Question: (Compute Delta from a Binomial Lattice) Assume that the (no dividend) underlying price follows d.St St payoff (ST) = pdt + odz where Z,
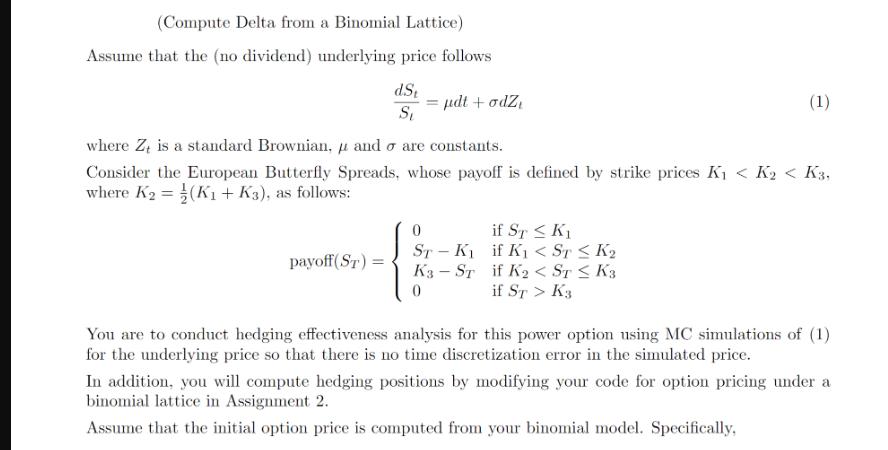

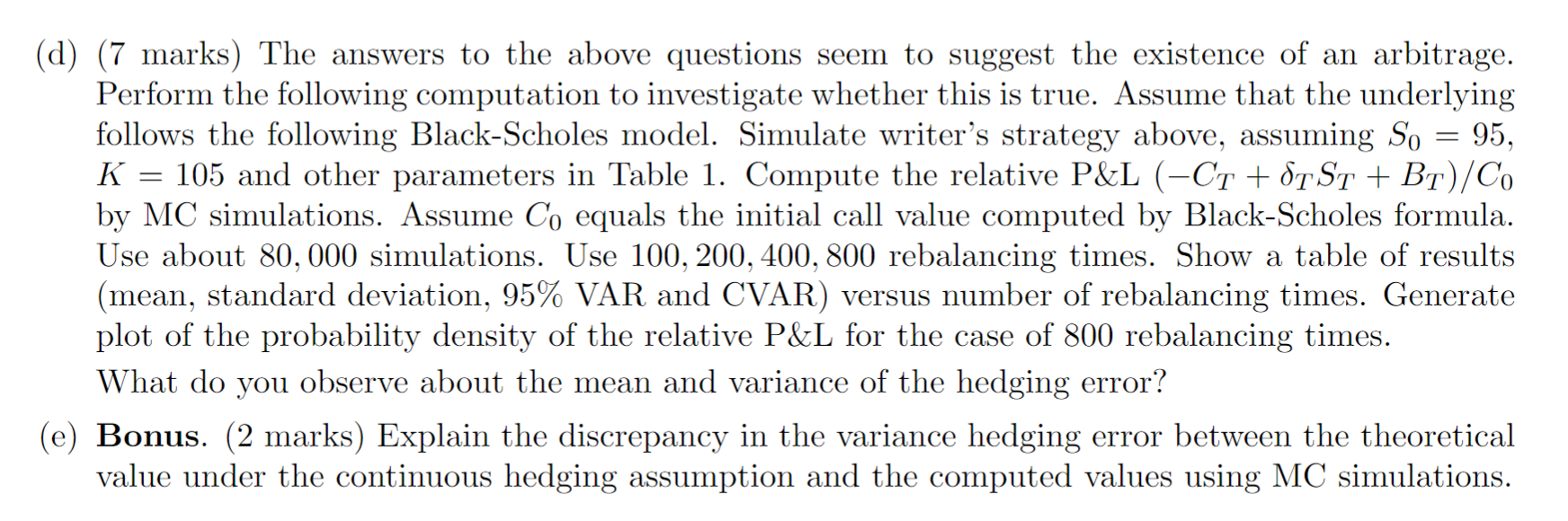
(Compute Delta from a Binomial Lattice) Assume that the (no dividend) underlying price follows d.St St payoff (ST) = pdt + odz where Z, is a standard Brownian, u and o are constants. Consider the European Butterfly Spreads, whose payoff is defined by strike prices K K < K3, where K = (K + K3), as follows: ST-K K3-ST 0 (1) if ST K if K < ST K2 if K < ST K3 if ST > K3 You are to conduct hedging effectiveness analysis for this power option using MC simulations of (1) for the underlying price so that there is no time discretization error in the simulated price. In addition, you will compute hedging positions by modifying your code for option pricing under a binomial lattice in Assignment 2. Assume that the initial option price is computed from your binomial model. Specifically, 4 [(10 marks)]. (Trading simulation) You think that you have discovered an arbitrage dynamic trading strategy. Does it work? Simulation can be used to analyze your strategy. Consider the following dynamic trading strategy Let's assume that it is possible to trade continuously in time, without transaction cost. For simplicity, we also assume that the interest r = = 0. Let S and Ct denote time t values of the stock and a European call with strike K and expiry T. Suppose that today you sell the European call option with strike K and expiry T. Assume that So < K, i.e. the initial asset price is less than K. Assume that you then implements the following simple hypothetic hedging strategy: As soon as St > K, you borrow from cash account and buy the stock at t. As soon as St < K, you sell the stock at t. Let & St + Bt denote the value of the hedging portfolio of the underlying and bond. At t = 0, the cash account is set such that Co + So So + Bo 0. Assume that the interest r = 0. - (a) (1 mark) What is the value of Bo? Write down a mathematical expression for the writer's trading strategy St, 0t = (d) (7 marks) The answers to the above questions seem to suggest the existence of an arbitrage. Perform the following computation to investigate whether this is true. Assume that the underlying follows the following Black-Scholes model. Simulate writer's strategy above, assuming So 95, K 105 and other parameters in Table 1. Compute the relative P&L (CT + ST ST + BT)/Co by MC simulations. Assume Co equals the initial call value computed by Black-Scholes formula. Use about 80, 000 simulations. Use 100, 200, 400, 800 rebalancing times. Show a table of results (mean, standard deviation, 95% VAR and CVAR) versus number of rebalancing times. Generate plot of the probability density of the relative P&L for the case of 800 rebalancing times. What do you observe about the mean and variance of the hedging error? - (e) Bonus. (2 marks) Explain the discrepancy in the variance hedging error between the theoretical value under the continuous hedging assumption and the computed values using MC simulations.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


