Question: Consider the following constrained optimization problem: = min f(x1, x) x + x Subject to g(x, x2) = 2x + x 5 OPT-1 (a)
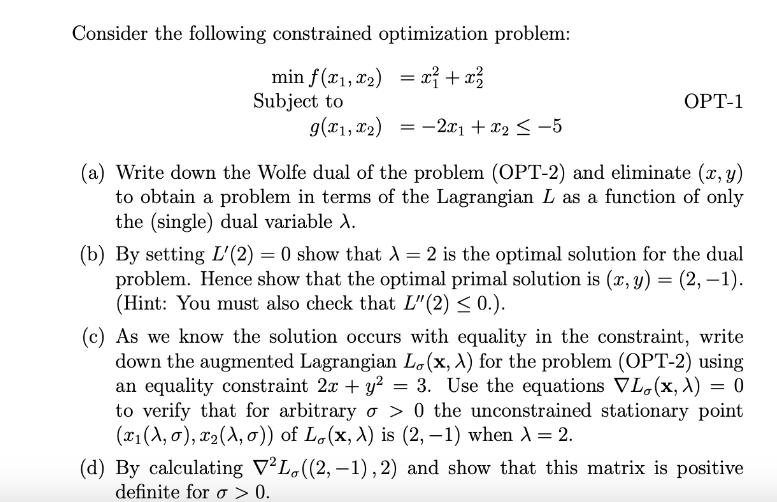
Consider the following constrained optimization problem: = min f(x1, x) x + x Subject to g(x, x2) = 2x + x 5 OPT-1 (a) Write down the Wolfe dual of the problem (OPT-2) and eliminate (x, y) to obtain a problem in terms of the Lagrangian L as a function of only the (single) dual variable X. (b) By setting L'(2) = 0 show that = 2 is the optimal solution for the dual problem. Hence show that the optimal primal solution is (x, y) = (2, -1). (Hint: You must also check that L"(2) 0.). (c) As we know the solution occurs with equality in the constraint, write down the augmented Lagrangian Lo (x, A) for the problem (OPT-2) using an equality constraint 2x + y = 3. Use the equations VL. (x,x) = 0 to verify that for arbitrary o> 0 the unconstrained stationary point (x(1, 0), (1, 0)) of Lo(x, X) is (2, -1) when = 2. (d) By calculating VL,((2, -1), 2) and show that this matrix is positive definite for a > 0.
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a To write down the Wolfe dual of the problem OPT2 we need to convert the constrained minimization p... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


