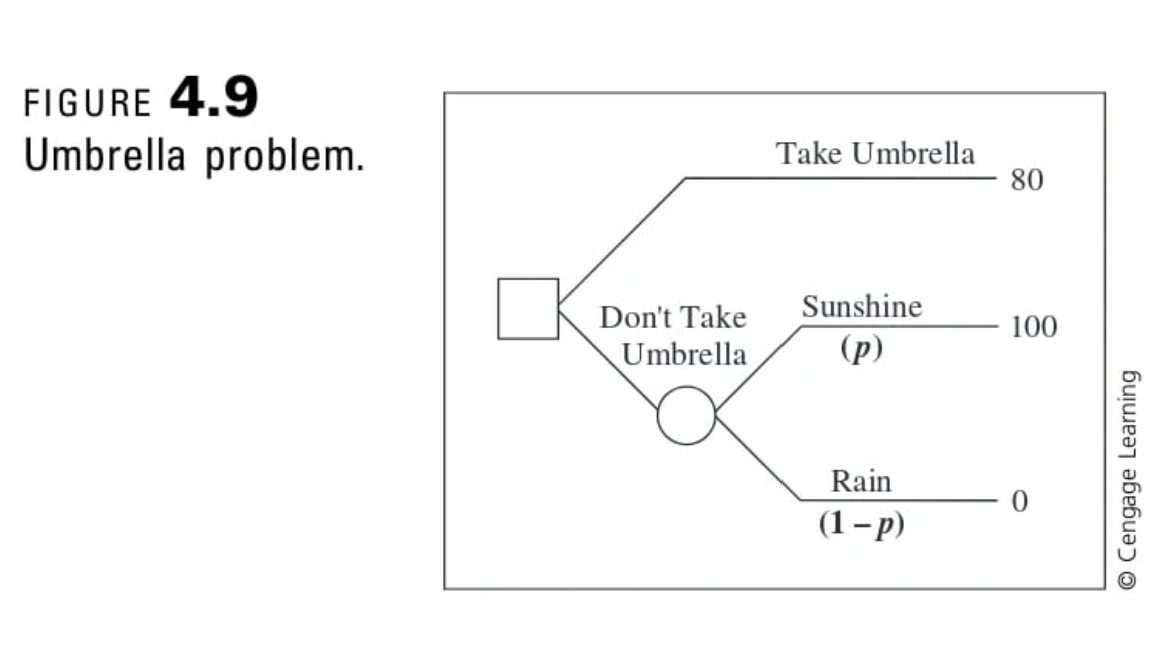
Question: Consider the decision problem shown in Figure 5.26. This basic decision tree often is called a cost- to-loss ratio problem and is characterized as a

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


