Question: Consider the learning task T = (B, E+, E-, M) given below: has Gene(a, g1). eat (a, gluten). eat (m, gluten). protein (gluten). gene(gl).
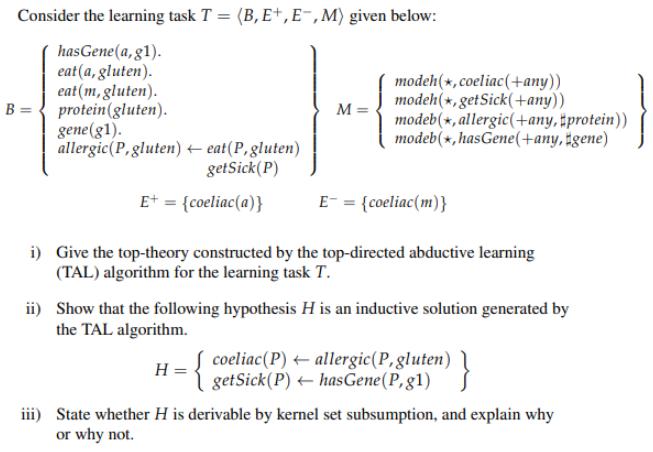
Consider the learning task T = (B, E+, E-, M) given below: has Gene(a, g1). eat (a, gluten). eat (m, gluten). protein (gluten). gene(gl). allergic (P, gluten) B = eat(P, gluten) getSick (P) E+ = {coeliac(a)} H M = i) Give the top-theory constructed by the top-directed abductive learning (TAL) algorithm for the learning task T. { modeh(*,coeliac(+any)) modeh(*, get Sick(+any)) modeb (*, allergic(+any, #protein)) modeb (*, hasGene(+any, #gene) ii) Show that the following hypothesis H is an inductive solution generated by the TAL algorithm. coeliac (P) getSick (P) E = {coeliac(m)} allergic (P, gluten) has Gene(P, g1) } iii) State whether H is derivable by kernel set subsumption, and explain why or why not.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The toptheory constructed by the topdirected abductive learning algorithm for the learning task T ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


