Question: Consider a conducting bar which moves with a constant speed in the presence of an external magnetic field as shown. B (a) Electrons in
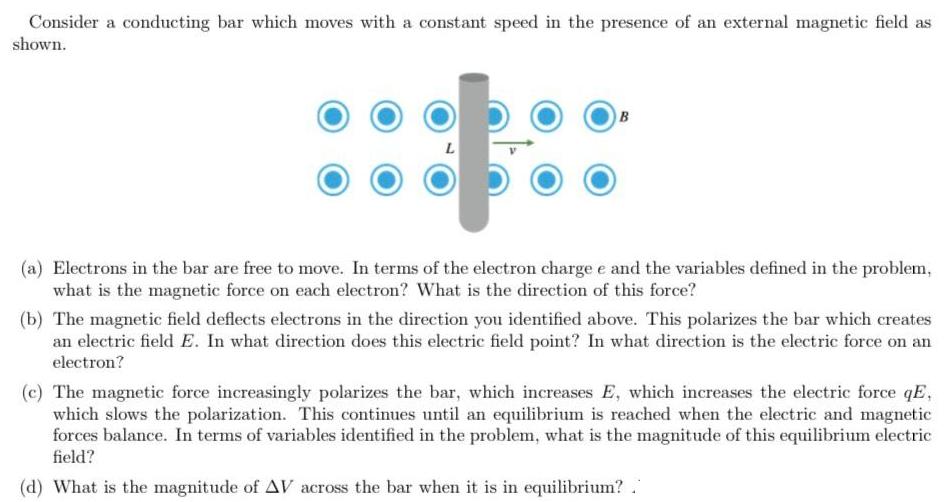
Consider a conducting bar which moves with a constant speed in the presence of an external magnetic field as shown. B (a) Electrons in the bar are free to move. In terms of the electron charge e and the variables defined in the problem, what is the magnetic force on each electron? What is the direction of this force? (b) The magnetic field deflects electrons in the direction you identified above. This polarizes the bar which creates an electric field E. In what direction does this electric field point? In what direction is the electric force on an electron? (c) The magnetic force increasingly polarizes the bar, which increases E, which increases the electric force qE, which slows the polarization. This continues until an equilibrium is reached when the electric and magnetic forces balance. In terms of variables identified in the problem, what is the magnitude of this equilibrium electric field? (d) What is the magnitude of AV across the bar when it is in equilibrium? .
Step by Step Solution
3.30 Rating (147 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
It appears that no images have ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


