Question: Computer Architecture: 5 Stage Pipeline This implementation has all the forwarding paths needed for better performance. The conditional branch is resolved in the ID stage.
Computer Architecture: 5 Stage Pipeline
This implementation has all the forwarding paths needed for better performance. The conditional branch is resolved in the ID stage. The implementation also use a static branch predictor that predicts not-taken. If the prediction is correct, there is no performance penalty on branches.
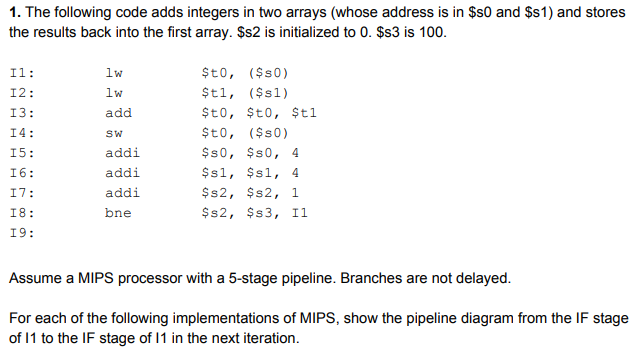
1. The following code adds integers in two arrays (whose address is in $s0 and $s1) and stores the results back into the first array. $s2 is initialized to 0. $s3 is 100 I1 I2: I3: I4: I5: I6: I7: I8: I9: add sw addi addi addi bne ?t0, ($s0) $tl, ($s1) $t0, $t0, $t1 ?t0, ($s0) $s0, $s0, 4 $sl, $sl, 4 $s2, $s2, 1 $s2, $s3, I1 Assume a MIPS processor with a 5-stage pipeline. Branches are not delayed For each of the following implementations of MIPS, show the pipeline diagram from the IF stage of 11 to the IF stage of 11 in the next iteration
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


