Question: Consolidating entries (market value differs from book value) Assume that on January 1, 2013, an investor company acquired 100% of the outstanding voting common stock
Consolidating entries (market value differs from book value) Assume that on January 1, 2013, an investor company acquired 100% of the outstanding voting common stock of an investee company. The following financial statement information was prepared immediately after the acquisition and presents the acquisition-date balance sheet for the pre-consolidation investor company, the investee company and the consolidated financial statements for the investor and investee.
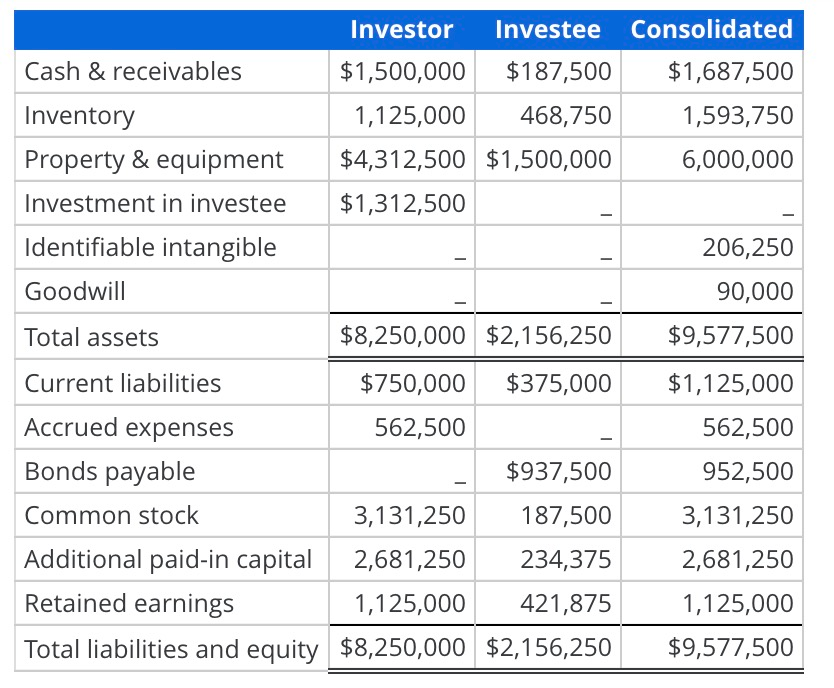
In preparing the consolidated financial statements, what is the amount of the debit or credit made to the "investment in investee" account as part of the [A] consolidating entry? (Recall from the chapter that the [A] consolidating entry reclassifies the acquisition accounting premium from the investment account to the individual net assets that require adjustment from book value to fair value.)
$90,000
$1,312,500
$483,750
$468,750
Investor Investee Consolidated Cash & receivables $1,500,000 $187,500 $1,687,500 Inventory 1,125,000 468,750 1,593,750 Property & equipment $4,312,500 $1,500,000 6,000,000 Investment in investee $1,312,500 Identifiable intangible 206,250 Goodwill 90,000 Total assets $8,250,000 $2,156,250 $9,577,500 Current liabilities $750,000 $375,000 $1,125,000 Accrued expenses 562,500 562,500 Bonds payable $937,500 952,500 Common stock 3,131,250 187,500 3,131,250 Additional paid-in capital 2,681,250 234,375 2,681,250 Retained earnings 1,125,000 421,875 1,125,000 Total liabilities and equity $8,250,000 $2,156,250 $9,577,500
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


