Question: Consider the experiment decided by the Vendiagram, with the sample pace containing live sample points. The sample points wend the probabil, 0.1, 0.3, E10.7. PE02,
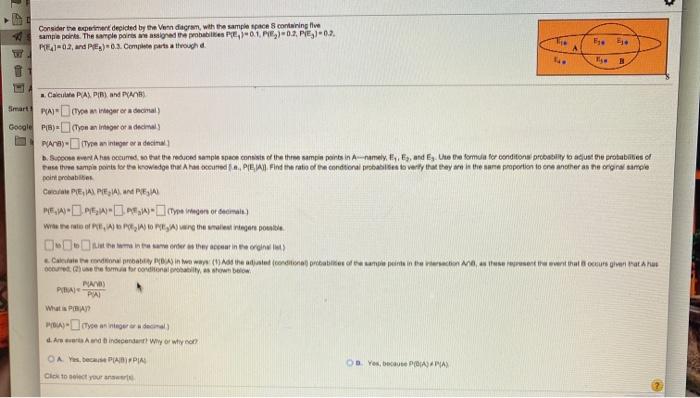
Consider the experiment decided by the Vendiagram, with the sample pace containing live sample points. The sample points wend the probabil, 0.1, 0.3, E10.7. PE02, and PE)*0.3. Come parts a touch 1. Bje Cale PAPIRN PA Smart come or a decimal Gocale PB - (Tonania or a decimal Pay-The an integer or a decina Soome event tumed, so that the reduced sample space consists of the the sampin points in A-namelyE, and Ehte the formula for conditions probability to adjust the probabilities of use the sample points for the knowledge that cand. PLEAL Find the ratio of the conditional probabies te verly that they are in the same proportion to one another as the original sample probabil CPE, APEA PEA NGA Presotera) When I, APO ME A wing the sales tapes pouble Cntament de se corner CRA) in two way the additional babies of printeinen aus what our heart but she formationally, ass PVD) PAPAI What is PBAN Toe anneer de d. Are Audio condan Wyo wye O AY PAPIA Click to see you OB Yes, POASPAS Consider the experiment depicted by the Venn diagram, with the sample space Scontaining five sample points. The sample points are assigned the probabilities P(E)=0.1, PE )=02.P/E)-02, PE)-0.2, and P(EX)-0.3. Complete parts a through d ogle P(A/B) - (Type an Integer or a decimal.) b. Suppose event A has occurred, so that the reduced sample space consists of the three sample points in Anamaly, E. E, and Ey. Use the formula for conditional probability these three sample points for the knowledge that has occurred ... PEJAI Find the ratio of the conditional probabilities to verify that they are in the same proportion to one an point probabilities Calculato PE, IA), PE,/A), and PE,A). PLE, A-O).PEGA-PE A (Type Ingern or decimals.) Who the ratio of P{E, A) to PE, A) to PE, ) using the smallest integer possible to list the terms in the same order as they appear in the original list) e. Calculate the conditional probability (BIA) in two ways: (1) Add the adjusted (conditional) probabilities of the sample points in the intersection AB, as those represent the ever occurred; (2) use the formula for conditional probability, as shown below. PAB) P(BA) PIA) What is PBIAY? PLBA=(type an integer or decimal.) d. Are events A and B independent? Why or why not? O A Yes, because PAB) PIA). OG. No, because P(AB)-PA) OE. Yes, because P(A/B) - P(A). OG. No, because PAB) PB) OB Yes, because PBA) PA) OD. No, because P(BA) PB) OF. Yes, because P(BA) P(6) OH, No, because P(BA)=P(B) Click to select your answer(s)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


