Question: Consider the mechanical system given in Figure 2. d, (t) and d(t) are the displacements of the two blocks with respect to their nominal
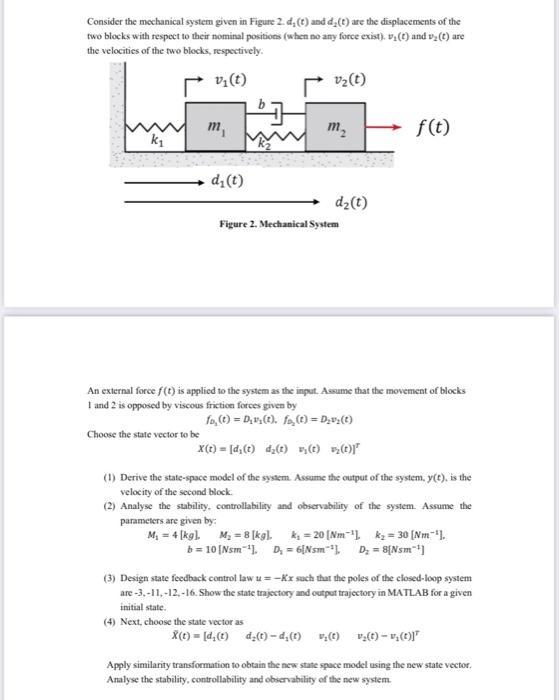
Consider the mechanical system given in Figure 2. d, (t) and d(t) are the displacements of the two blocks with respect to their nominal positions (when no any force exist). vy(t) and v (t) are the velocities of the two blocks, respectively. v (t) k m Choose the state vector to be d(t) 11 v (t) m d (t) Figure 2. Mechanical System An external force f(t) is applied to the system as the input. Assume that the movement of blocks 1 and 2 is opposed by viscous friction forces given by fo, (t) = Dv(t). f(t) = Dv (t) f(t) X(t)= [d, (t) d(t) vy(t) vy(t)]" (1) Derive the state-space model of the system. Assume the output of the system, y(t), is the velocity of the second block. (2) Analyse the stability, controllability and observability of the system. Assume the parameters are given by: M = 4 [kg], M=8 [kg]. k, = 20 [Nm], k= 30 [Nm], b = 10 [Nsm ], D = 6[Nsm1, D = 8{Nsm] (3) Design state feedback control law u=-Kx such that the poles of the closed-loop system are -3,-11,-12,-16. Show the state trajectory and output trajectory in MATLAB for a given initial state. (4) Next, choose the state vector as X(t) = [d(t) d(t)-d (t) (t) (t)-(c)] Apply similarity transformation to obtain the new state space model using the new state vector. Analyse the stability, controllability and observability of the new system.
Step by Step Solution
3.33 Rating (147 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
SOLUTION To derive the statespace model of the system we can start by writing the equations of motion for the two blocks Lets denote the displacements of the two blocks with respect to their nominal p... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


