you will need to create a test function called testDeleteContact() that passes in various contact information directly into deleteNode () to see if it works correctly. 1. Linked lists may be used to implement many real world applications. Recall, linked lists are data structures, which represent collections of nodes that may be accessed sequentially via a pointer to the first node. A node contains data and a pointer to the next node in sequence. When the last node in the list is reached, its next pointer is NULL. A logical view of a singly linked list of integers is illustrated below: 42 100 235 Build an application, in C, for storing contact information (you must have one header file and two source files). For each contact you must store a name, phone number, email, and professional title. Your application must support insertions in order (based on last name), deletions, modifications, and printings of contacts. For this task you will be required to implement a dynamic singly linked list, which grows and shrinks at runtime. Build a menu that allows the user to add, remove, edit, print, store, and load contact information. The store feature should write contact information found in the list to a file. The load feature should read contact information from the same file into the list. Note: you should store the contact information in a struct called contact. Each Node must be a struct, which consists of a contact and a pointer to the next contact in the list. Please see below. typedef enum boolean { FALSE, TRUE } Boolean; typedef struct contact { char name[50]; char phone[12]; // 18005557577 char email[50]; char title[20]; } Contact; typedef struct node { Contact data; struct node *pNext; } Node; Which list operations should you support? There are more than the ones listed below! // Description: Allocates space for a Node on the heap and initializes the Node with the information found in newData. // Returns: The address of the start of the block of memory on the heap or NULL if no memory was allocated Node * makeNode(Contact newData); // Description: Uses makeNode () to allocate space for a new Node and inserts the new Node into the list in alphabetic order ('a' . 'z') // based on the name field // Returns: TRUE if memory was allocated for a Node; FALSE otherwise Boolean insertContactInOrder (Node **pList, Contact newData); // Description: Deletes a Contact in the list based on the name field; deletes the first occurence of the name // Returns: TRUE if the Contact was found; FALSE otherwise Boolean deleteContact(Node **pList, Contact searchcontact); // Description: Edits a Contact in the list based on the name field; edits the first occurence of the name // Returns: TRUE if the contact was found; FALSE otherwise Boolean editContact(Node *pList, Contact searchcontact); // Description: Loads all Contact information from the given file, in alphabetic order, based on the name, into the list // Returns: TRUE if all contacts were loaded; FALSE otherwise Boolean loadcontacts (FILE *infile, Node **plist); // Description: Stores all Contact information from the list into the given file // Returns: TRUE if all Contacts were stored; FALSE otherwise Boolean storeContacts (FILE *infile, Node *plist); // Description: Prints all contact information in the list // Returns: Nothing void printList(Node *plist); 2. Test your application. In the same project, create one more header file testList.h and source file testList.c (for a total of at least five files). The testList.h file should contain function prototypes for test functions you will use on your list functions. The testList.c source file should contain the implementations for these test functions. You will be designing and implementing unit tests. You will have at least one test function per application function. Your test functions must display a message "test failed" or "test passed" depending on the results. For example, you will have an application function called deleteContact() (or a function very similar) that was used to remove contact information from the list. In this task, you will need to create a test function called testDeleteContact() that passes in various contact information directly into deleteNode () to see if it works correctly
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


