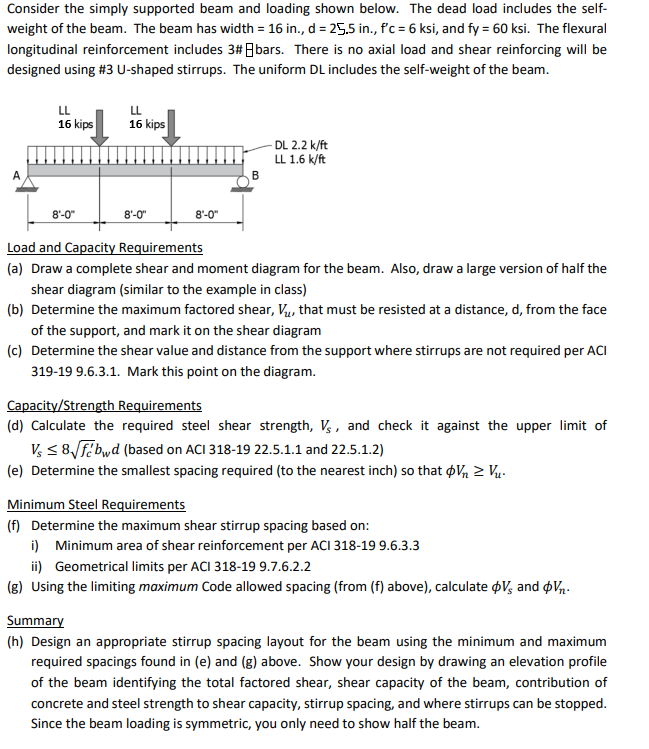
Question: Consider the simply supported beam and loading shown below. The dead load includes the selfweight of the beam. The beam has width ( =
Consider the simply supported beam and loading shown below. The dead load includes the selfweight of the beam. The beam has width mathrminmathrmdmathrminmathrmfprimemathrmcmathrmksi and mathrmfymathrmksi The flexural longitudinal reinforcement includes # Bbars. There is no axial load and shear reinforcing will be designed using # Ushaped stirrups. The uniform DL includes the selfweight of the beam.
Load and Capacity Requirements
a Draw a complete shear and moment diagram for the beam. Also, draw a large version of half the shear diagram similar to the example in class
b Determine the maximum factored shear, Vu that must be resisted at a distance, d from the face of the support, and mark it on the shear diagram
c Determine the shear value and distance from the support where stirrups are not required per ACl Mark this point on the diagram.
CapacityStrength Requirements
d Calculate the required steel shear strength, Vs and check it against the upper limit of Vsleq sqrtfcprime bw d based on ACl and
e Determine the smallest spacing required to the nearest inch so that phi Vngeq Vu
Minimum Steel Requirements
f Determine the maximum shear stirrup spacing based on:
i Minimum area of shear reinforcement per ACl
ii Geometrical limits per ACI
g Using the limiting maximum Code allowed spacing from f above calculate phi Vs and phi Vn
Summary
h Design an appropriate stirrup spacing layout for the beam using the minimum and maximum required spacings found in e and g above. Show your design by drawing an elevation profile of the beam identifying the total factored shear, shear capacity of the beam, contribution of concrete and steel strength to shear capacity, stirrup spacing, and where stirrups can be stopped. Since the beam loading is symmetric, you only need to show half the beam.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


