Question: Consider the matrix > A == {(2,1 + I, a)|(1 1, 2, 1)|(-1, 1, 1+b1)); 2 1 - 1 -1 A:=1+1 2 1 a 1
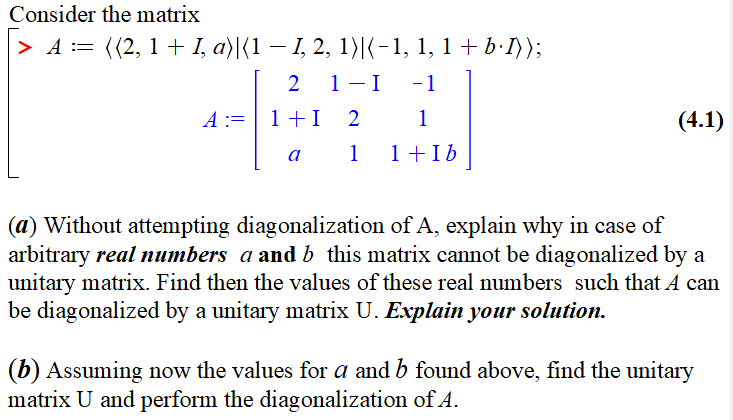
Consider the matrix > A == {(2,1 + I, a)|(1 1, 2, 1)|(-1, 1, 1+b1)); 2 1 - 1 -1 A:=1+1 2 1 a 1 1+Ib (4.1) (a) Without attempting diagonalization of A, explain why in case of arbitrary real numbers a and b this matrix cannot be diagonalized by a unitary matrix. Find then the values of these real numbers such that A can be diagonalized by a unitary matrix U. Explain your solution. (b) Assuming now the values for a and b found above, find the unitary matrix U and perform the diagonalization of A. Consider the matrix > A == {(2,1 + I, a)|(1 1, 2, 1)|(-1, 1, 1+b1)); 2 1 - 1 -1 A:=1+1 2 1 a 1 1+Ib (4.1) (a) Without attempting diagonalization of A, explain why in case of arbitrary real numbers a and b this matrix cannot be diagonalized by a unitary matrix. Find then the values of these real numbers such that A can be diagonalized by a unitary matrix U. Explain your solution. (b) Assuming now the values for a and b found above, find the unitary matrix U and perform the diagonalization of A
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


