Question: Cost Behavior Patterns Example Constant reference FIXED VARIABLE MIXED Fred Cost Behavior Total Fixed Cost of Renting the Bullding Fixed costs remain constant in total
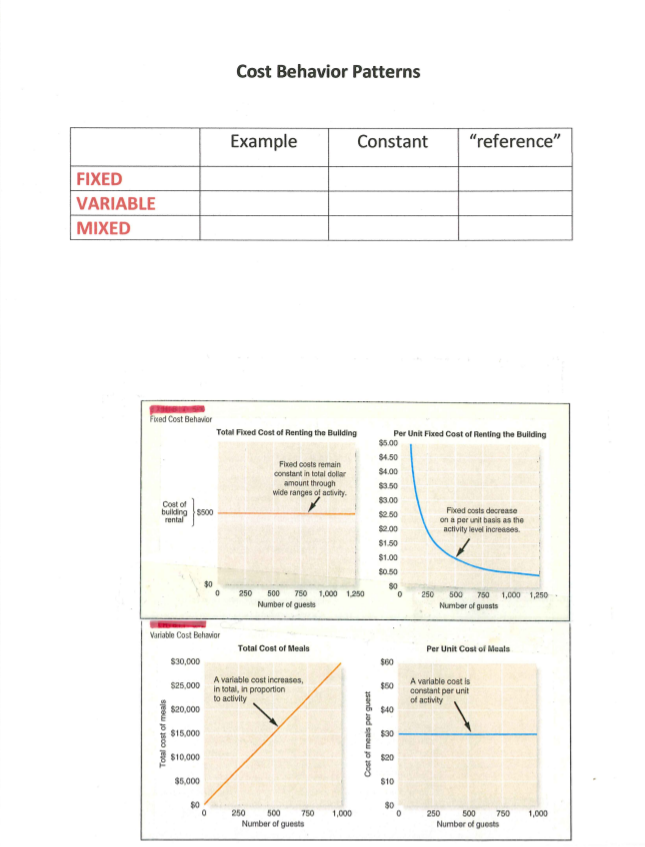

Cost Behavior Patterns Example Constant "reference" FIXED VARIABLE MIXED Fred Cost Behavior Total Fixed Cost of Renting the Bullding Fixed costs remain constant in total dollar amount through wide ranges of activity Cost of building 5500 rental Per Unit Flved Cast of Renting the Building $5.00 84.50 $4.00 $3.50 83.00 $2.50 Fixed costs decrease on a per unit basis as the $2.00 activity level increases $1.50 $1.00 $0.50 80 0 250 500 750 1,000 1,250 Number of guests $0 0 250 500 750 1.000 1.250 Number of guests Variable Cost Behavior Total Cost of Meals Per Unit Cost of Meals $30,000 $60 $25,000 A variable cost increases, In total, in proportion to activity $50 A variable cost is constant per unit of activity $20,000 $40 Total cost of meals $15,000 Cost of meals per guest $30 $10,000 $20 $5,000 10 $0 1,000 30 0 1,000 250 500 750 Number of guests 250 500 750 Number of guests Demo - High Low Method Madison Company manufactures major appliances. In preparing the budget for next year, the controller compiled the following information: Month July August September October November December Six-month Total Volume in Mach Hours 6,000 5,000 4,500 4,000 3,500 3,000 26,000 Total Electricity Cost $ 60,000 53,000 49,500 46,000 42,500 36,000 $287,000 Using the high-low method, determine the variable electricity cost per machine hour and the monthly fixed electricity cost. Express the mixed cost as a linear equation and calculate the mixed cost if the company projects to use 4,800 machine hours next month. Step 1: Determine the VC per unit High-Low "Cost" High-Low "Activity" Step 2: Determine the FC in total Hint; per unit cost x activity = VC VC + FC = Total Cost Step 3: Express it using the Linear Equation Hint; y = A(x) + B
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


