Question: Consider a composite solid of materials A and B, shown in the Figure 1. An electrical resistance heater embedded in solid B generates heat at
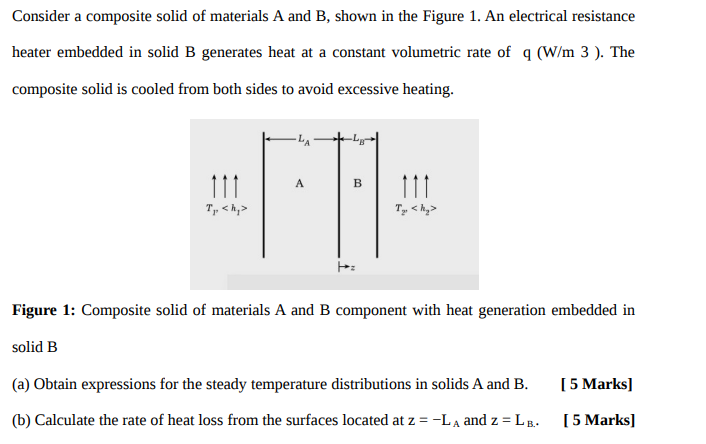

Consider a composite solid of materials A and B, shown in the Figure 1. An electrical resistance heater embedded in solid B generates heat at a constant volumetric rate of 2 (W/m 3 ). The composite solid is cooled from both sides to avoid excessive heating. 111 A B 111 T,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


