Question: Consider a two-period economy with 2 securities, Lambda (security 1) and Omega (security 2), which are both in unit supply. They are traded in the
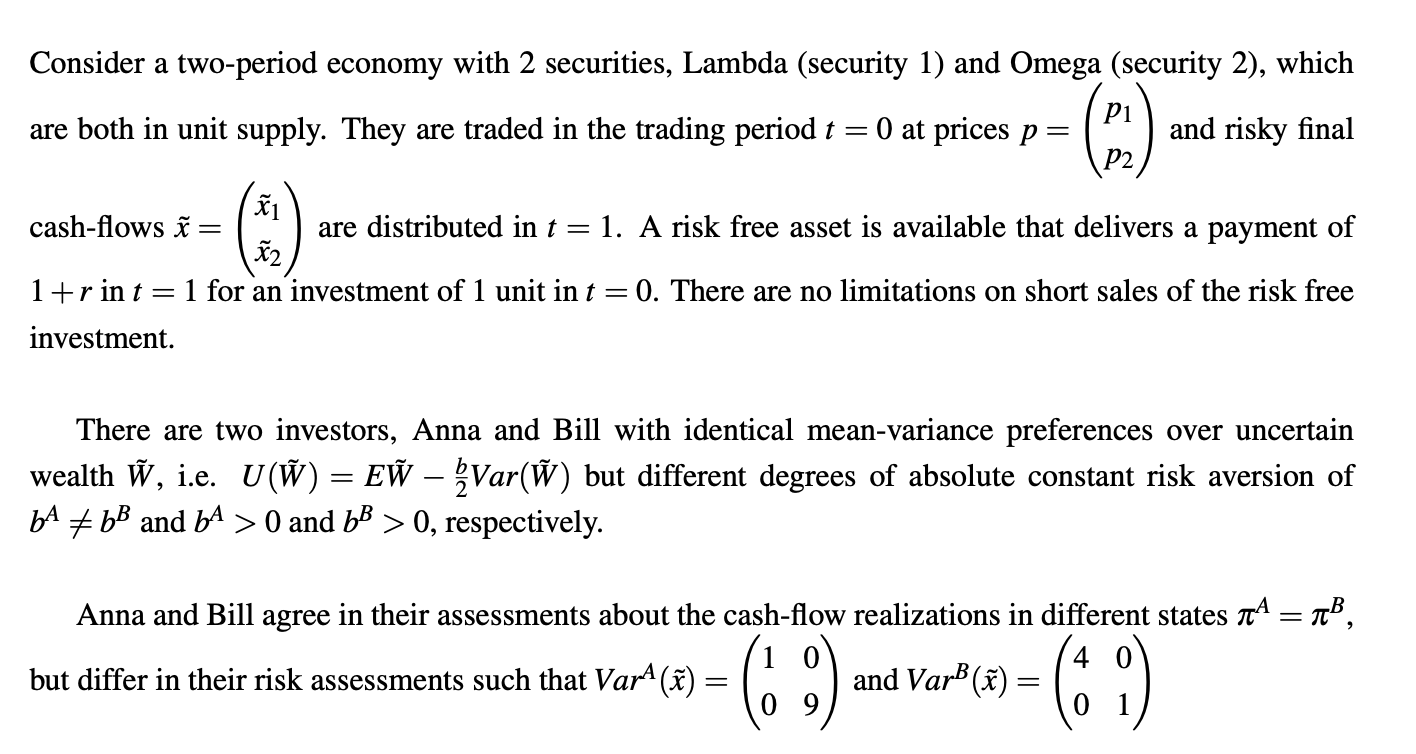

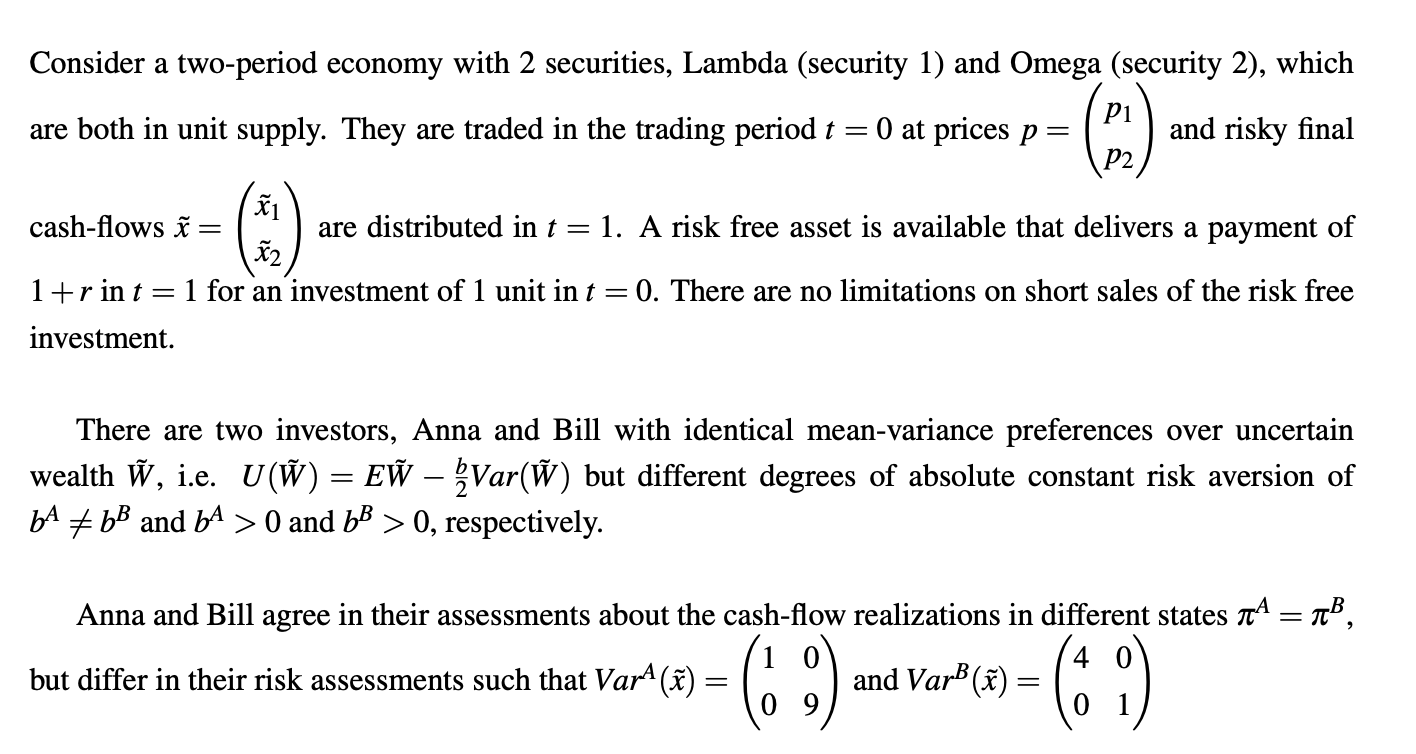

Consider a two-period economy with 2 securities, Lambda (security 1) and Omega (security 2), which are both in unit supply. They are traded in the trading period = O at prices p = (pl) and risky final D2 cash-flows = {1 are distributed in r = 1. A risk free asset is available that delivers a payment of X2 1+rint =1 for an investment of 1 unit in t = 0. There are no limitations on short sales of the risk free investment. There are two investors, Anna and Bill with identical mean-variance preferences over uncertain wealth W, ie. U(W) = EW 2Var(W) but different degrees of absolute constant risk aversion of bA b8 and b* > 0 and b8 > 0, respectively. Anna and Bill agree in their assessments about the cash-flow realizations in different states e 10 4 0 but differ in their risk assessments such that Var? (%) = (O 9) and VarB (%) = (0 1) a. Which fundamental functions of asset markets are modelled in this example? (2 points) b. Can you define and determine equilibrium prices for all traded securities? How can you interpret those prices? (4 points) . Should short sales be prohibited in this example, and if so, why? (2 points)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


