Question: Consider the k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) classifier for 2 classes 1 and 2 . Suppose that we have N training samples. (a) For a 2-NN classifier,
Consider the k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) classifier for 2 classes 1 and 2. Suppose that we have N training samples.
(a) For a 2-NN classifier, we have the following tie-breaking rule: if the two nearest neighbors have opposing labels, we discard the sample, and no error is recorded. Show that as N , the conditional error of the 2-NN classier, P2-NN(error|x), is half of that of the 1-NN classifier.
(b) Now consider the alternative tie-breaking rule: if the two nearest neighbors have opposing labels, we flip a fair coin and assign 1 for heads and 2 for tails. As N , find the conditional error of the 2-NN classifier, P2-NN(error|x).
(c) If P(z Se) > 0 for a hypersphere Se of radius e > 0, then for any of m k nearest neighbors of a point x, we have: x(m) a.s. x, as N .
(d) For the k-NN classifier, with odd k, show that as N , Pk-NN(error|x)
converges almost surely to:
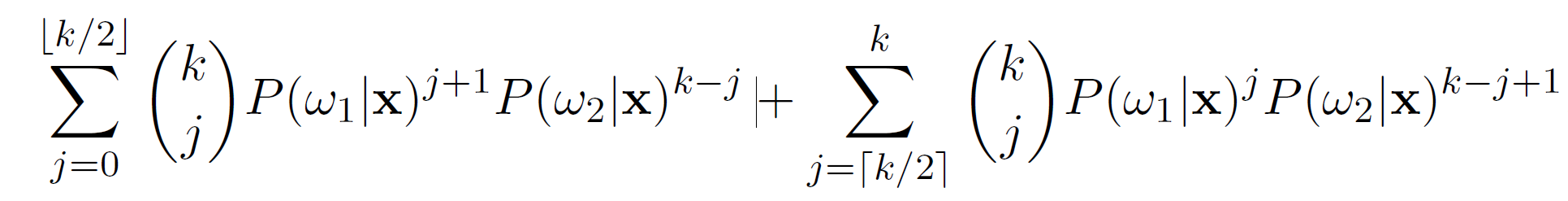
\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


