Question: Consider the matrix A = -2 1. Calculate the determinant of A, and determine whether or not A is invertible. (1 mark) 2. The trace
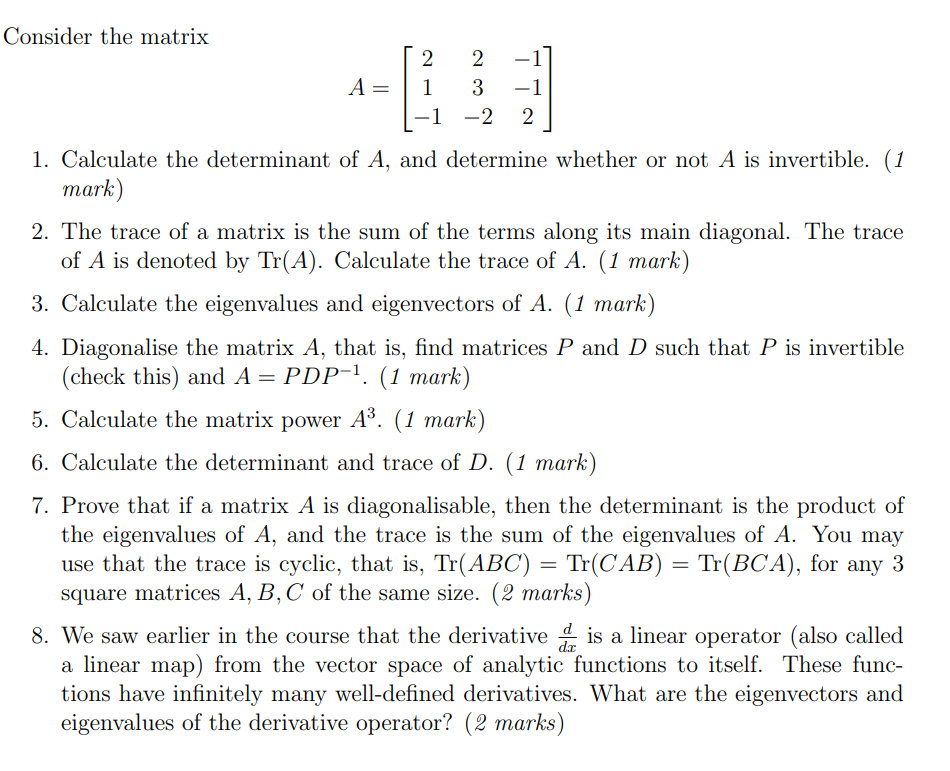
Consider the matrix A = -2 1. Calculate the determinant of A, and determine whether or not A is invertible. (1 mark) 2. The trace of a matrix is the sum of the terms along its main diagonal. The trace of A is denoted by Tr(A). Calculate the trace of A. (1 mark) 3. Calculate the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of A. (1 mark) 4. Diagonalise the matrix A, that is, find matrices P and D such that P is invertible (check this) and A = PDP-1. (1 mark) 5. Calculate the matrix power A3. (1 mark) 6. Calculate the determinant and trace of D. (1 mark) 7. Prove that if a matrix A is diagonalisable, then the determinant is the product of the eigenvalues of A, and the trace is the sum of the eigenvalues of A. You may use that the trace is cyclic, that is, Tr(ABC) = Tr(CAB) = Tr(BCA), for any 3 square matrices A, B, C of the same size. (2 marks) 8. We saw earlier in the course that the derivative & is a linear operator (also called a linear map) from the vector space of analytic functions to itself. These func- tions have infinitely many well-defined derivatives. What are the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the derivative operator? (2 marks)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


