Question: Common stock value-Variable growth (Example and example steps included) Common stock value-Variable growth Lawrence Industries' most recent annual dividend was $1.92 per share (D =


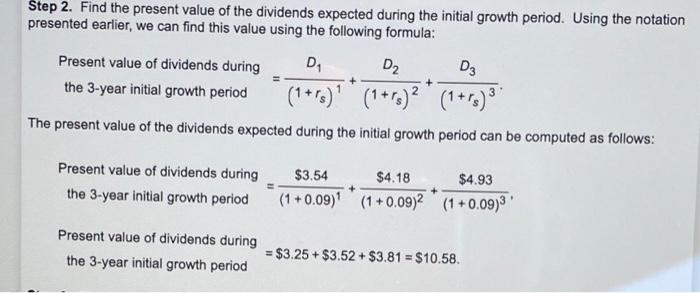



Common stock value-Variable growth Lawrence Industries' most recent annual dividend was $1.92 per share (D = $1.92), and the firm's required return is 13%. Find the market value of Lawrence's shares when dividends are expected to grow at 20% annually for 3 years, followed by a 7% constant annual growth rate in years 4 to Infinity The market value of Lawrence's shares is $(Round to the nearest cent.) Step 1. Find the value of the cash dividends at the end of each year, D., during the initial growth period. This step may require adjusting the most recent dividend, Do, using the initial growth rate, 9. to calculate the dividend amount for each year using the following formula: D. = Do *(1+91) The dividend amounts in years 1 through 3 are computed as follows: D4 = Do *(1+91) * = $3.00 x (1 +0.18)] = $3.54. D2 = Do X (1+94)2 = $3.00 x (1 +0.18)2 = 4.18. D3 = D. *(1+91) 9 = $3.00 x (1 +0.18)9 = $4.93. Step 2. Find the present value of the dividends expected during the initial growth period. Using the notation presented earlier, we can find this value using the following formula: Present value of dividends during D D2 D3 the 3-year initial growth period (1+r)** (1+r)2 *(1+r) 3 The present value of the dividends expected during the initial growth period can be computed as follows: + Present value of dividends during the 3-year initial growth period $3.54 $4.18 $4.93 (1 + 0.09) (1 +0.09)2 (1 + 0.09)3' + Present value of dividends during the 3-year initial growth period = $3.25 + $3.52 +$3.81 = $10.58. Step 3. Find the value of the stock at the end of the initial growth period, which is the present value of all dividends expected from year 4 to infinity, assuming a constant dividend growth rate, 92. This value is found by applying the Gordon model to the dividends expected from year 4 to infinity, as shown below: DA P3 D3 *(1 +92) is-92 Is-92 The dividend amount at the end of year 4 is computed as: DA = D3 *(1+92) = $4.93x (1 +0.04)' = $5.13. Therefore, the stock price at the end of the initial growth period can be estimated with the Gordon model, as shown in the following formula: DA $5.13 I P3 = $102.60 's -92 0.09 -0.04 The present value of P3 would represent the value today of all dividends that are expected to be received from year 4 to infinity. This value can be calculated using the following formula: The present value of P, would represent the value today of all dividends that are expected to be received from year 4 to infinity. This value can be calculated using the following formula: Present value, Po. of the stock price, P3, at the end of the initial growth period P3 $102.60 (1+r) 3 (1 +0.0933 $79.23. Step 4. Add the present value components found in Steps 2 and 3 to find the value of the stock, Po using the following formula: D D2 D3 P3 Po + + + (1+r%)** (1+rs)2 * (1+r) 3 * (1+r)** Therefore, Po = $3.25 + $3.52 + $3.81 + $79.23 = $10.58 + $79.23 = $89.81. The market value of Lawrence's shares is $89.81. Common stock valueVariable growth Lawrence Industries' most recent annual dividend was $3.00 per share (D = $3.00), and the firm's required return is 9%. Find the market value of Lawrence's shares when dividends are expected to grow at 18% annually for 3 years, followed by a 4% constant annual growth rate in years 4 to infinity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


