Question: Complete the binary adder ) function, which takes two strings of equal length function uses the procedure above to return a new string corresponding to


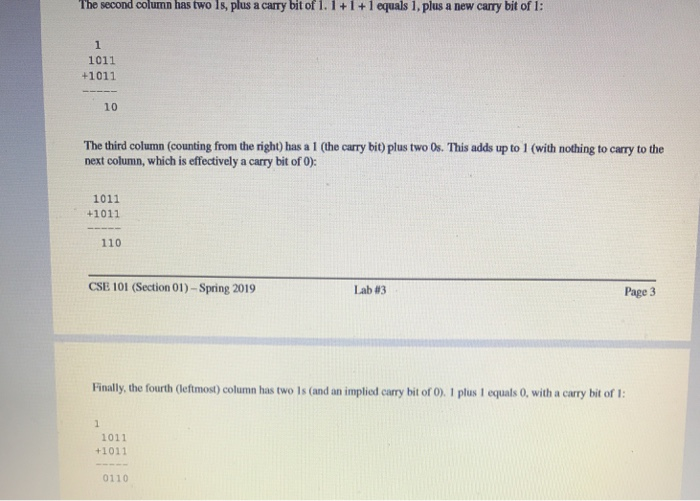


Complete the binary adder ) function, which takes two strings of equal length function uses the procedure above to return a new string corresponding to the (binary) sum of its arguments. consisting entirely of Os and is. The The basic algorithm is as follows: 1. Set the result to the empty string 2. Set the carry value to 0 3. For each operand index value, from the last (rightmost) index down through index 0: (a) Add the (integer) value at the current index from each of the operands (b) Add the carry value to the sum from the previous step (c) Examine the final sum (two bits from the operands, plus the carry bit): .If the sum is less than 2, set the carry bit to 0 and attach the sum (as a string) to the beginning of the result If the sum is 2, set the carry bit to 1 and attach the string "0 to the beginning of the result . If the sum is 3, set the carry bit to 1 and attach the string 'I' to the beginning of the result When the loop ends, if the carry bit is I, attach the string 'I' to the beginning of the result. Some examples are as follows (note that the return value will always be the same length as (or exactly one bit longer than) the arguments): Examples: Function Call Return Value (a string, not an integer!) binary addor ("1011", 101110110 binary adder ("011" 111-) binary addor ("11010 *11101) 110111 binary adder ("100, 010 1010 110 Complete the binary adder ) function, which takes two strings of equal length function uses the procedure above to return a new string corresponding to the (binary) sum of its arguments. consisting entirely of Os and is. The The basic algorithm is as follows: 1. Set the result to the empty string 2. Set the carry value to 0 3. For each operand index value, from the last (rightmost) index down through index 0: (a) Add the (integer) value at the current index from each of the operands (b) Add the carry value to the sum from the previous step (c) Examine the final sum (two bits from the operands, plus the carry bit): .If the sum is less than 2, set the carry bit to 0 and attach the sum (as a string) to the beginning of the result If the sum is 2, set the carry bit to 1 and attach the string "0 to the beginning of the result . If the sum is 3, set the carry bit to 1 and attach the string 'I' to the beginning of the result When the loop ends, if the carry bit is I, attach the string 'I' to the beginning of the result. Some examples are as follows (note that the return value will always be the same length as (or exactly one bit longer than) the arguments): Examples: Function Call Return Value (a string, not an integer!) binary addor ("1011", 101110110 binary adder ("011" 111-) binary addor ("11010 *11101) 110111 binary adder ("100, 010 1010 110 3. For each operand index value, from the last (rightmost) index down through index 0: (a) Add the (integer) value at the current index from each of the operands (b) Add the carry value to the sum from the previous step (c) Examine the final sum (two bits from the operands, plus the carry bit): . If the sum is less than 2, set the carry bit to 0 and attach the sum (as a string) to the beginning of the result . If the sum is 2 set the carry bit to 1 and attach the string '0' to the beginning of the result . If the sum is 3, set the carry bit to 1 and attach the string 'I' to the beginning of the result When the loop ends, if the carry bit is 1, attach the string '1' to the beginning of the result. Some examples are as follows (note that the return value will always be the same length as (or exactly one bit longer than) the arguments): Examples: Function Call Return Value (a string, not an integer!) binary adder ("1011", 1011) 10110 binary adder ("011, 111" binary adder ("11010, 11101) 110111 binary adder ("100, *010 1010 110 Part II: Binary Addition (5 polnts) Place your answer to this problem in the "binary adder.py" file) In lecture, we discussed data representation, including binary (base 2) representation. Addition is a common arithmetic operation, and it can be performed on numbers in any base. In fact, binary addition is simpler than base 10 addition because there are fewer rules. Like base 10 addition, binary addition works from right-to-left, adding one pair or column of digits at a time, according to the following rules: 1+0-1 1+10,plus a carry bit of 1 (for the next column)- recall that 1+12, and 2 is represented as 10 in binary If you have three Is to ad (I + 1. plus a carry bit of 1 from the previous column), the sum is 1, with a carry bit of 1 (1 +1+ 1 # 3, and 3 is represented as 1 1 in binary). For example, consider the following addition problem (11 +11, in base 10) 1011 1011 We start by adding the rightmost column. 1 plus 1 gives us O, plus a carry bit of 1 1011 +1011 Finally, the fourth (leftmost) column has two Is (and an implied carry bit of 0). 1 plus 1 equals 0, with a carry bit of I 1011 +1011 0110 There are no columns left to process, but we have a non-zero carry bit, so the carry bit "falls down" and is added to the left of the existing result, giving us a final answer of 10110 (which is 22 in base 10). Complete the binary adder O function, which takes two strings of equal length consisting entirely of Os and 1s. function uses the procedure above to return a new string corresponding to the (binary) sum of its arguments The The basic algorithm is as follows: 1. Set the result to the empty string " 2. Set the carry value to 0 3. For each operand index value, from the last (rightmost) index down through index 0: (a) Add the (integer) value at the current index from each of the operands (b) Add the carry value to the sum from the previous step (c) Examine the final sum (two bits from the operands, plus the carry bit: . If the sum is less than 2, set the carry bit to 0 and attach the sum (as a string) to the beginning of the result If the sum is 2, set the carry bit to 1 and attach the string '0' to the beginning of the result . If the sum is 3, set the carry bit to 1 and attach the string '1 to the beginning of the result When the loop ends, if the carry bit is 1, attach the string '1' to the beginning of the result Some examples are as follows (note that the returm value will always be the same length as (or exactly one bit longer than) the arguments): Examples
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


