Question: CoursHeroTranscribedText: A technique for cooling a multichip module involves submerging the module in saturated fluorocarbon liquid. Vapor generated due to boiling at the module surface
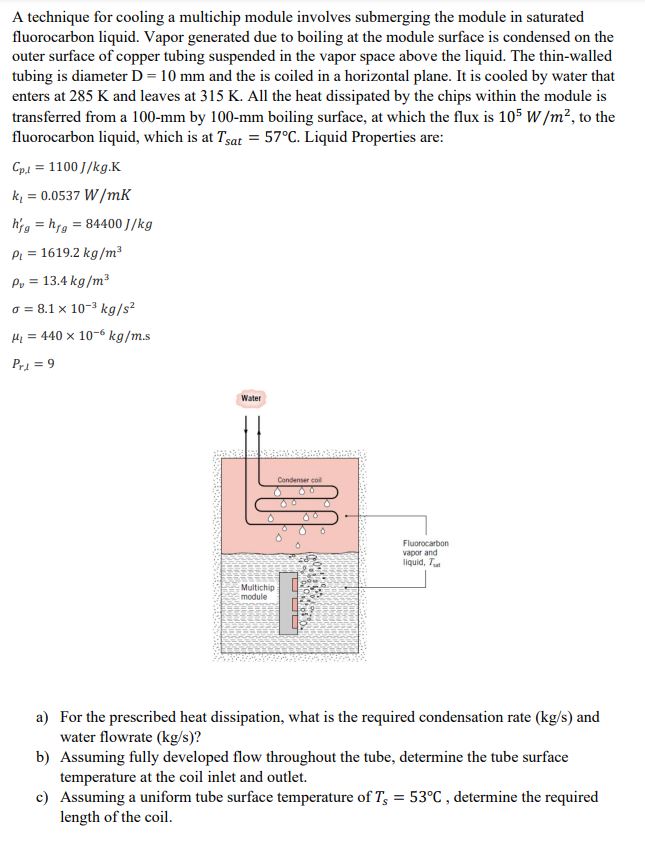
CoursHeroTranscribedText: A technique for cooling a multichip module involves submerging the module in saturated fluorocarbon liquid. Vapor generated due to boiling at the module surface is condensed on the outer surface of copper tubing suspended in the vapor space above the liquid. The thin-walled tubing is diameter D = 10 mm and the is coiled in a horizontal plane. It is cooled by water that enters at 285 K and leaves at 315 K. All the heat dissipated by the chips within the module is transferred from a 100-mm by 100-mm boiling surface, at which the flux is 105 W /m, to the fluorocarbon liquid, which is at Tsar = 57C. Liquid Properties are: Cp.1 = 1100 //kg.K K = 0.0537 W/mk hig = hig = 84400 ]/kg Pi = 1619.2 kg/m3 Pp = 13.4 kg/m3 0 = 8.1 x 10-3 kg/s2 Hi = 440 x 10-kg/m.s Prl = 9 Water Candenter call Fluorocarbon vapor and liquid, Multichip module a) For the prescribed heat dissipation, what is the required condensation rate (kg/s) and water flowrate (kg/s)? b) Assuming fully developed flow throughout the tube, determine the tube surface temperature at the coil inlet and outlet. c) Assuming a uniform tube surface temperature of T's = 53'C , determine the required length of the coil
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


