Question: Consider hosts A,B,C,D that transmit on a shared medium, using a multiple access protocol. Each host has exactly one frame to send, and the transmission
Consider hosts A,B,C,D that transmit on a shared medium, using a multiple access protocol. Each host has exactly one frame to send, and the transmission time for each frame is equal to 2 time slots. Hosts A, B, C,D want to transmit a frame at times t A = 0, t B = 0.5, t C = 1.3 and t D = 4 , respectively; a frame shown to arrive a time t, is ready for transmission at time t.
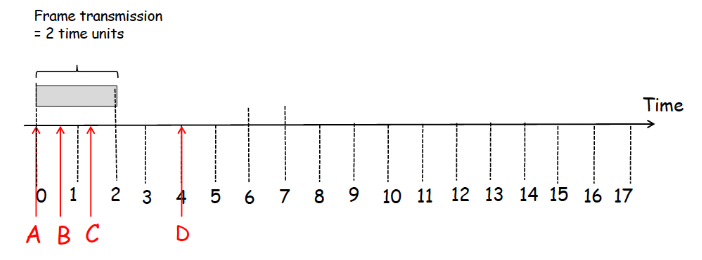
In Questions 7, 8, 9 below, nodes are assumed to use a different multiple access protocol (TDMA, slotted aloha or CSMA/CD, respectively) and you are asked to consider all transmissions until all frames are successfully transmitted and compute the time when this happens (referred to as completion time).
Each node has access to the following sequence of random numbers, drawn uniformly at random between 0 and 1:
- Node A draws numbers: 0.2, 0.6, 0.3, 0.7, 0.1, 0.9 ....
- Node B draws numbers: 0.6, 0.6, 0.1, 0.9, 0.3, 0.2 ....
- Node C draws numbers: 0.7, 0.9, 0.7, 0.2, 0.1, 0.7 ....
- Node D draws numbers: 0.6, 0.1, 0.2, 0.8, 0.7, 0.2 ....
When the protocol needs to make a randomized decision, it picks the next (not yet used) random number in its list. A node might not need to use all the available random numbers. The numbers must be used in the order they are provided (from left to right) and each random number must be used only once. You should use the same random numbers for all Questions 7,8,9 below, starting from scratch.
You should use the above random numbers to make randomize decisions using the following general rule: Given a random number r in [0,1], if you want to choose among N options, choose the k-th option (k=1,2....N) where k = r N (i.e., the ceiling of rN).
- Example 1: In Slotted Aloha, if you want to decide between Option 1 (transmit) and Option 2 (do not transmit), use the random numbers as follows: if r is in [0,0.5], Transmit; if r is in (0,5, 1], then Do Not Transmit.
- Example 2: In CSMA/CD, if you want to pick one slot randomly out of two slots total to transmit do the following: if r is in [0,0.5] then pick the first slot; otherwise r is in (0.5,1] then pick the second slot.
- Example 3: In CSMA/CD, if you want to pick one slot randomly out of four slots total to transmit, do the following: if r in [0, 0.25], (0.25, 0.5], (0.5, 0.75], (0.75,1], then pick the first, second, third or fourth timeslot, respectively.
Question 9:
Consider that hosts use Ethernet, i.e., (1-persistent) CSMA/CD with exponential backoff. Assume that every node can detect instantaneously whether the channel is idle, but it needs one time unit to detect and abort a collision. (Hint: Therefore, the slots for contention in exponential backoff are 1 time unit).
Completion Time: All frames on all nodes are successfully transmitted at time..... A. 10
B. 12
C. 14
D. 16
E. none of the above
Frame transmission = 2 time units Time 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 A B C D Frame transmission = 2 time units Time 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 A B C D
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


