Question: Computer architecture answer question number 7 - NOTE: computer architecture subjects 7. Explain the following figure - add $50, $t0,$t1 sub $t2, $50, $t3 200
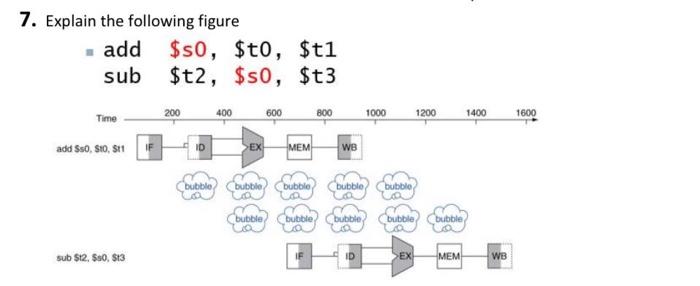

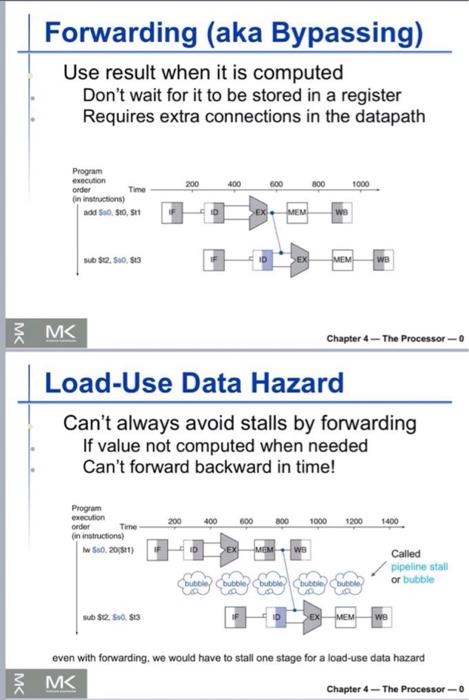
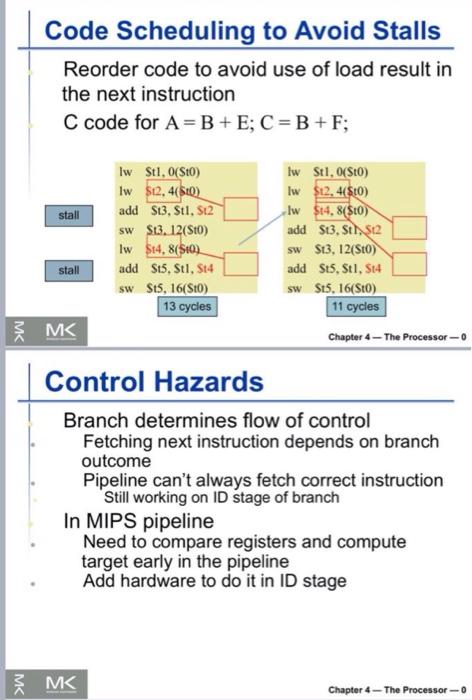
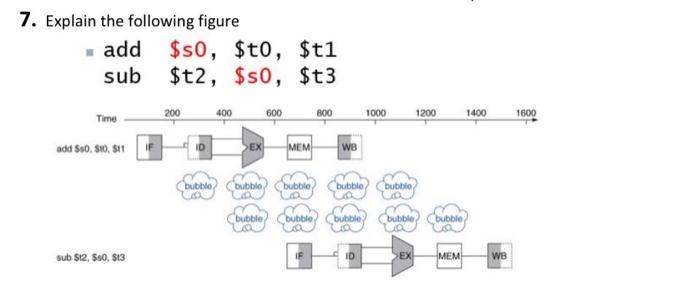
7. Explain the following figure - add $50, $t0,$t1 sub $t2, $50, $t3 200 400 600 800 Time 1000 1200 1400 1600 add $50. SO, S11 D EX MEM WB bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble sub $12, 50, 513 IF ID >EX MEM WB 7. Explain the following figure - add $50, $t0,$t1 sub $t2, $50, $t3 200 400 600 800 Time 1000 1200 1400 1600 add $50. SO, S11 D EX MEM WB bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble sub $12, 50, 513 IF ID >EX MEM WB Data Hazards data hazard Also called a pipeline data hazard. When a planned instruction cannot execute in the proper clock cycle because data that is needed to execute the instruction is not yet available. arise from the dependence of one instruction on an earlier one that is still in the pipeline IMC Chapter 4 - The Processor-o Data Hazards An instruction depends on completion of data access by a previous instruction add $s0, $t0,$t1 sub $t2, $s0, $t3 Time 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 add $50, 80, 811 D EX MEM we bubble bubble but bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble bubble LA bubble sub $12, 50, 513 EX MEM WB M
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


