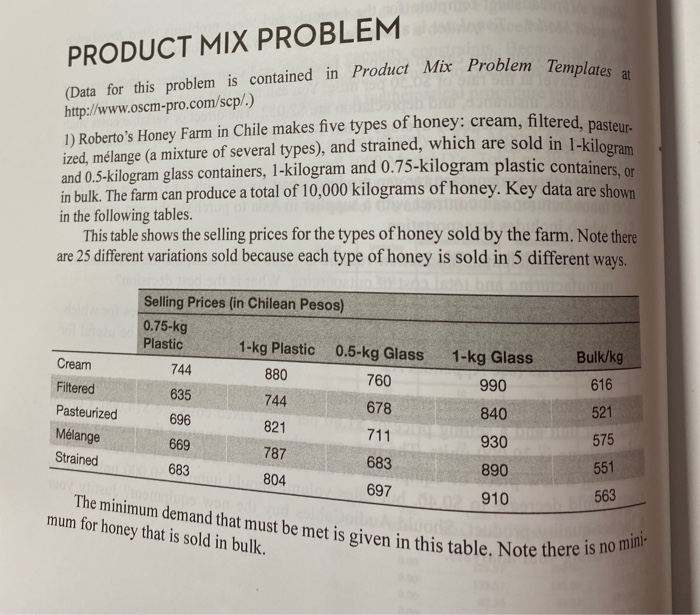
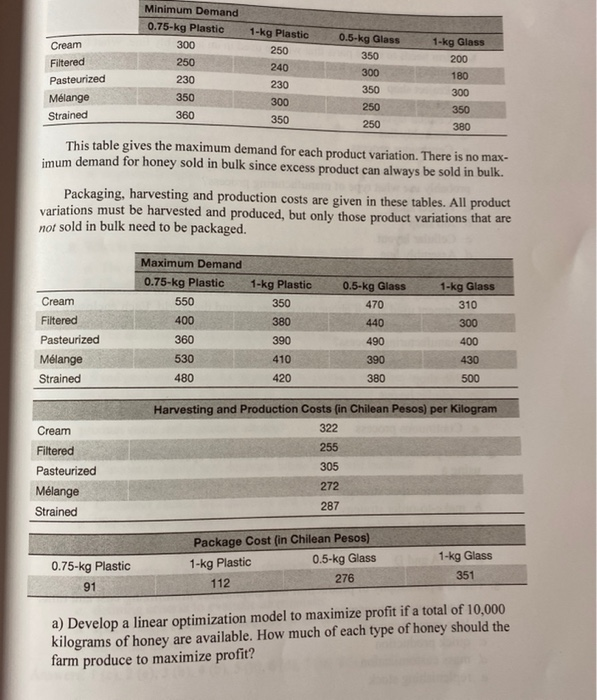
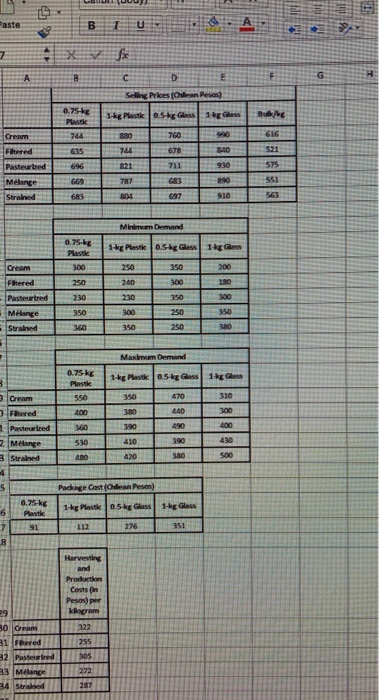
Question: complete this problem using the template PRODUCT MIX PROBLEM (Data for this problem is contained in Product Mir Problem Templates at The minimum demand that
complete this problem using the template
PRODUCT MIX PROBLEM (Data for this problem is contained in Product Mir Problem Templates at The minimum demand that must be met is given in this table. Note there is no mini- http://www.oscm-pro.com/scp/.) 1) Roberto's Honey Farm in Chile makes five types of honey: cream, filtered, pasteur- ized, mlange (a mixture of several types), and strained, which are sold in 1-kilogram and 0.5-kilogram glass containers, 1-kilogram and 0.75-kilogram plastic containers, or in bulk. The farm can produce a total of 10,000 kilograms of honey. Key data are shown in the following tables. This table shows the selling prices for the types of honey sold by the farm. Note there are 25 different variations sold because each type of honey is sold in 5 different ways. Selling Prices (in Chilean Pesos) 0.75-kg Plastic 1-kg Plastic 0.5-kg Glass 1-kg Glass Bulk/kg Cream 744 880 760 990 616 Filtered 635 744 678 Pasteurized 840 521 696 821 711 Mlange 930 787 Strained 683 683 890 697 Triko plati 669 575 551 804 910 563 mum for honey that is sold in bulk. 1-kg Plastic 250 Minimum Demand 0.75-kg Plastic 300 250 230 350 360 0.5-kg Glass 350 300 Cream Filtered Pasteurized Mlange Strained 1-kg Glass 200 180 240 230 300 350 350 250 300 350 380 250 This table gives the maximum demand for each product variation. There is no max- imum demand for honey sold in bulk since excess product can always be sold in bulk. Packaging, harvesting and production costs are given in these tables. All product variations must be harvested and produced, but only those product variations that are not sold in bulk need to be packaged. Maximum Demand 0.75-kg Plastic 550 0.5-kg Glass 470 Cream 1-kg Plastic 350 380 390 1-kg Glass 310 300 400 440 490 360 400 Filtered Pasteurized Mlange Strained 410 390 430 530 480 420 380 500 Harvesting and Production Costs (in Chilean Pesos) per kilogram 322 255 305 Cream Filtered Pasteurized Mlange Strained 272 287 0.75-kg Plastic 91 Package Cost (in Chilean Pesos) 1-kg Plastic 0.5-kg Glass 112 276 1-kg Glass 351 a) Develop a linear optimization model to maximize profit if a total of 10,000 kilograms of honey are available. How much of each type of honey should the farm produce to maximize profit? Grill Model Selling Price/Unit Variable Cost/Unit Minimum Monthly Sales Requirements Maximum Monthly Sales Potential $210 0 4.000 3,000 B $240 0 Nm til $250 $300 $400 $650 c 500 $300 $520 2,000 1,000 D 500 6 A B Hours Available C To 40 30 10 10 320 20 10 10 320 25 15 15 12 320 20 20 25 15 320 320 50 40 40 30 B B D Total 7. Department 8 Stamping 9 Painting 10 Assembly 11 Inspection 12 Packaging 13 14 15 Production 16 Profit 17 18 Stamping 19 Painting 20 Assembly 21 Inspection 22 Packaging 23 24 25 26 27 28 Paste B 1 U 8. A V f A B D G Selling Prices (Chilean Pesos) 1g Plastk 0.5kg Glass 1kg Glass Bullet 0.75kg Plastk 744 760 616 635 Cream Filtered Pasteurtred Mlange Strained 830 744 821 521 678 711 840 930 696 575 551 669 787 683 697 804 910 Miha Demand 1 kg Plastko.sk Glass 1kg Glass 0.75 kg Plastic 300 250 350 Cream Filtered Pasteurtred 250 240 300 350 200 180 100 230 230 350 300 Melange Strained 250 250 360 Maximun Demand 0.75 kg Plast 1kg Plastk 0.5kg Glass 1kg Cream 550 350 470 310 Flered 400 380 440 300 400 1 Pasteurtred 390 360 530 480 2 Mange 3 Strained 30 410 420 390 380 SOO 4 5 Package Cast (Chilean Pesos) 1 kg Plastk 0.5 kg Glass 1 kg Glass 6 7 0.75 kg Plastic 91 112 276 351 8 Harvesting and Production Cests in Pesos) per klogram 322 29 30 Cream 81 Fiered 32 Pastewbed 33 Melange 34 Strained 255 305 272 287 a) Develop a linear optimization model to maximize profit if a total of 10,000 kilograms of honey are available. How much of each type of honey should the farm produce to maximize profit? PRODUCT MIX PROBLEM (Data for this problem is contained in Product Mir Problem Templates at The minimum demand that must be met is given in this table. Note there is no mini- http://www.oscm-pro.com/scp/.) 1) Roberto's Honey Farm in Chile makes five types of honey: cream, filtered, pasteur- ized, mlange (a mixture of several types), and strained, which are sold in 1-kilogram and 0.5-kilogram glass containers, 1-kilogram and 0.75-kilogram plastic containers, or in bulk. The farm can produce a total of 10,000 kilograms of honey. Key data are shown in the following tables. This table shows the selling prices for the types of honey sold by the farm. Note there are 25 different variations sold because each type of honey is sold in 5 different ways. Selling Prices (in Chilean Pesos) 0.75-kg Plastic 1-kg Plastic 0.5-kg Glass 1-kg Glass Bulk/kg Cream 744 880 760 990 616 Filtered 635 744 678 Pasteurized 840 521 696 821 711 Mlange 930 787 Strained 683 683 890 697 Triko plati 669 575 551 804 910 563 mum for honey that is sold in bulk. 1-kg Plastic 250 Minimum Demand 0.75-kg Plastic 300 250 230 350 360 0.5-kg Glass 350 300 Cream Filtered Pasteurized Mlange Strained 1-kg Glass 200 180 240 230 300 350 350 250 300 350 380 250 This table gives the maximum demand for each product variation. There is no max- imum demand for honey sold in bulk since excess product can always be sold in bulk. Packaging, harvesting and production costs are given in these tables. All product variations must be harvested and produced, but only those product variations that are not sold in bulk need to be packaged. Maximum Demand 0.75-kg Plastic 550 0.5-kg Glass 470 Cream 1-kg Plastic 350 380 390 1-kg Glass 310 300 400 440 490 360 400 Filtered Pasteurized Mlange Strained 410 390 430 530 480 420 380 500 Harvesting and Production Costs (in Chilean Pesos) per kilogram 322 255 305 Cream Filtered Pasteurized Mlange Strained 272 287 0.75-kg Plastic 91 Package Cost (in Chilean Pesos) 1-kg Plastic 0.5-kg Glass 112 276 1-kg Glass 351 a) Develop a linear optimization model to maximize profit if a total of 10,000 kilograms of honey are available. How much of each type of honey should the farm produce to maximize profit? Grill Model Selling Price/Unit Variable Cost/Unit Minimum Monthly Sales Requirements Maximum Monthly Sales Potential $210 0 4.000 3,000 B $240 0 Nm til $250 $300 $400 $650 c 500 $300 $520 2,000 1,000 D 500 6 A B Hours Available C To 40 30 10 10 320 20 10 10 320 25 15 15 12 320 20 20 25 15 320 320 50 40 40 30 B B D Total 7. Department 8 Stamping 9 Painting 10 Assembly 11 Inspection 12 Packaging 13 14 15 Production 16 Profit 17 18 Stamping 19 Painting 20 Assembly 21 Inspection 22 Packaging 23 24 25 26 27 28 Paste B 1 U 8. A V f A B D G Selling Prices (Chilean Pesos) 1g Plastk 0.5kg Glass 1kg Glass Bullet 0.75kg Plastk 744 760 616 635 Cream Filtered Pasteurtred Mlange Strained 830 744 821 521 678 711 840 930 696 575 551 669 787 683 697 804 910 Miha Demand 1 kg Plastko.sk Glass 1kg Glass 0.75 kg Plastic 300 250 350 Cream Filtered Pasteurtred 250 240 300 350 200 180 100 230 230 350 300 Melange Strained 250 250 360 Maximun Demand 0.75 kg Plast 1kg Plastk 0.5kg Glass 1kg Cream 550 350 470 310 Flered 400 380 440 300 400 1 Pasteurtred 390 360 530 480 2 Mange 3 Strained 30 410 420 390 380 SOO 4 5 Package Cast (Chilean Pesos) 1 kg Plastk 0.5 kg Glass 1 kg Glass 6 7 0.75 kg Plastic 91 112 276 351 8 Harvesting and Production Cests in Pesos) per klogram 322 29 30 Cream 81 Fiered 32 Pastewbed 33 Melange 34 Strained 255 305 272 287 a) Develop a linear optimization model to maximize profit if a total of 10,000 kilograms of honey are available. How much of each type of honey should the farm produce to maximize profit