Question: Consider the initial value problem with f(t, x) = -tx y'(t) = -ty(t) y(0) = 1. Use the exact solution y(t) +2/2 to show that
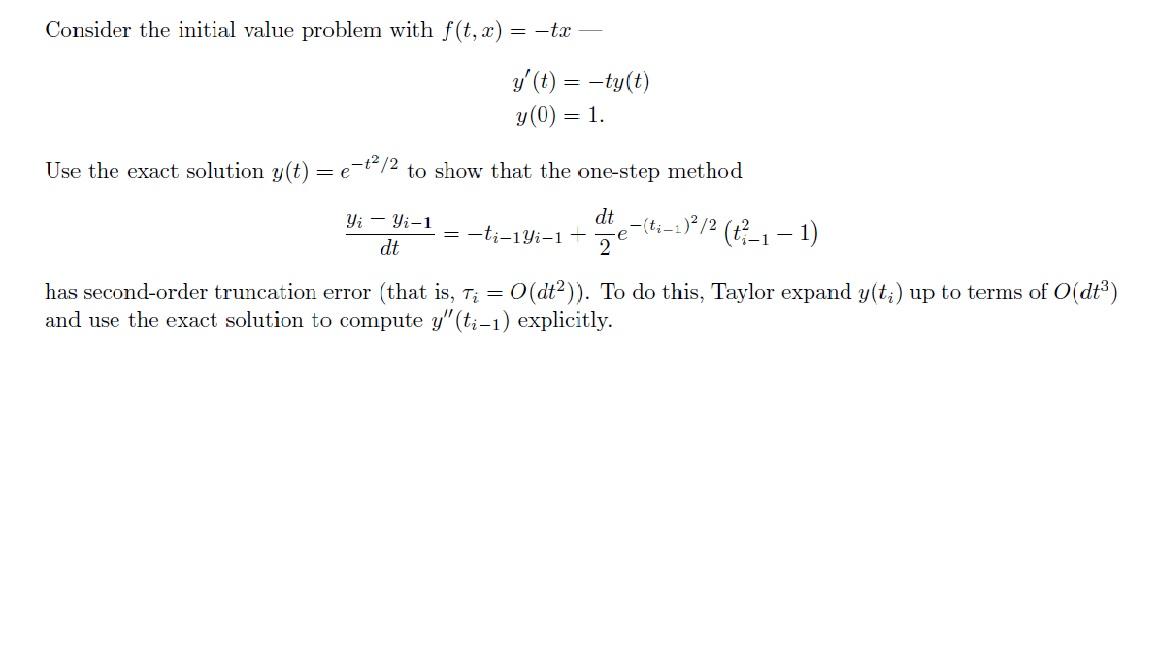
Consider the initial value problem with f(t, x) = -tx y'(t) = -ty(t) y(0) = 1. Use the exact solution y(t) +2/2 to show that the one-step method dt Yi - Yi-1 dt = -ti-1 Yi-1- ze-(i-:)?/2 (t-1 - 1) has second-order truncation error (that is, ti = O(dta)). To do this, Taylor expand y(t;) up to terms of Od+3) and use the exact solution to compute y"(ti1) explicitly. Consider the initial value problem with f(t, x) = -tx y'(t) = -ty(t) y(0) = 1. Use the exact solution y(t) +2/2 to show that the one-step method dt Yi - Yi-1 dt = -ti-1 Yi-1- ze-(i-:)?/2 (t-1 - 1) has second-order truncation error (that is, ti = O(dta)). To do this, Taylor expand y(t;) up to terms of Od+3) and use the exact solution to compute y"(ti1) explicitly
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


