Question: Create a class named Account that contains: A private int data field named id for the account (default 0). A private double data field

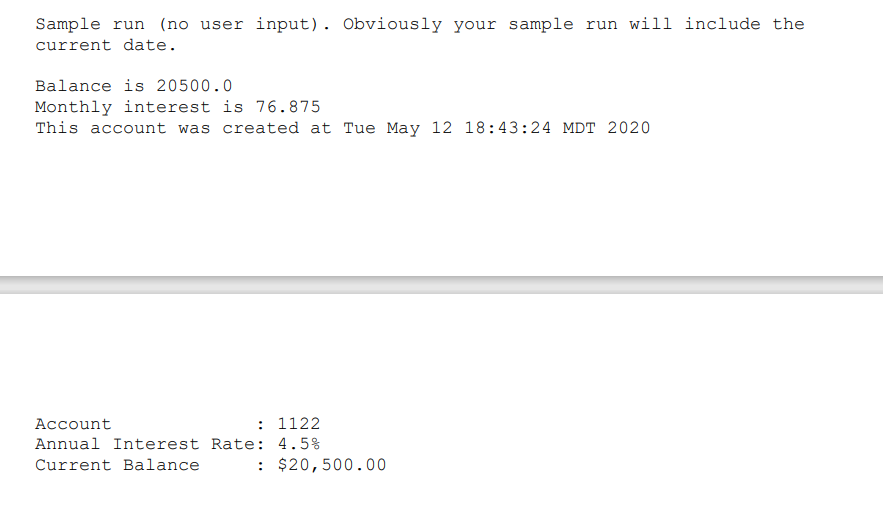
Create a class named Account that contains: A private int data field named id for the account (default 0). A private double data field named balance for the account (default 0). A private double data field named annualInterestRate that stores the current interest rate (default 0). Assume that all accounts have the same interest rate. A private Date data field named dateCreated that stores the date when the account was created. Create an Account class with a constructor and methods need to support the code in driver program shown below (additional methods are NOT necessary). Make sure your toString() method generates output similar to the sample run, use String.format() to format the output string. Some helpful formulas; Note: annuallnterestRate is a percentage, for example 4.5%. MonthlyInterest Rate is annuallnterestRate / 1200. Monthly interest = balance * MonthlyInterestRate. Source code: public class Account Driver { public static void main (String[] args) { Account account = new Account (1122, 20000); Account.setAnnual InterestRate (4.5); account.withdraw (2500); account.deposit (3000); System.out.println("Balance is " + account.getBalance () ); System.out.println("Monthly interest is " + account.getMonthly Interest ()); System.out.println("This account was created at account.getDate Created()); + } System.out.println(account); } Sample run (no user input). Obviously your sample run will include the current date. Balance is 20500.0 Monthly interest is 76.875 This account was created at Tue May 12 18:43:24 MDT 2020 Account Annual Interest Rate: 4.5% Current Balance : 1122 : $20,500.00
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


