Question: . Consider the following simple neural network with only one output node. Ignore the bias node for this example. The values on the edges indicate
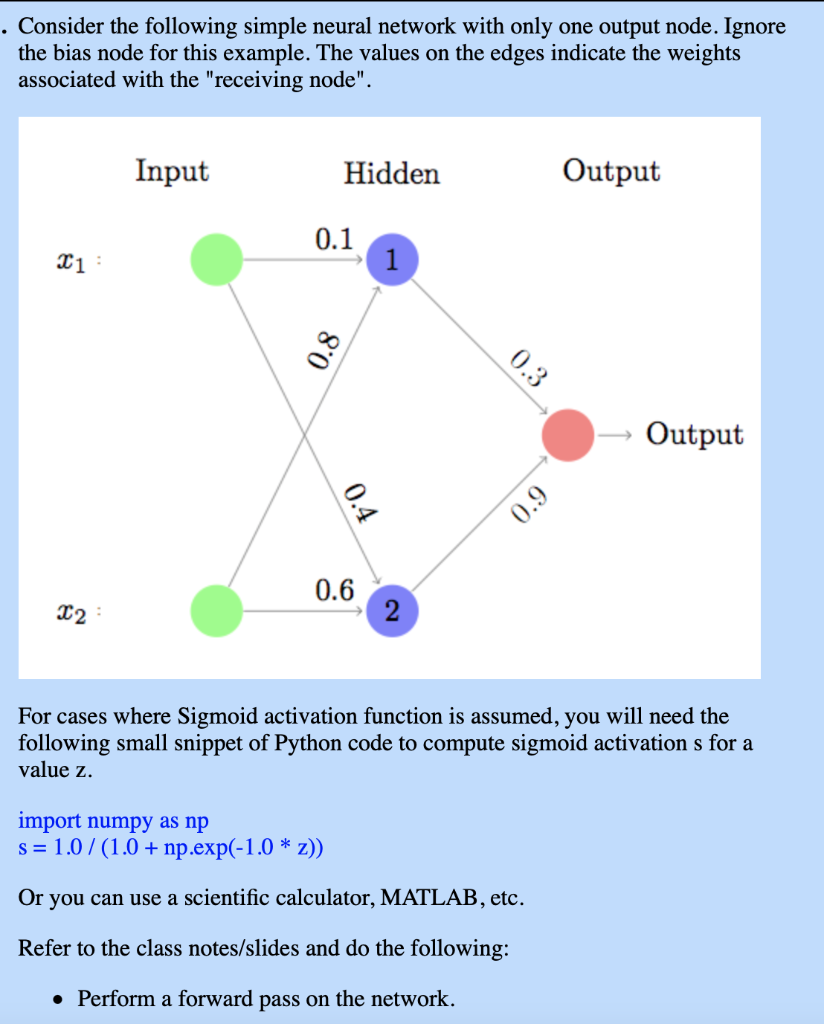

. Consider the following simple neural network with only one output node. Ignore the bias node for this example. The values on the edges indicate the weights associated with the "receiving node". Input Hidden Output 0.1 21: 1 0.8 0.3 Output 0.4 0.9 0.6 12 2 For cases where Sigmoid activation function is assumed, you will need the following small snippet of Python code to compute sigmoid activation s for a value z. import numpy as np s=1.0 /(1.0+ np.exp(-1.0 * z)) Or you can use a scientific calculator, MATLAB, etc. Refer to the class notes/slides and do the following: Perform a forward pass on the network. Consider two neural networks, A and B with the same exact architecture as above, such that A uses Sigmoid activation at each node/unit and B uses RELU activation at each node/unit. Remember that RELU activation is equal to max(0,x), i.e., it simply outputs the input if it is positive, and 0, otherwise. After performing the forward pass using the two activation functions, compare the final output activation for networks A and B for different inputs: a) If x1 = -4 and x2 = 1, the output activation for A will be same as the output activation for B. b) If x1 = 1 and x2 = -4, the output activation for A will be larger than the output activation for B. c) If x1 = 1 and x2 = -4, the output activation for A will be same as the output activation for B. d) If x1 = 4 and x2 = 2, the output activation for A will be larger than the output activation for B
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


